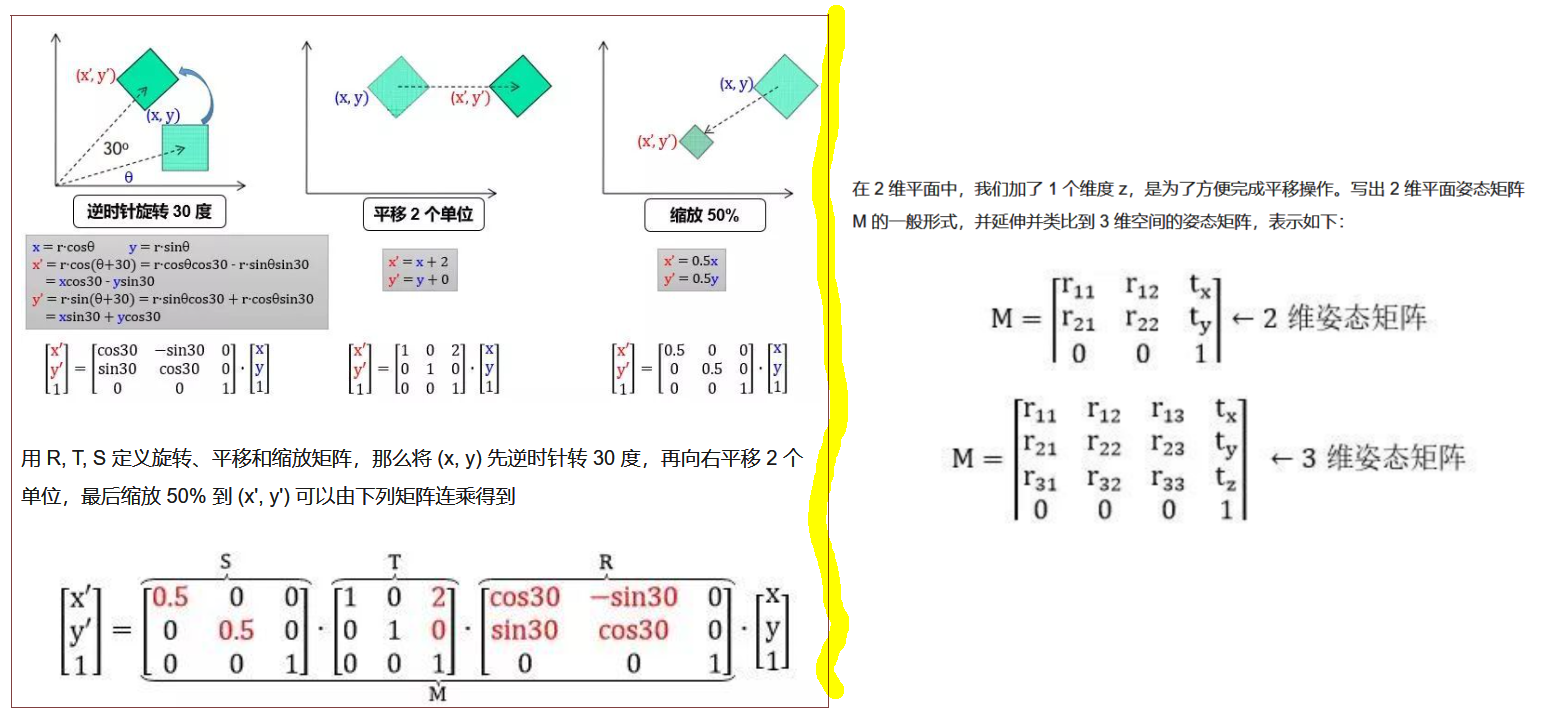
图像的仿射变换原理
首先我们看看 2 维平面中姿态矩阵是如何平移、旋转和放缩物体:
from: https://www.sohu.com/a/226611009_633698
def random_rotate_xy(img, box, angle_range=(-25, 25), scale_range=(0.80, 1.0)): height, width = img.shape[:2] # 获取图像的高和宽 center = (width / 2., height / 2.) # 取图像的中点 angle = random.randrange(*angle_range) scale = random.randrange(int(scale_range[0] * 100), int(scale_range[1]) * 100) / 100. M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale) # 获得图像绕着某一点的旋转矩阵 # cv2.warpAffine()的第二个参数是变换矩阵,第三个参数是输出图像的大小 rotated_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (width, height)) img_h, img_w = rotated_img.shape[:2] # box: [x1,y1, x2,y2] x1, y1, x2, y2 = box w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1 cx, cy = (x1 + x2) / 2, (y1 + y2) / 2 cx1 = M[0, 0] * cx + M[0, 1] * cy + M[0, 2] cy1 = M[1, 0] * cx + M[1, 1] * cy + M[1, 2] x11 = max(0, int(cx1 - w * scale / 2)) y11 = max(0, int(cy1 - h * scale / 2)) x22 = min(img_w - 1, int(cx1 + w * scale / 2)) y22 = min(img_h - 1, int(cy1 + h * scale / 2)) box_rotated = [x11, y11, x22, y22] return rotated_img, box_rotated
# numpy bboxes版本
def random_rotate_with_bboxes(img, bboxes, angle_range=(-25, 25), scale_range=(0.80, 1.0)): """ 旋转 :param img: :param bboxes: [b, 4], format: x1y1x2y2 :param angle: 旋转角度, >0 表示逆时针, :param scale: :return: """ height, width = img.shape[:2] # 获取图像的高和宽 center = (width / 2, height / 2) # 取图像的中点 angle = random.randrange(*angle_range) scale = random.randrange(int(scale_range[0] * 100), int(scale_range[1]) * 100) / 100. M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale) # 获得图像绕着某一点的旋转矩阵 # cv2.warpAffine()的第二个参数是变换矩阵,第三个参数是输出图像的大小 rotated = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (width, height)) height, width = rotated.shape[:2] if isinstance(bboxes, np.ndarray): bboxes_np = bboxes else: bboxes_np = np.asarray(bboxes) bboxes_w, bboxes_h = bboxes_np[:, 2] - bboxes_np[:, 0], bboxes_np[:, 3] - bboxes_np[:, 1] bboxes_wh = np.concatenate([bboxes_w[:, None], bboxes_h[:, None]], axis=1) cx, cy = (bboxes_np[:, 0] + bboxes_np[:, 2]) / 2., (bboxes_np[:, 1] + bboxes_np[:, 3]) / 2. cxy = np.concatenate([cx[:, None], cy[:, None]], axis=1) M_t = np.transpose(M) rt_cxy = np.matmul(cxy, M_t[:2, :]) + M_t[2, :2] x1y1 = rt_cxy - (bboxes_wh * scale / 2) x2y2 = rt_cxy + (bboxes_wh * scale / 2) x1y1[x1y1 < 0] = 0 x2y2[:, 0][x2y2[:, 0] > width - 1] = width x2y2[:, 1][x2y2[:, 1] > height - 1] = height bboxes_rotated = np.concatenate([x1y1, x2y2], axis=1) return rotated, bboxes_rotated


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号