java JDBC Statement的用途
对比Statement与prepareStatement
1. Statement 存在SQL注入 ,PrepareStatement不存在SQL注入
2.Statement 是编译一次执行一次,PrepareStatement编译一次可执行多次,PrepareStatement 执行效率高
3.PrepareStatement会在编译阶段做类型的检查
什么情况下使用Statement?
业务方面要求支持SQL注入的时候
SQL语句需要拼接的时候
例如:用户控制台输入desc进行降序,输入asc进行升序
新建java空项目,新建类JdbcTest_Statement
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
3 System.out.println("请输入desc或asc,desc表示降序,asc表示升序");
4 System.out.print("请输入:");
5 //读取输入的这一行,并赋值给keyWords
6 String keyWords = s.nextLine();
7 //执行SQL,JDBC编程六步
8 Connection conn = null;
9 Statement stmt = null;
10 ResultSet rs = null; //ResultSet是封装了结果集的对象
11
12 try {
13 //注册驱动
14 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
15 //然后获取连接
16 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user","root","root");
17
18
19 //获取数据库操作对象
20 stmt = conn.createStatement();
21
22 //执行SQL
23 String sql="select loginName from t_user order by loginName "+keyWords;
24 rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
25
26 //结果集进行遍历循环
27 while(rs.next()){//如果结果集有数据
28 System.out.println(rs.getString("loginName"));
29
30 }
31 } catch (Exception e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 } finally {
34 if (rs != null){
35 try {
36 rs.close();
37 } catch (SQLException e) {
38 e.printStackTrace();
39 }
40 }
41 //资源释放
42 if (conn != null){
43 try {
44 conn.close();
45 } catch (SQLException e) {
46 e.printStackTrace();
47 }
48 }
49
50 if (stmt != null){
51 try {
52 stmt.close();
53 } catch (SQLException e) {
54 e.printStackTrace();
55 }
56 }
57 }
58 }
运行结果:输入desc
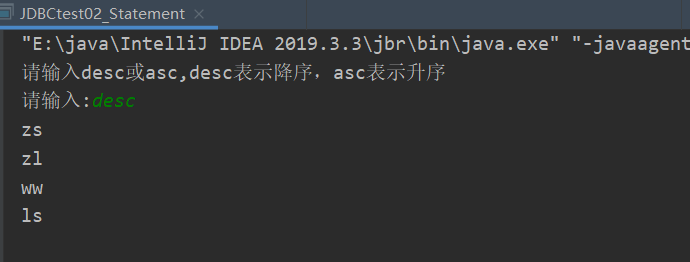
输入asc
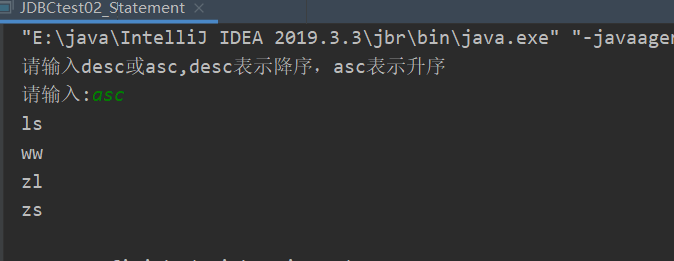
String sql="select loginName from t_user order by loginName "+keyWords;
此处的SQL语句进行拼接,程序读取用户输入的keywords,拼接成一整句完整的SQL语句,用户输入的信息参与了编译过程,产生了SQL注入,实现了用户的要求
本文来自博客园,作者:大星星不见了,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/dxxbjl/p/15085503.html



