稀疏数组和队列
稀疏数组
所谓稀疏数组就是当数组中大部分的内容值都未被使用(或都为零),在数组中仅有少部分的空间使用。因此造成内存空间的浪费,为了节省内存空间,并且不影响数组中原有的内容值,我们可以使用稀疏数组去压缩数据。OK,如果你不明白,那我们来看一个例子。
在一个五子棋中,有存盘和续上盘的功能
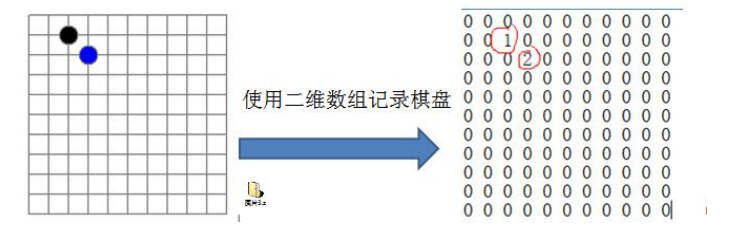
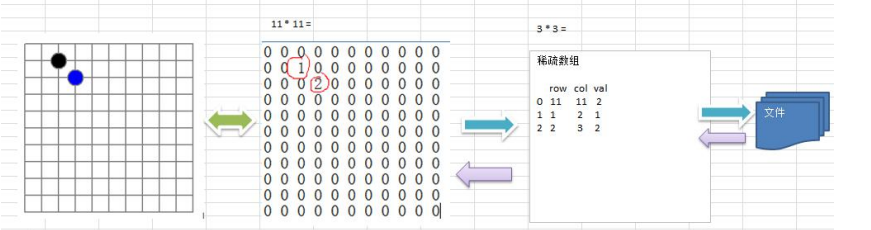
分析问题:因为该二维数组的很多默认值是 0,因此记录了很多没有意义的数据 > 稀疏数组
解决方法
思路
-
记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同的值
-
把具有不同值的元素的行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的范围

应用实例
- 使用稀疏数组,来保留类似前面的二维数组(棋盘、地图等等)
- 把稀疏数组存盘,并且可以从新恢复为原来的二维数组
- 整体思路
代码实现
public class SparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个二维数组
//0:表示没有棋子 1表示黑子 2表示蓝子
int chessArr[][] = new int[11][10];
chessArr[1][2] = 1;
chessArr[2][3] = 2;
for(int[] row:chessArr){
for(int data:row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();
}
int[][] array = getSparseArray(chessArr);
System.out.println("-------");
for(int i = 0 ; i< array.length;i++){
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t\n",array[i][0],array[i][1],array[i][2]);
}
System.out.println("--------");
int[][] startArr = recovery(array);
for(int[] row:startArr){
for(int data:row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 将普通数组转换为稀疏数组
* @param chessArr
* @return
*/
public static int[][] getSparseArray(int[][] chessArr){
if(!checkIsRight(chessArr)){
return null;
}
//1.拿到数组后 首先获取元素的个数,然后才能建立稀疏数组
int sum = 0;
for(int[] arr:chessArr){
for(int i:arr){
if(i != 0){
sum++;
}
}
}
//2.建立稀疏数组
int[][] sparseArr = new int[sum+1][3];
sparseArr[0][0] = chessArr.length; //行
sparseArr[0][1] = chessArr[0].length;//列
sparseArr[0][2] = sum; //元素个数
//3.数组存放
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <chessArr.length; i++ ){
for(int j = 0; j <chessArr[i].length;j++ ){
if(chessArr[i][j] != 0){
sparseArr[++count][0] = i;//行
sparseArr[count][1] = j;//列
sparseArr[count][2] = chessArr[i][j];
}
}
}
return sparseArr;
}
/**
* 将稀疏数组转回普通数组
* @param sparseArr
* @return
*/
public static int[][] recovery(int[][] sparseArr){
if(!checkIsRight(sparseArr)){
return null;
}
//获取原数组的 行数和列数 并创建原数组
int arr[][] = new int[sparseArr[0][0]][sparseArr[0][1]];
for(int i = 1; i < sparseArr.length;i++){
arr[sparseArr[i][0]][sparseArr[i][1]] = sparseArr[i][2];
}
return arr;
}
public static boolean checkIsRight(int[][] arr){
if(arr == null || arr.length <= 1 ){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
队列
- 队列是一个有序列表,可以用数组或链表来实现
- 遵循先入先出的原则

数组模拟队列
- 队列本身是有序列表,若使用数组的数据结构来存储队列的数据,则队列的数组声明如上图,其中maxSize是该队列的最大容量
- 因为队列的输出、输入分别从头尾端来处理,因此需要两个变量front及rear分别记录队列头尾端的下标,front会随着数据输出而改变,而rear会随着队列的输入而改变
- 当我们将数据输入队列时称为 addQueue,addQueue 的处理有两个步骤:思路分析
(1) 将尾指针往后移:rear+1,当front == rear [空]
(2) 若尾指针rear小于队列的最大下标 maxSize - 1,则数据输入rear 所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入数据。
rear == maxSize - 1
代码实现
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(10);
queue.addQueue(1);
queue.addQueue(2);
queue.addQueue(3);
queue.addQueue(4);
queue.getQueue();
queue.showQueue();
}
}
//使用数组模拟队列-编写一个ArrayQueue类
class ArrayQueue{
private int maxSize; //表示数组的最大容量
private int front;//队列头
private int rear;//队列尾
private int[] arr; //该数组用于存放数据,模拟队列
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
this.front = -1;
this.rear = -1;
}
//判断队列是否已满
public boolean isFull(){
return rear == maxSize - 1;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front == rear;
}
//添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n){
//判断队列是否满
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
arr[++rear] = n;
}
//获取队列的数据,出队列
public int getQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列已空");
}
return arr[++front];
}
//显示队列所有数据
public void showQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列已空");
return;
}
for(int i = front+1 ;i <= rear;i++){
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i,arr[i]);
}
}
}
数组模拟环形队列
之前实现的队列存在一个明显的问题,就是数组使用一次就不能再用了,出队列数据的位置始终空在那,没有达到一个复用的效果,因此我们要对这个队列进行一次优化,将此队列变成一个环形队列
思路
-
front 变量的含义做一个调整:front就指向队列的第一个元素,也就是 arr[front] 就代表队列的第一个元素,
front初始值 = 0 -
rear 的变量含义做一个调整:rear指向最后一个元素的后一个位置,因为希望空出一个空间作为约定,rear的初始值 = 0
-
当队列满时,条件是 (rear + 1) % maxSize == front 【满】
-
当队列为空的条件,rear == front 空
-
当我们这样分析,队列中有效的数据的个数 (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize
-
我们就可以在原来的队列上修改得到 一个环形队列
代码实现
public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一把
System.out.println("测试数组模拟环形队列的案例");
//创建一个环形队列 说明设置4,其队列数据最大是3
CircleArray queue = new CircleArray(4);
char key = ' ';//接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
//输出一个菜单
while(loop){
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输出一个数字");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h'://查看队列头的数据
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n",res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e'://退出
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
class CircleArray{
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public CircleArray(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
//判断队列是否已满
public boolean isFull(){
return (rear+1)%maxSize == front;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rear == front;
}
//添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n){
//判断队列是否已满
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("队列满,不能加入数据");
return;
}
//直接将数据加入
arr[rear] = n;
//将rear后移,这里必须考虑取模
rear = (rear+1)%maxSize;
}
//获取队列的数据
public int getQueue(){
//判断队列是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
//通过抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front+1)%maxSize;
return value;
}
//显示队列的所有数据
public void showQueue(){
//遍历
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空,没有数据");
return;
}
for(int i = front; i < front + size() ; i++){
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i%maxSize,arr[i%maxSize]);
}
}
//求出当前队列有效数据的个数
public int size(){
//加上maxSize 防止模出负数 因为这是一个环形队列
return (rear + maxSize - front)%maxSize;
}
//显示队列的头数据
public int headQueue(){
//判断
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列是空的,~没有数据");
}
return arr[front];
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理