网络编程
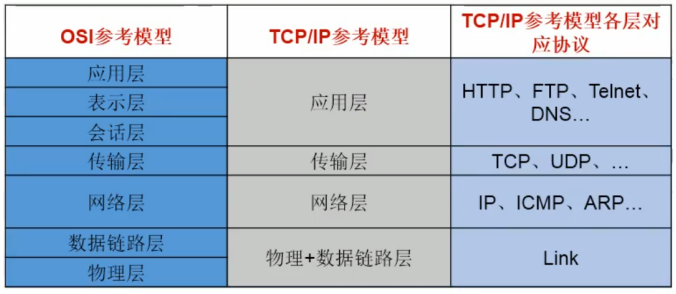
网络通信模型
Inet Address
ip地址:Inet Address
- 唯一标识internet上的计算机
- IP地址分类方式1
- IPV4: 4个字节组成,4个0-255,大概42亿个,30亿在北美,亚洲4亿、2011年初用完,以点分十进制表示如192.168.0.1
- IPV6: 128位,16个字节组成,写成8个无符号整数,每个整数用4个16进制位表示,数之间用:隔开,如2001:0db8:3c4d:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:1a2b
- IP地址分类方式2:
- 公网地址:万维网使用
- 私网地址:局域网使用,192.168开头就是私网地址,范围192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255
由于IP地址不便于记忆,于是使用域名来访问,流程如下:
输入域名=>本机host文件,判断是否有输入的域名地址,没有就通过DNS服务器来找主机
host文件地址:c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
Java的InetAdress类代表IP
public class JavaTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { try{ //获取ip地址 InetAddress inetAddress1=InetAddress.getByName("192.168.0.1"); System.out.println(inetAddress1); InetAddress inetAddress2=InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com"); System.out.println(inetAddress2); //获取本地ip InetAddress inetAddress3=InetAddress.getLocalHost(); System.out.println(inetAddress3); //获取主机名 System.out.println(inetAddress2.getHostName()); //获取主机地址 System.out.println(inetAddress2.getHostAddress()); System.out.println(inetAddress2.getCanonicalHostName()); }catch(UnknownHostException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
端口号
端口号识别正在计算机上运行的进程
- 不同的进程有不同的端口号,用来区分软件
- 被规定为一个16位的整数0-65535
- TCP和UDP协议各有65535个端口,单个协议下端口不能冲突
- 端口分类:
-
- 公认端口:0-1023.被预先定义的服务通信占用的端口
- HTTP默认端口:80
- HTTPS默认端口:443
- FTP默认端口:21
- Telnet默认端口:23
- 注册端口:1024-49151,分配给用户进程或应用程序
- tomcat默认端口:8080
- Mysql默认端口:3306
- Oracle默认端口:1521
- 动态,私有端口:49152-5535
- 公认端口:0-1023.被预先定义的服务通信占用的端口
netstat -ano 查看所有端口
netstat -ano|findstr "6808" 查看指定端口
端口号和IP地址组合就得出一个网络套接字:Socket
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8080); InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress1=new InetSocketAddress("localhost",9000); //获取主机名 System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getHostName()); //获取ip地址 System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getAddress()); //获取端口号 System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getPort()); //获取主机名 System.out.println(inetSocketAddress1.getHostName()); //获取ip地址 System.out.println(inetSocketAddress1.getAddress()); //获取端口号 System.out.println(inetSocketAddress1.getPort()); }
网络通信协议
计算机网络中实现通信必须有一些约定,即通信协议,对速率,传输代码,代码结构,传输控制步骤,出错控制等制定标准
TCP/IP协议簇
- 传输层两个重要协议
- 用户传输协议TCP
- 用户数据报协议UDP
- TCP/IP得名:传输控制协议TCP,网络互联协议IP。实际上是一组协议
- IP协议是网络层的协议,支持网间互联通信
- 四层体系结构:wu
Inet Address
ip地址:Inet Address
唯一标识internet上的计算机
IP地址分类方式1
IPV4: 4个字节组成,4个0-255,大概42亿个,30亿在北美,亚洲4亿、2011年初用完,以点分十进制表示如192.168.0.1
IPV6: 128位,16个字节组成,写成8个无符号整数,每个整数用4个16进制位表示,数之间用:隔开,如2001:0db8:3c4d:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:1a2b
IP地址分类方式2:
公网地址:万维网使用
私网地址:局域网使用,192.168开头就是私网地址,范围192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255
由于IP地址不便于记忆,于是使用域名来访问,流程如下:
输入域名=>本机host文件,判断是否有输入的域名地址,没有就通过DNS服务器来找主机
host文件地址:c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
Java的InetAdress类代表IP
public class JavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try{
//获取ip地址
InetAddress inetAddress1=InetAddress.getByName("192.168.0.1");
System.out.println(inetAddress1);
InetAddress inetAddress2=InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(inetAddress2);
//获取本地ip
InetAddress inetAddress3=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(inetAddress3);
//获取主机名
System.out.println(inetAddress2.getHostName());
//获取主机地址
System.out.println(inetAddress2.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(inetAddress2.getCanonicalHostName());
}catch(UnknownHostException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
端口号
端口号识别正在计算机上运行的进程
不同的进程有不同的端口号,用来区分软件
被规定为一个16位的整数0-65535
TCP和UDP协议各有65535个端口,单个协议下端口不能冲突
端口分类:
公认端口:0-1023.被预先定义的服务通信占用的端口
HTTP默认端口:80
HTTPS默认端口:443
FTP默认端口:21
Telnet默认端口:23
注册端口:1024-49151,分配给用户进程或应用程序
tomcat默认端口:8080
Mysql默认端口:3306
Oracle默认端口:1521
动态,私有端口:49152-5535
netstat -ano 查看所有端口
netstat -ano|findstr "6808" 查看指定端口
端口号和IP地址组合就得出一个网络套接字:Socket
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8080);
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress1=new InetSocketAddress("localhost",9000);
//获取主机名
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getHostName());
//获取ip地址
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getAddress());
//获取端口号
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress.getPort());
//获取主机名
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress1.getHostName());
//获取ip地址
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress1.getAddress());
//获取端口号
System.out.println(inetSocketAddress1.getPort());
}
网络通信协议
计算机网络中实现通信必须有一些约定,即通信协议,对速率,传输代码,代码结构,传输控制步骤,出错控制等制定标准
TCP/IP协议簇
传输层两个重要协议
用户传输协议TCP
用户数据报协议UDP
TCP/IP得名:传输控制协议TCP,网络互联协议IP。实际上是一组协议
IP协议是网络层的协议,支持网间互联通信
四层体系结构:物理链路层,网络层,传输层,应用层
TCP协议与UDP协议对比
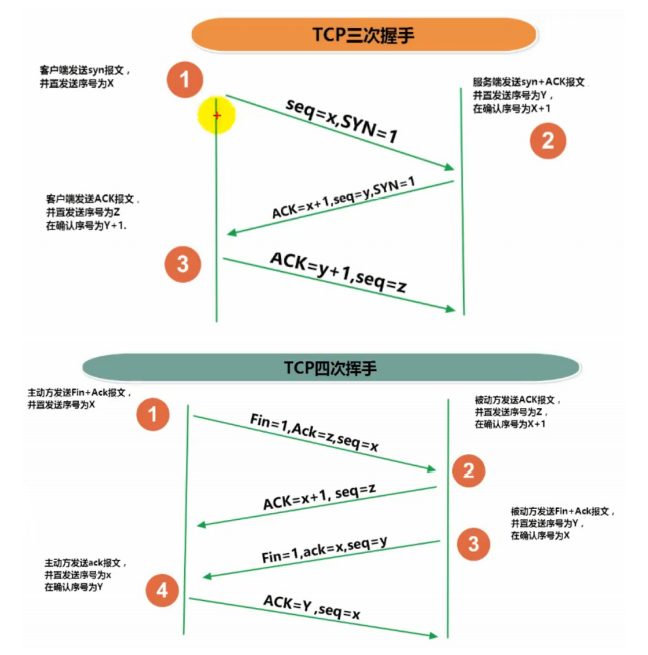
- TCP协议
- 使用TCP协议必须建立TCP连接,形成传输数据通道
- 传输前,3次握手,点对点通信,是可靠的
- 传输完毕,四次挥手断开连接
- UDP协议
- 将数据,源,目的封装成数据报,不需要建立连接
- 每个数据报的大小为64k以内
- 不可靠
- 可以广播发送
客户端发送消息,服务端接收消息
客户端
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { Socket socket = null; OutputStream os = null; try { //连接服务器地址 InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("localhost"); int port = 8000; //创建套接字socket socket = new Socket(inetAddress, port); //创建输出流 os = socket.getOutputStream(); os.write("hhhhjhjasdh".getBytes()); } catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try{ if(os!=null){ os.close(); } if(socket!=null){ socket.close(); } }catch(IOException e1){ e1.printStackTrace(); } } } }
服务端
public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) { ServerSocket serverSocket=null; Socket socket=null; InputStream is=null; ByteArrayOutputStream baos=null; try{ //创建ServiceSocket开放服务器端口 serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8000); //等待客户端连接 socket=serverSocket.accept(); //读取客户端数入 is=socket.getInputStream(); baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte[] buffer=new byte[1024]; int a=0; while ((a=is.read(buffer))!=-1) { baos.write(buffer,0,a); } System.out.println(baos.toString()); System.out.println("客户端地址"+socket.getInetAddress().getHostName()); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try{ baos.close(); is.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); }catch(Exception e1){ e1.printStackTrace(); } } } }
UDP网络编程
- DatagramSocket和DatagramPacket两个类实现了基于UDP协议的网络程序
- UDP数据报通过数据报套接字DatagramSocket发送和接收
- DatagramPacket对象封装UDP数据报,在数据报中包含了发送端的IP地址和端口号和接收端的IP地址和端口号
- 由于每个数据报都给出了完整的地址信息,因此无需建立发送方和接收方的连接
发送接收
发送方
public class Send { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //建立DatagramSocket DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket(); //封装数据包 String msg="songsongsong"; byte[] data=msg.getBytes(); InetAddress inetAddress=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"); DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(data,0,data.length,inetAddress,9000); //发送packet socket.send(packet); socket.close(); } }
接收方
public class Rev { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //建立DatagramSocket,开放端口 DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9000); //接收数据 byte[] buffer=new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buffer,0,buffer.length); socket.receive(packet); //输出,packet.getData()获取packet中的数据 System.out.println(new String(packet.getData())); socket.close(); } }
URL类
URL:统一资源定位符
结构由5部分组成
传输协议://主机名:端口号/文件名#片断名?参数列表
片段名即锚链接,直接定位到某个位置
public class Rev { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { URL url=new URL("http://localhost:8080/helloworld/index.jsp?username=kuangshen&password=123"); System.out.println(url.getProtocol());//获取协议名 System.out.println(url.getHost());//获取主机名 System.out.println(url.getPort());//获取端口名 System.out.println(url.getPath());//文件路径 /helloworld/index.jsp System.out.println(url.getFile());//获取文件名 /helloworld/index.jsp?username=kuangshen&password=123 System.out.println(url.getQuery());//获取查询名 username=kuangshen&password=123 } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号