WordCount java实现
这里是该项目作业的要求:
https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xnsy/2018Systemanalysisanddesign/homework/2152 ---陈汶滨老师
项目已经上传github:
https://github.com/DngLing/CountWord
个人PSP表:
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
|
|
|
Development |
开发 |
|
|
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
30 |
60 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
5 |
5 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
5 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
400 |
250 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
15 |
30 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
20 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
30 |
90 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
15 |
30 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
5 |
10 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
20 |
|
|
合计 |
385 |
780 |
一、语言选择
我选择了java来完成我的项目作业,我选择的理由是:
1.最近真正学习java的常用的类以及IO流;
2.项目中很多功能的实现都可以使用java中一些已有的类(例如在解析大段文字时,Stirng类提供了很多实用方法);
3.我没有打算做界面系统,不然我还是倾向于学过的C#
二、需求分析与可行性
需求分析
1.通过文件地址获得该文件的内容(这个文件是一个文本文件,保存着代码);
2.得到目标文件中的字符数、单词数、行数、代码行、空行、注释行。且对这六种中一些数据做了解释:
1)字符:所有的空格也算字符;
2)单词:由空格或逗号隔开的单词,并且不做有效性判断;
3)代码行:非空行注释行;
4)注释行 以“ // ”,“ /* ”,“ * ”开头的行,或者以“ */ ”,“ // ”结尾的行,如果一行代码后跟了注释,那么改行也算代码行。
5)空行:改行没有代码,全部是空格或者控制符,如果有,不能超过一个可显示字符,例如“ { ”。
3.将2中的得到的信息写出到一个新的文本文件,且 该文件与传入的文件在同一文件夹下;
4.非图形界面需要输入一些指令来执行操作
可行性分析
1.通过IO流可以轻松实现文件的读写
三、具体设计与编码
这是我在ProcessON上制作的类设计图
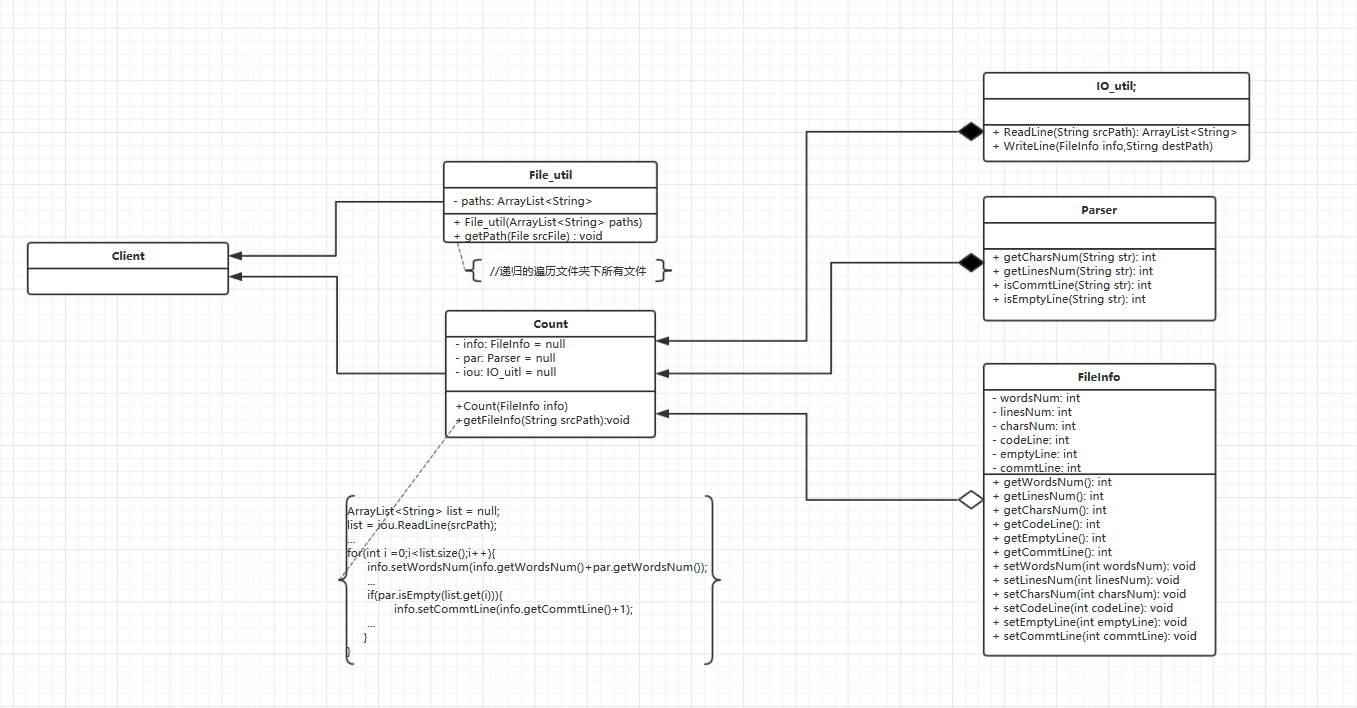
下面将给出这些类的设计理念和一些核心代码
IO_uitl
这个类实现了IO流的输入与输出,他有两个方法,ReadLine()和WriteLine(),下面是ReadLine()方法
public ArrayList<String> ReadLine(String srcPath) throws IOException{ ArrayList<String> strs = new ArrayList<String>(); File srcFile = new File(srcPath); BufferedReader bReader = null; try { bReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFile)); String line; while(null!=(line =bReader.readLine())){ strs.add(line); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ bReader.close(); } return strs; }
Parser该类将对字串进行解析,得到所需要的结果
下面是部分代码:
public int getCommtLineNum(ArrayList<String> str){ int num =0; for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++){ String temp = str.get(i).trim(); if(temp.startsWith("//")||temp.startsWith("/*")||temp.startsWith("*")||temp.endsWith("*/")){ num++; } } return num; } public boolean isCommtLine(String str){ boolean flag =false; String temp = str.trim(); if(temp.startsWith("//")||temp.startsWith("/*")||temp.startsWith("*")||temp.endsWith("*/")||temp.startsWith("}//")){ flag = true; } return flag; } public boolean isEmptyLine(String str){ boolean flag = false; if(this.getWordsNum(str)==0&&!this.isCommtLine(str)){ flag = true; } return flag; }
FileInfo 是一个JavaBean,用于传递一个文件的信息。
代码略
Count(统计)类,它拥有一个IO_util和一个Parser的实例对象,并维持了一个FileInfo的实例对象的引用。
通过构造函数声明这个实例并通过getFileInfo方法将所有所有需要的数据注入到实例的字段中。下面是代码:
package com.dyf.test; /** * 该方法拥有 * 一个IO_util类的对象 * 一个Parser类的对象 * 该方法维持了一个FileInfo对象的引用 */ import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Count { private IO_util iou = null; private Parser par= null; private FileInfo info = null; public Count(FileInfo info){ this.info = info; par = new Parser(); iou = new IO_util(); } /** * 该方法依赖IO_util对象和Parser对象的方法 * 该方法将给引用的FileInfo对象的字段注入数据 * @param srcPath 文件的绝对地址 * @throws IOException */ public void getFileInfo(String srcPath) throws IOException{ ArrayList<String> list = null; list = iou.ReadLine(srcPath); info.setLinesNum(list.size()); for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){ info.setWordsNum(info.getWordsNum()+par.getWordsNum(list.get(i))); info.setCharsNum(info.getCharsNum()+par.getCharsNum(list.get(i))); if(par.isEmptyLine(list.get(i))){ info.setEmptyLine(info.getEmptyLine()+1); }else if(par.isCommtLine(list.get(i))){ info.setCommtLine(info.getCommtLine()+1); }else{ info.setCodeLine(info.getCodeLine()+1); } } } }
File_util提供一个通过遍历得到目标文件夹下的所有子文件夹和文件的路径并返回
下面是代码:
package com.dyf.test; /** * 该类用于对文件进行操作 * 该类维持了一个ArrayList<String> 的使用,它将保存一个文件夹路径下的所有子文件夹和文件的路径 */ import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; public class File_util { private ArrayList<String> paths; public File_util(ArrayList<String> paths){ this.paths = paths; } /** * 该方法 递归的遍历srcFile路径下所有的文件和子文件夹的地址 * @param srcFile */ public void getPath(File srcFile){ if(null == srcFile||!srcFile.exists()){ return; } paths.add(srcFile.getAbsolutePath()); if(srcFile.isDirectory()){ for(File file:srcFile.listFiles()) getPath(file); } } }
TestClient 客户端 代码如下
package com.dyf.test; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Scanner; public class TestClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { boolean switchflag = true; while(switchflag){ System.out.println("-----COUNTWORD-----"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("输入 -c 获得当前文件字符数"); System.out.println("输入 -w 获得当前文件单词数"); System.out.println("输入 -l 获得当前文件行数"); System.out.println("输入 -e 获得当前文件所有信息(上述信息加上代码行、注释行和空行)"); System.out.println("输入 -s 遍历当前文件夹下所有文件的信息"); System.out.println("输入 -x:end结束程序"); System.out.println("输入实例 -e E:/www/exple.java"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("请输入操作符:\n"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.nextLine(); int pointins = str.indexOf("-"); int pointpath = str.indexOf(":"); String ins = null; String path = null; try{ ins =str.substring(pointins, pointins+2); path = str.substring(pointpath-1).trim(); }catch(StringIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("你的输入有问题,请检查并重新输入:\n"); continue; } switch(ins){ case "-e": FileInfo info = new FileInfo(); Count cou = new Count(info); cou.getFileInfo(path); System.out.println("-----------"); System.out.println(info); break; case "-s": ArrayList<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>(); File_util fu = new File_util(paths); fu.getPath(new File(path)); for(int i=0;i<paths.size();i++){ String line = paths.get(i); if(line.endsWith(".txt")){ FileInfo info1 = new FileInfo(); Count cou1 = new Count(info1); cou1.getFileInfo(line); System.out.println("---------"); System.out.println(line); System.out.println(info1); System.out.println("\n"); } } break; case "-c": FileInfo info2 = new FileInfo(); Count cou2 = new Count(info2); cou2.getFileInfo(path); System.out.println("CharNum:"+info2.getCharsNum()); System.out.println("\n"); break; case "-w": FileInfo info3 = new FileInfo(); Count cou3 = new Count(info3); cou3.getFileInfo(path); System.out.println("WordsNum:"+info3.getWordsNum()); System.out.println("\n"); break; case "-l": FileInfo info4 = new FileInfo(); Count cou4 = new Count(info4); cou4.getFileInfo(path); System.out.println("LinesNum:"+info4.getLinesNum()); System.out.println("\n"); break; case "-x": switchflag =false; break; default: System.out.println("输入了无效的操作符\n"); System.out.println("\n"); break; } } System.out.println("程序结束"); }
}
四、效果
目标文件E:/www/cd.txt 这是一个保存了java代码的文件,其中包含空行,代码行和注释行。
package com.dyf.io.BufferedChar; /** * 使用字符缓冲流实现纯文本文件的copy * BufferReader(),BufferWriter(); * */ import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class CopyFile { public void copy(File src,File dest){ BufferedReader bReader =null; BufferedWriter bWriter = null; try { bReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); bWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); String line = null; while(null != (line = bReader.readLine())){ bWriter.write(line); bWriter.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ try { bReader.close(); bWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
实现功能

获得单词数信息:
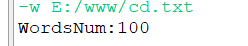
获得行数信息:

获得当前文件的所有信息:
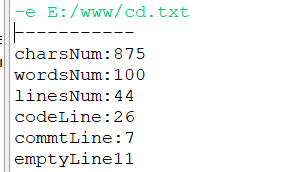
遍历某一文件夹并获得所有文件的信息:

五、拓展功能,写出文件
具体代码如下:
/** * 该方法用于将一个FileInfo对象的所有字段写到 destPath这个文件路径下 * @param info:FileInfo * @param destPath : 目标路径 */ public void writeLine(FileInfo info,String destPath){ BufferedWriter bWriter = null; File file = new File(destPath+"/info.txt"); try { bWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); bWriter.write("CharsNum:"+info.getCharsNum()+'\n'); bWriter.newLine(); bWriter.write("LinesNum:"+info.getLinesNum()+"\n"); bWriter.newLine(); bWriter.write("WordsNum:"+info.getWordsNum()+'\n'); bWriter.newLine(); bWriter.write("CodeLine:"+info.getCodeLine()+'\n'); bWriter.newLine(); bWriter.write("CommtLine:"+info.getCommtLine()+'\n'); bWriter.newLine(); bWriter.write("EmptyLine:"+info.getEmptyLine()+'\n'); bWriter.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("写出文件失败"); }finally{ if(bWriter!=null){ try { bWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
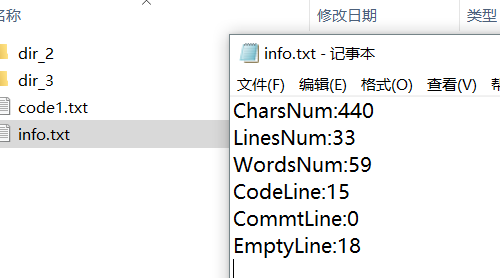
效果展示 :


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号