题意:对一个k元向量, 每次左乘一个k*k的矩阵得到新的向量.问经过一定次数的左乘后,能否使得该向量不再变化. (同时要求此时向量非零)。
析:设初始向量为A,矩阵为P.由于每次矩阵P都是左乘A, 那么可以把若干个P合并. 则题目的条件是: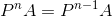
化简为: 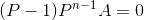 由于要求
由于要求 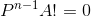 所以 P-1 必须不可逆.可以直接用高斯消元求P-1的秩,判断是否可逆(满秩即可逆).
所以 P-1 必须不可逆.可以直接用高斯消元求P-1的秩,判断是否可逆(满秩即可逆).
所以这个题,并不用求解,只要判断秩就好。
代码如下:
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#define freopenr freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin)
#define freopenw freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const LL LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int maxn = 1e2 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int dr[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
const int dc[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
const char *Hex[] = {"0000", "0001", "0010", "0011", "0100", "0101", "0110", "0111", "1000", "1001", "1010", "1011", "1100", "1101", "1110", "1111"};
int n, m;
const int mon[] = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
const int monn[] = {0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
inline int Min(int a, int b){ return a < b ? a : b; }
inline int Max(int a, int b){ return a > b ? a : b; }
inline LL Min(LL a, LL b){ return a < b ? a : b; }
inline LL Max(LL a, LL b){ return a > b ? a : b; }
inline bool is_in(int r, int c){
return r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m;
}
double a[25][25];
bool Gauss(){
int ans = 0, r = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
for(int j = r; j < n; ++j)
if(fabs(a[j][i]) > eps){
for(int k = i; k < n; ++k)
swap(a[j][k], a[r][k]);
break;
}
if(fabs(a[r][i]) < eps){ ++ans; continue; }
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if(j != r && fabs(a[j][i]) > eps){
double tmp = a[j][i]/a[r][i];
for(int k = i; k < n; ++k)
a[j][k] -= tmp * a[r][k];
}
++r;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int T; cin >> T;
for(int kase = 1; kase <= T; ++kase){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
scanf("%lf", a[i]+j);
a[i][i] -= 1.0;
}
printf("%d", Gauss());
if(kase == T) continue;
printf("%c", kase % 5 ? ' ' : '\n');
}
if(T % 5) printf("\n");
return 0;
}


