Pollard_Rho 整数分解法【学习笔记】
引文:如果要对比较大的整数分解,显然之前所学的筛选法和是试除法都将不再适用。所以我们需要学习速度更快的Pollard_Rho算法。
算法原理:
生成两个整数a和b,计算p=gcd(a-b, n),知道p不为1或a,b出现循环为止,若p=n,则n为质数,否则p为n的一个约数。
对于如何生成这两个数,选取一个小的随机数x1,迭代生成
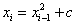
通过这个方式,我们只需要知道x1和c就可以生成一系列数值,c可以取任意给定值,一般取c=1。
若序列出现循环,则退出。
计算p=gcd(xi-1-xi, n), 若p=1,返回上一步,直到p>1为止;若p=n,则n为素数,否则p为一个约数并递归分解p和n/p。
例题:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1811
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <fstream> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <cmath> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 typedef long long LL; 12 const int Test[] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19}; 13 const int Times = 8; 14 vector<LL> Factor; 15 16 LL gcd(LL a, LL b) 17 { 18 return b==0?a:gcd(b, a%b); 19 } 20 21 LL Multi(LL a, LL b, LL mod) 22 { 23 LL ans = 0; 24 while(b) 25 { 26 if(b&1) 27 ans = (ans + a)%mod; 28 a = (a+a)%mod; 29 b>>=1; 30 } 31 return ans; 32 } 33 34 LL Pow(LL a, LL b, LL mod) 35 { 36 LL ans = 1; 37 while(b) 38 { 39 if(b&1) 40 { 41 ans = Multi(ans, a, mod); 42 } 43 b>>=1; 44 a=Multi(a, a, mod); 45 } 46 return ans; 47 } 48 49 bool Miller_Rabin(LL n) 50 { 51 if(n < 2) return false; 52 LL s = n-1, t = 0, x, next; 53 while(!(s&1) ) //根据运算符的优先级必须加括号 54 { 55 s>>=1; 56 t++; 57 } 58 for(int i = 0; i < Times; i++) 59 { 60 if(n== Test[i]) return true; 61 x = Pow(Test[i], s, n); 62 for(int j = 1; j <= t; j++) 63 { 64 next = Multi(x, x, n); 65 if(next == 1 && x != 1 && x != n-1) 66 return false; 67 x = next; 68 } 69 if(x != 1) 70 return false; 71 } 72 return true; 73 } 74 75 LL Pollard_Rho(LL n, int c) 76 { 77 LL i = 1, k = 2; 78 LL x = rand()%(n-1) + 1, y; //保证随机数在(0,n)内 79 y = x; 80 while(1) 81 { 82 i++; 83 x = (Multi(x, x, n) + c)%n; //继续生成数 84 LL p = gcd(x>y?x-y:y-x, n); 85 if(p!=1 && p!=n) //因为p>1 86 return p; 87 if(y == x) 88 return n; 89 if(i == k) 90 { 91 y = x; 92 k<<=1; 93 } 94 } 95 } 96 97 void Find(LL n, int c) 98 { 99 if(n == 1) 100 return; 101 if(Miller_Rabin(n)) 102 { 103 Factor.push_back(n); 104 return; 105 } 106 LL p = n, k = c; 107 while(p >= n) 108 { 109 p = Pollard_Rho(n, c--); 110 } 111 Find(p, k); 112 Find(n/p, k); 113 } 114 115 116 int main() 117 { 118 int T; 119 LL x; 120 cin >>T; 121 while(T--) 122 { 123 Factor.clear(); 124 cin >> x; 125 Find(x, 107); //107足矣 126 if(Factor.size() == 1) 127 printf("Prime\n"); 128 else 129 { 130 sort(Factor.begin(), Factor.end()); 131 printf("%I64d\n", Factor[0]); 132 } 133 } 134 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号