作业要求一
PTA作业的提交列表
第一次作业
![]()
第二次作业
![]()
一道编程题:
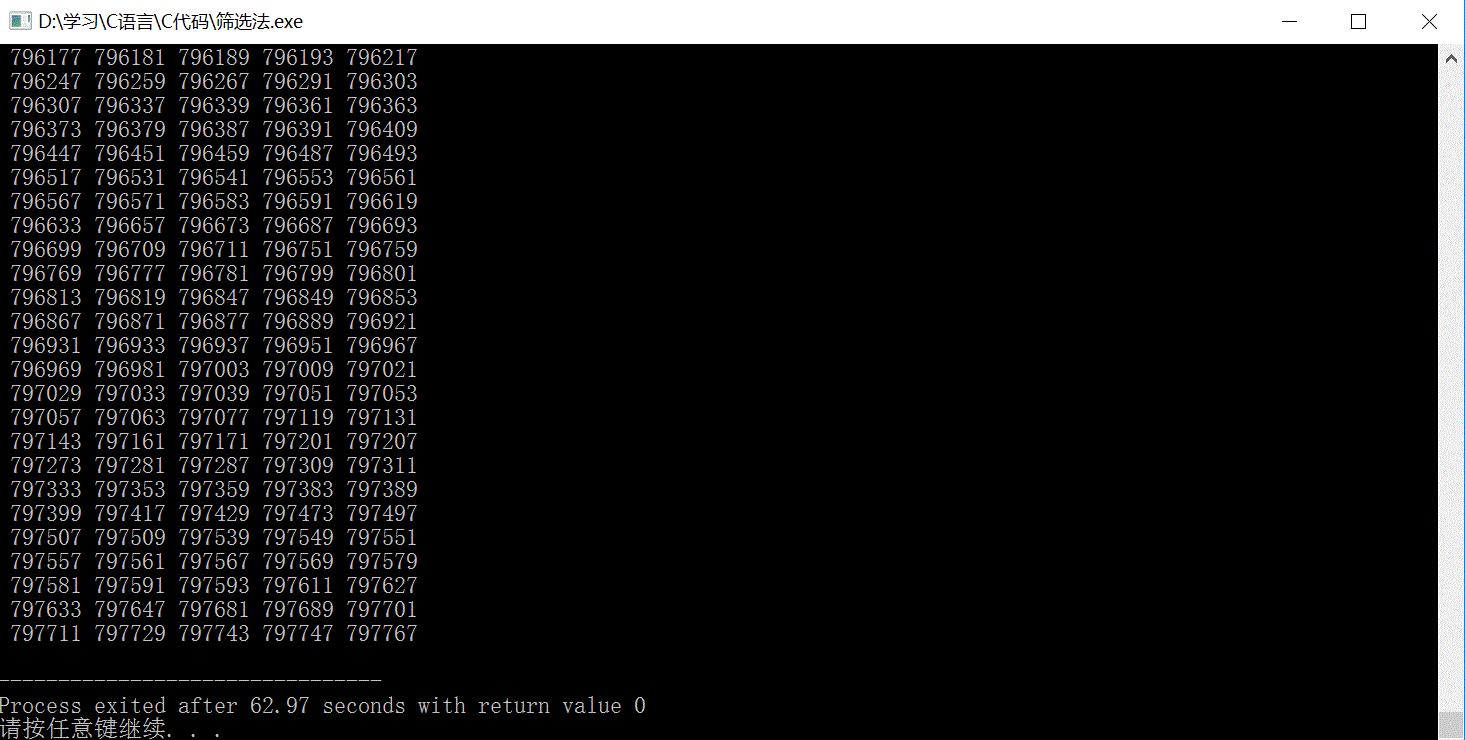
有一个axb的数组,该数组里面顺序存放了从1到a*b的数字。其中a是你大学号的前三位数字,b是你大学号的后四位数字,比如你的学号是2017023936,那么数组大小是201 x 3936,数组中顺序存放了1到791136(201和3936的积)的整数. 要求用筛选法,把该数组里的质数找出并打印出来,打印格式为5个质数一行,数字间用空格隔开。
筛选法具体做法是:先把N个自然数按次序排列起来。1不是质数,也不是合数,要划去。第二个数2是质数留下来,而把2后面所有能被2整除的数都划去。2后面第一个没划去的数是3,把3留下,再把3后面所有能被3整除的数都划去。3后面第一个没划去的数是5,把5留下,再把5后面所有能被5整除的数都划去。这样一直做下去,就会把不超过N的全部合数都筛掉,留下的就是不超过N的全部质数。
实验代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
int main(void)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b); //我的学号输入201和3969
int i, j;
int *as=(int *)malloc(1000000*sizeof(int));
for(i = 2; i <= a * b; i++)
as[i] = i;
for(i = 2; i <= (a * b) / i; i++)
for(j = i + i; j <= a * b; j = i + j)
as[j] = NULL;
for(i = 2, j = 0; i <= a * b; i++)
if(as[i] != NULL)
{
printf("%7d", as[i]);
j++;
if(j % 5 == 0)
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
输出结果
![]()
作业要求二
题目1.输出月份英文名(函数题)
1.设计思路
- (1)算法
第一步:定义二维字符数组为全局变量。
第二步:调用定义的函数。
第三步:判断n是否为月份数值,若是,返回对应字符串地址;若不是,使地址为空,返回。
- (2)流程图:略。
2.实验代码
char s[12][10]={"January","February","March","April","May","June","July","August","September","October","November","December"};
char *getmonth( int n )
{
char *month;
if(n > 0 && n <= 12)
{
month = s[n-1];
return month;
}
month = NULL;
return month;
}
完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
char *getmonth( int n );
int main()
{
int n;
char *s;
scanf("%d", &n);
s = getmonth(n);
if ( s==NULL ) printf("wrong input!\n");
else printf("%s\n", s);
return 0;
}
char s[12][10]={"January","February","March","April","May","June","July","August","September","October","November","December"};
char *getmonth( int n )
{
char *month;
if(n > 0 && n <= 12)
{
month = s[n-1];
return month;
}
month = NULL;
return month;
}
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
本题出现了较大的问题。
我做这道题目时,是先使用switch语句做的,简单易行不易出错。但是做完以后觉得switch语句和我们最近练习的知识点关系不大,就换了一种方式重写,也因此出现了问题。改正错误其实很容易,但是我却迟迟无法理解错误原因。经过数日的探讨交流和之后老师的讲解,终于明白了错误是内存分配导致的。
题目2.查找星期(函数题)
1.设计思路
- (1)算法
第一步:调用定义的函数。
第二步:定义表示星期的二维数组。
第三步:使用循环语句判断是否存在同输入字符串相同的字符数组,若存在跳出循环,结束调用;否则,返回-1。
- (2)流程图
2.实验代码
int getindex( char *s )
{
int i;
char day[7][10]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"};
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
if(strcmp(s,day[i]) == 0)
break;
if(i == 7)
i = -1;
return i;
}
完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXS 80
int getindex( char *s );
int main()
{
int n;
char s[MAXS];
scanf("%s", s);
n = getindex(s);
if ( n==-1 ) printf("wrong input!\n");
else printf("%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
int getindex( char *s )
{
int i;
char day[7][10]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"};
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
if(strcmp(s,day[i]) == 0)
break;
if(i == 7)
i = -1;
return i;
}
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
无。
题目3.计算最长的字符串长度(函数题)
1.设计思路
- (1)算法
第一步:调用定义的函数。
第二步:使用选择排序法判断字符串长度。
第三步:返回最长的字符串地址。
- (2)流程图:略。
2.实验代码
int max_len( char *s[], int n )
{
int i,t,k,j;
for(i=0;i<(n-1);i++)
{
k=i;
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(strlen(*(s+j))>strlen(*(s+k)))
{
k=j;
}
}
if(i!=k)
{
t=*(s+i); *(s+i)=*(s+k); *(s+k)=t;
}
}
return strlen(*s);
}
完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXN 10
#define MAXS 20
int max_len( char *s[], int n );
int main()
{
int i, n;
char *string[MAXN] = {NULL};
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*MAXS);
scanf("%s", string[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", max_len(string, n));
return 0;
}
int max_len( char *s[], int n )
{
int i,t,k,j;
for(i=0;i<(n-1);i++)
{
k=i;
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(strlen(*(s+j))>strlen(*(s+k)))
{
k=j;
}
}
if(i!=k)
{
t=*(s+i); *(s+i)=*(s+k); *(s+k)=t;
}
}
return strlen(*s);
}
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
无。
题目4.指定位置输出字符串(函数题)
1.设计思路
- (1)算法
第一步:调用定义的函数,定义指针,使其指向为空。
第二步:使用双重循环结构,在外循环内判断输入字符串中是否存在与ch1匹配的字符,如存在,指针指向s[i];再次使用循环结构,内循环内判断输入字符串中是否存在与ch2匹配的字符,如存在,返回指针p,若不存在,内循环结束后返回指针p。
第三步:若外循环内在输入字符串中无法查找到与ch1匹配的字符,使指针指向 '\0' ,返回指针p。
- (2)流程图:略。
2.实验代码
char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 )
{
int i, j;
char *p = NULL;
for(i = 0; s[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if(s[i] == ch1)
{
p = &s[i];
for(j = i; s[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
if(s[j] != ch2)
printf("%c",s[j]);
else
{
printf("%c\n",s[j]);
return p;
}
}
printf("\n");
return p;
}
}
if(s[i] == '\0')
p = &s[i];
printf("\n");
return p;
}
完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXS 10
char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 );
int main()
{
char str[MAXS], ch_start, ch_end, *p;
scanf("%s\n", str);
scanf("%c %c", &ch_start, &ch_end);
p = match(str, ch_start, ch_end);
printf("%s\n", p);
return 0;
}
char *match( char *s, char ch1, char ch2 )
{
int i, j;
char *p = NULL;
for(i = 0; s[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if(s[i] == ch1)
{
p = &s[i];
for(j = i; s[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
if(s[j] != ch2)
printf("%c",s[j]);
else
{
printf("%c\n",s[j]);
return p;
}
}
printf("\n");
return p;
}
}
if(s[i] == '\0')
p = &s[i];
printf("\n");
return p;
}
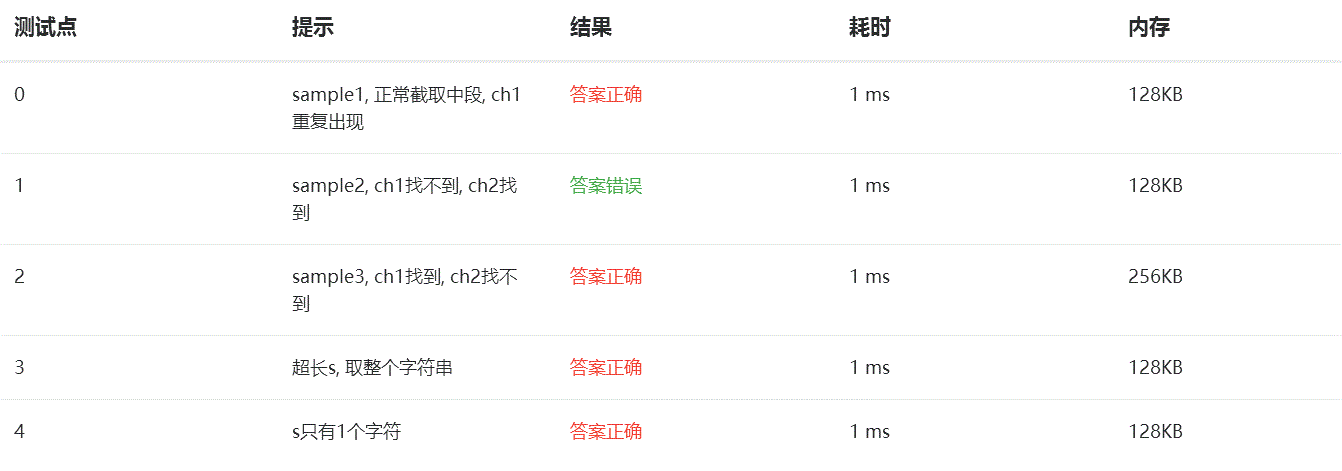
3.本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
本题测试点1出现多次答案错误。
![]()
错误原因:当ch1找不到, ch2找到时,主函数需要输出空行,但是由于初始代码定义指针指向为空,无法输出空行。
解决办法:使指针指向字符串结束字符即可输出空行。
题目5. 奇数值结点链表(函数题)
实验代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode
{
int data;
struct ListNode *next;
};
struct ListNode *readlist();
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L );
void printlist( struct ListNode *L )
{
struct ListNode *p = L;
while (p) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
struct ListNode *L, *Odd;
L = readlist();
Odd = getodd(&L);
printlist(Odd);
printlist(L);
return 0;
}
struct ListNode *readlist()
{
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*tail=NULL,*p=NULL;
int data;
scanf("%d",&data);
while(data!=-1)
{
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); //动态内存分配
p->data = data; //赋值
p->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL) //判断是否为头指针
head=p;
else
tail->next=p;
tail=p; //使尾指针指向p所指向
scanf("%d",&data);
}
return head; //返回头指针
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L )
{
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*head1=NULL,*p=NULL,*str=NULL,*str1=NULL; //动态内存分配
p=*L; //使p指针指向L的地址
if(p == NULL) //p指向为空时,返回0
return 0;
for(; p!=NULL; p=p->next)
{
if(p->data % 2 == 0) //判断变量p->data是否为奇数,将不是奇数的连接起来,形成链表
{
if(head == NULL)
head = p;
else
str->next = p;
str = p;
}
else //将是奇数的连接起来,形成新的链表
{
if(head1 == NULL)
head1 = p;
else
str1->next = p;
str1 = p;
}
}
if(str1 != NULL) //使链表最后指向空
str1->next = NULL;
if(str != NULL) //使链表最后指向空
str->next = NULL;
*L = head;
return head1;
}
本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
问题:链表题目每道都存在相同的问题,就是看到题目有一种无从下手的感觉。
待解决方法:查找链表相关资料,查阅老师PPT,多加练习。
题目6. 学生成绩链表处理(函数题)
实验代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct stud_node
{
int num;
char name[20];
int score;
struct stud_node *next;
};
struct stud_node *createlist();
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score );
int main()
{
int min_score;
struct stud_node *p, *head = NULL;
head = createlist();
scanf("%d", &min_score);
head = deletelist(head, min_score);
for ( p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next )
printf("%d %s %d\n", p->num, p->name, p->score);
return 0;
}
struct stud_node *createlist()
{
struct stud_node *head=NULL,*tail=NULL,*p=NULL; //动态分配空间
int num=0;
char name[20];
int score;
scanf("%d %s %d",&num,name,&score);
while(num!=0)
{
p=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node)); //动态分配空间
p->num=num; //赋值
strcpy(p->name,name);
p->score=score;
p->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL) //判断是否为头指针
head=p;
else
tail->next=p;
tail=p;
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num==0) //当输入num输入为0时,跳出,循环结束
break;
else //否则,输入,循环继续
scanf("%s %d",name,&score);
}
return head;
}
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score )
{
struct stud_node *ptr = head, *ptr1=head; //动态分配内存
if(head==NULL) //p指向为空时,返回NULL
return NULL;
for(; ptr!=NULL; ptr=ptr->next)
{
if(ptr->score < min_score) //判断学生成绩是否小于设置的最低成绩
{
if(ptr==head) ////判断是否为头指针
head = ptr->next;
else
ptr1->next = ptr->next;
free(ptr); //动态分配释放
ptr=ptr1;
}
ptr1 = ptr;
}
return head;
}
本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
问题:如图
![]()
解决办法:当学生成绩小于设置的最低成绩时,未设置ptr=ptr1,添加即可。
题目7. 链表拼接(函数题)
实验代码
本题调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
本题在PTA时间结束时并未书写正确,存在超时错误。
struct ListNode *mergelists(struct ListNode *list1, struct ListNode *list2)
{
struct ListNode *head1=list1, *head2=list2, *p1=head1, *p2=head2, *str1=NULL, *str2=NULL,*q=NULL;
if(p1==NULL)
return head2;
if(p2==NULL)
return head1;
for(;p2!=NULL;p2=str2)
{
str2=p2->next;
q=p2;
for(; p1!=NULL;p1=str1->next)
{
if(p2->data <= p1->data)
{
p2->next = p1;
if(p1==head1)
head1 = p2;
else
str1->next = p2;
str1=q;
break;
}
str1 = p1;
}
if(p1==NULL)
str1->next = head2;
}
return head1;
}
![]()
作业要求三
1、学习总结
(1)如何理解指针数组,它与指针、数组有何关系?为何可以用二级指针对指针数组进行操作?
答:指针数组是数组元素为指针的数组,此数组内每个元素都为指向地址的指针。二级指针可以对指针数组的地址进行操作。
(2)将C高级第三次PTA作业(1)任何一个题目改为使用二级指针对指针数组进行操作。
输出月份英文名
char *getmonth( int n ) {
char *s[12] = {"January","February","March","April","May","June","July","August","September","October","November","December"};
char **p = &s, *q = '\0';
if(n > 0 && n <= 12)
q = *(p+n-1);
return q;
}
(3)用指针数组处理多个字符串有何优势?可以直接输入多个字符串给未初始化的指针数组吗?为什么?
答:当每个字符串长度不同时,可以节省空间,而且不易出现内存分配问题。
不可以。因为未初始化的指针可能会指向一些不确定的地址。
![]()
3、点评链接
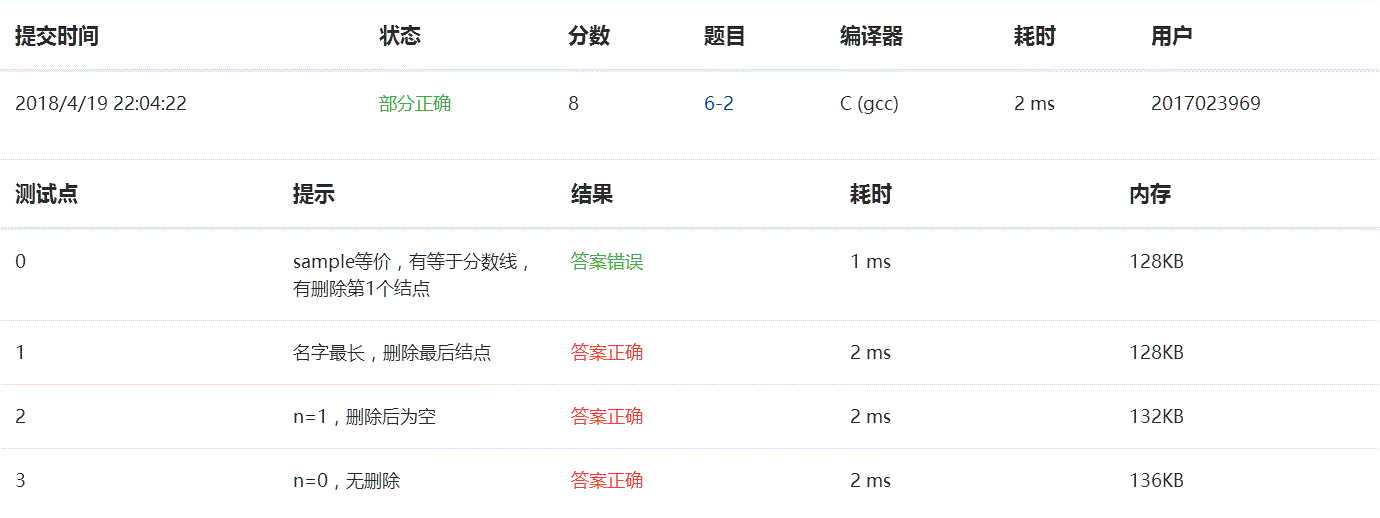
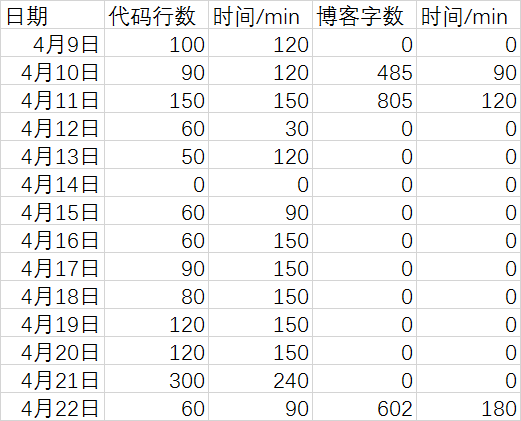
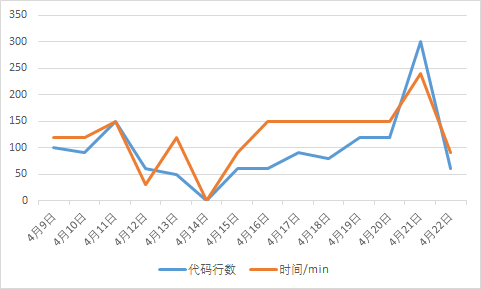
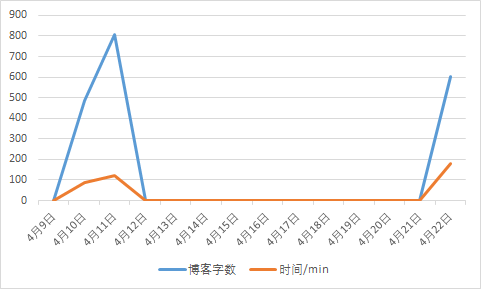
4、图表
![]()
![]()
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号