DFT介绍
1. 可测试性特点
- 可控性:能够设定某些电路节点到某种状态或逻辑值
- 可观察:能够观测芯片内部节点的状态或逻辑值
2. 如何测试
1)建立模型
- 电路建模(circuit modeling)
- 故障建模(fault modeling)
2)ATPG
- Logic simulation
- Fault simulation
- Test generation
3)可测试设计
- Design for test(DFT)
- ad hoc techniques
- Scan design
- Boundary Scan(JTAG)
- Built-in self test(BIST)
- Random number generator (RNG)
- Signature Analyzer (SA)
4)可测性综合
- 自动化或半自动化
- EDA工具
- Testability analysis tools
- Full / partial scan insertion
- BIST insertion
- Boundary scan insertion
5)测试与质量
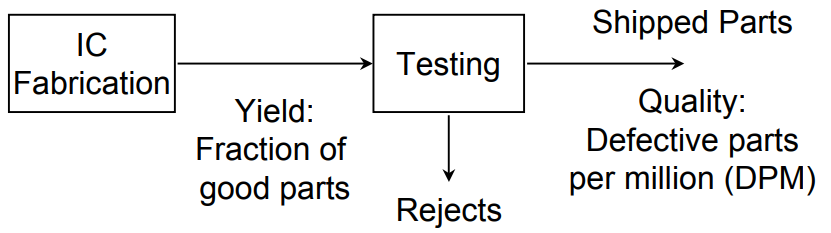
缺陷程度DL(DPM)= 1 - Y (1-T),其中
DL: defect level(缺陷程度per million)
Y: yield(产量)
T: fault coverage(故障覆盖率)
3. 建模
3.1 电路建模
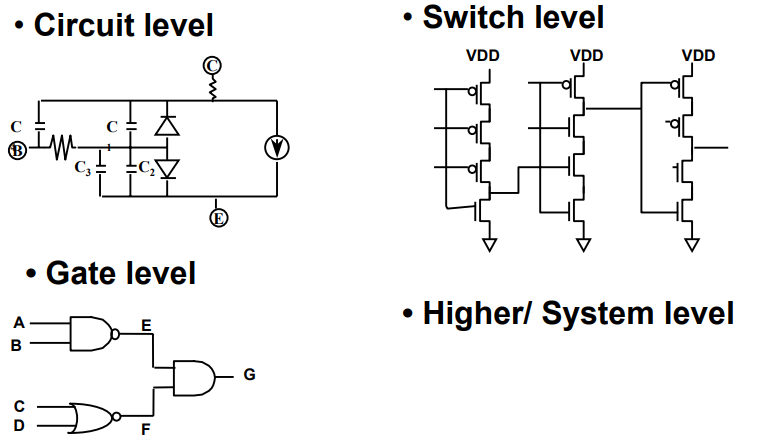
3.2 故障建模
故障模型有:
- Single stuck-at fault
- Break faults
- Bridging faults
- Transistor stuck-open faults
- Transistor stuck-on faults
- Delay faults
其中Single stuck-at fault模型最常用

4. 测试矢量生成

为了检测D是否s-a-0,我们需要使得D为1,并在F端输出观测,因此测试矢量为:
A=1, B=1, C=0
5. 自动测试模型生成(ATPG)
给定一个电路,确定一组测试矢量检测所有故障

6. 测试策略
- BIST for large memories/arrays
- Special BIST for small buffers
- Scan for random logic
- Shadow registers where necessary
- Boundary Scan for test control and board level testing
7. 可测试设计flow

其中:
mentor本身的MbistAchitect在2009年已不再更新,MBIST插入目前主要基于mentor收购的LogicVision产品;
Design Compiler为Synopsys的综合工具
DFTAdvisor为mentor的scan-chain insertion工具
作者:星雨夜澈
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/dxs959229640/
声明:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号