代码随想录Day10
LeetCode 459重复字符串
给定一个非空的字符串,判断它是否可以由它的一个子串重复多次构成。给定的字符串只含有小写英文字母,并且长度不超过10000。
示例 1:
输入: "abab"
输出: True
解释: 可由子字符串 "ab" 重复两次构成。
示例 2:
输入: "aba"
输出: False
示例 3:
输入: "abcabcabcabc"
输出: True
解释: 可由子字符串 "abc" 重复四次构成。 (或者子字符串 "abcabc" 重复两次构成。)
思想:
暴力解法:
就是一个for循环获取 子串的终止位置, 然后判断子串是否能重复构成字符串,又嵌套一个for循环,所以是O(n^2)的时间复杂度。
子串的开始位置位于第一个元素的位置,且子串的长度不能大于字符串长度的一半,大于一半肯定是不可以。
移动匹配法:
由于字符串如果是重复之后得到的,那么前半部分+后半部分=完整字符串。
所以 S(减前半部分)+S(减后半部分) = S 就说明是由于重复字符串组成。
KMP算法:
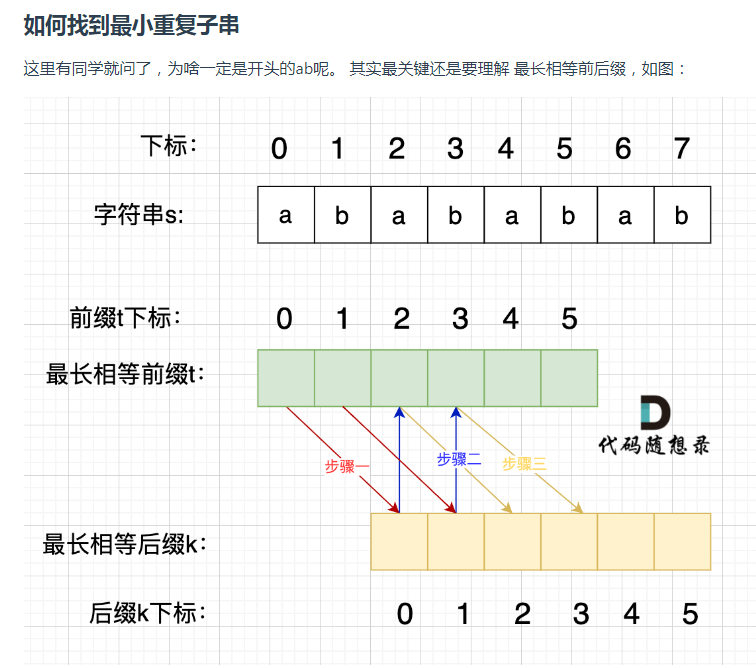
由于数组t和数组k是相等的。
步骤一:因为 这是相等的前缀和后缀,t[0] 与 k[0]相同, t[1] 与 k[1]相同,所以 s[0] 一定和 s[2]相同,s[1] 一定和 s[3]相同,即:,s[0]s[1]与s[2]s[3]相同 。
步骤二: 因为在同一个字符串位置,所以 t[2] 与 k[0]相同,t[3] 与 k[1]相同。
步骤三: 因为 这是相等的前缀和后缀,t[2] 与 k[2]相同 ,t[3]与k[3] 相同,所以,s[2]一定和s[4]相同,s[3]一定和s[5]相同,即:s[2]s[3] 与 s[4]s[5]相同。
步骤四:循环往复。
所以字符串s,s[0]s[1]与s[2]s[3]相同, s[2]s[3] 与 s[4]s[5]相同,s[4]s[5] 与 s[6]s[7] 相同。
正是因为 最长相等前后缀的规则,当一个字符串由重复子串组成的,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串就是最小重复子串。
代码:
class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) { if (s.equals("")) return false; int len = s.length(); // 原串加个空格(哨兵),使下标从1开始,这样j从0开始,也不用初始化了 s = " " + s; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); int[] next = new int[len + 1]; // 构造 next 数组过程,j从0开始(空格),i从2开始 for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= len; i++) { // 匹配不成功,j回到前一位置 next 数组所对应的值 while (j > 0 && chars[i] != chars[j + 1]) j = next[j]; // 匹配成功,j往后移 if (chars[i] == chars[j + 1]) j++; // 更新 next 数组的值 next[i] = j; } // 最后判断是否是重复的子字符串,这里 next[len] 即代表next数组末尾的值 if (next[len] > 0 && len % (len - next[len]) == 0) { return true; } return false; } }
LeetCode232:用栈实现队列
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) -- 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
pop() -- 从队列首部移除元素。
peek() -- 返回队列首部的元素。
empty() -- 返回队列是否为空。
思路:
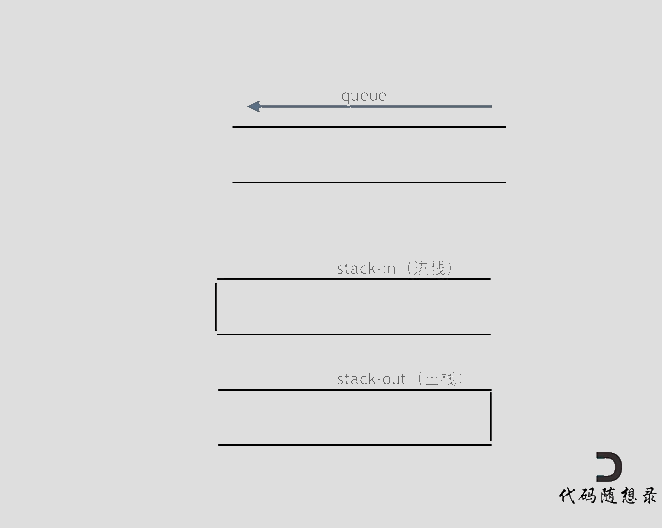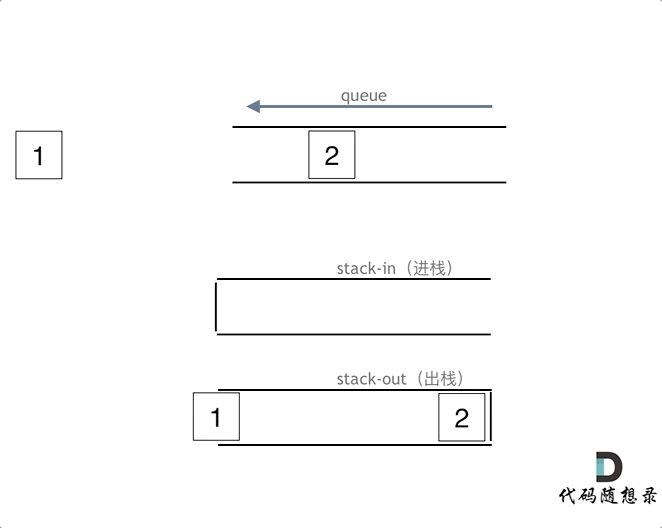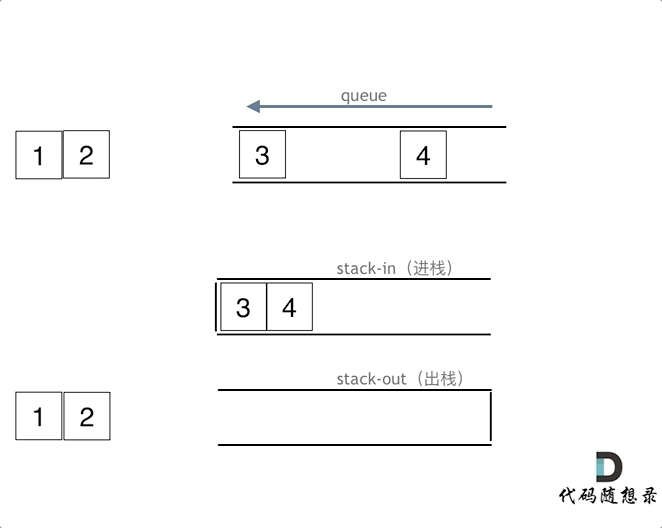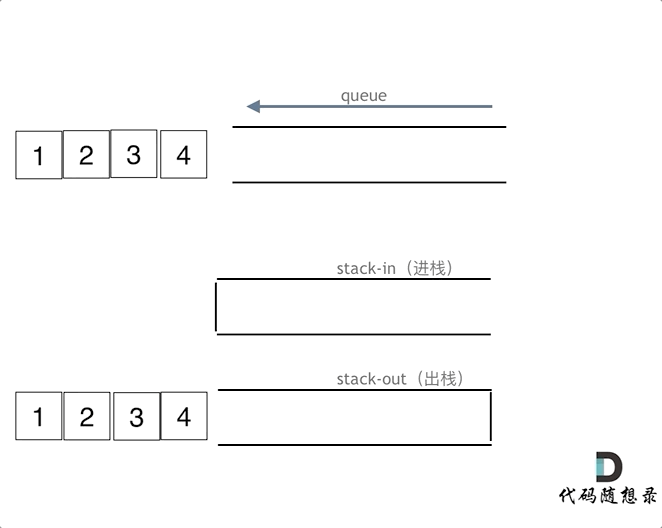
使用两个栈来实现队列操作,一个进栈一个出栈。每次进两个出两个就可以保证和队列的顺序一致
代码:
class MyQueue { Stack<Integer> stackIn; Stack<Integer> stackOut; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyQueue() { stackIn = new Stack<>(); // 负责进栈 stackOut = new Stack<>(); // 负责出栈 } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ public void push(int x) { stackIn.push(x); } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ public int pop() { dumpstackIn(); return stackOut.pop(); } /** Get the front element. */ public int peek() { dumpstackIn(); return stackOut.peek(); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return stackIn.isEmpty() && stackOut.isEmpty(); } // 如果stackOut为空,那么将stackIn中的元素全部放到stackOut中 private void dumpstackIn(){ if (!stackOut.isEmpty()) return; while (!stackIn.isEmpty()){ stackOut.push(stackIn.pop()); } } }
LeetCode225. 用队列实现栈
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
思路:
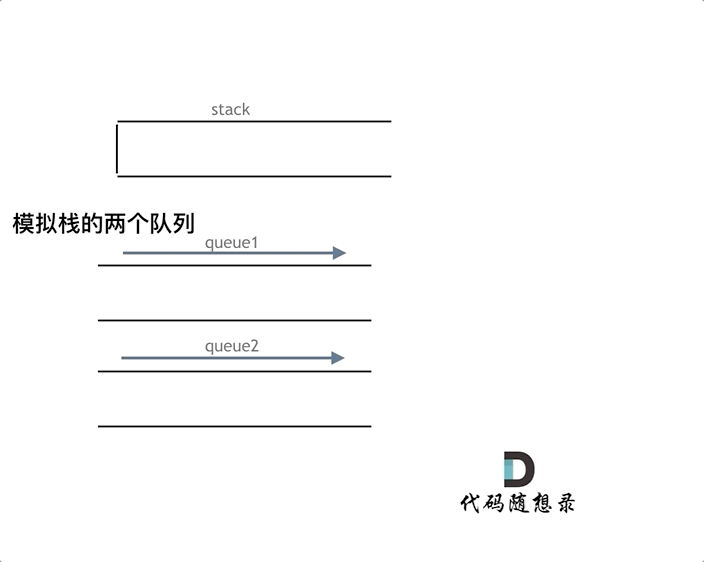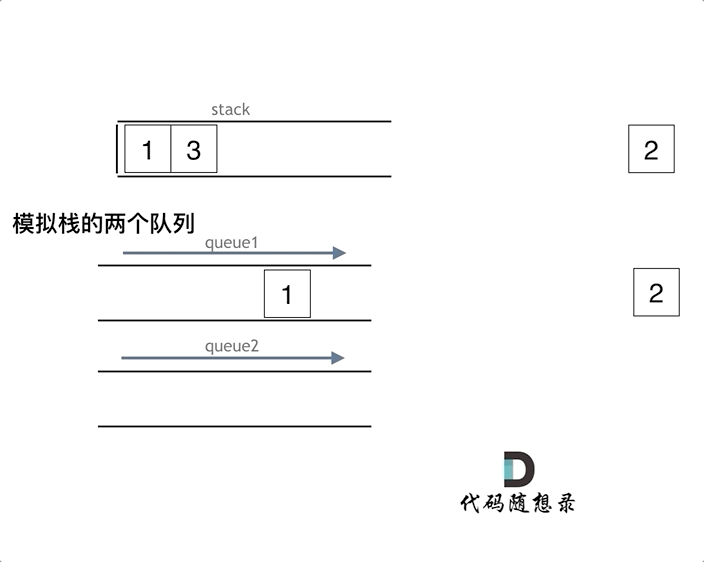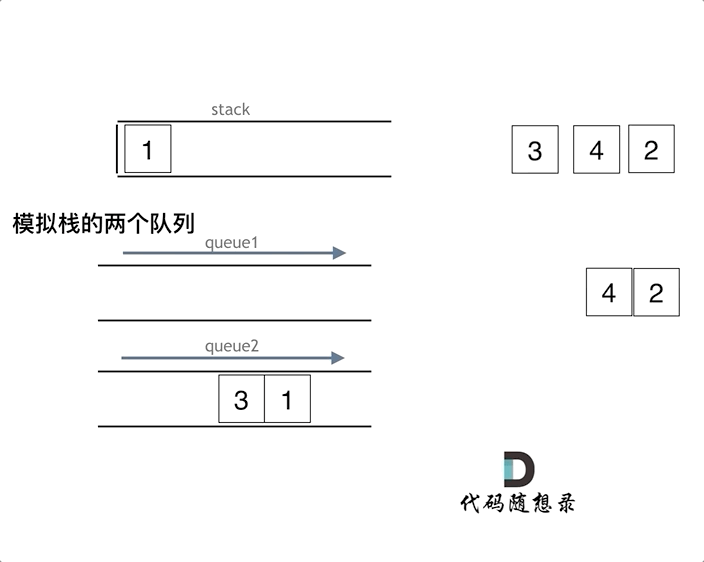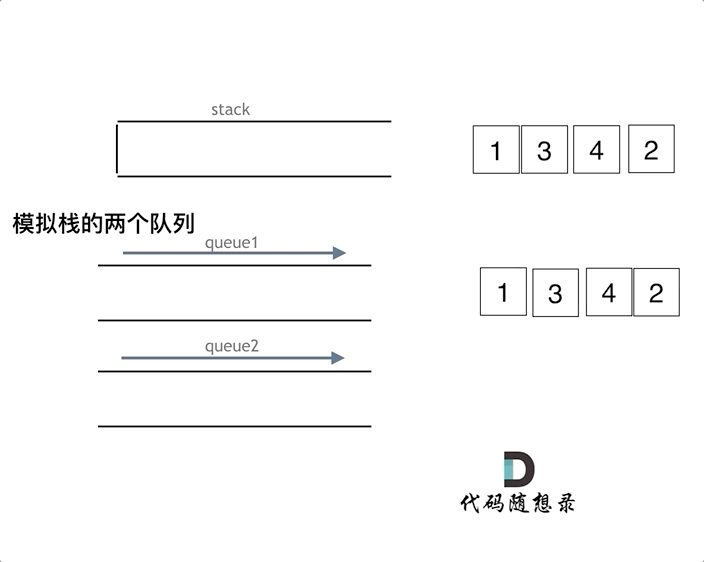
可以用两个队列实现,也可以用一个队列来实现。如果用两个队列实现栈,一个队列用来存放要出的元素之前的元素,一个元素用来存需要输出的元素
如果用一个队列实现,只要每次添加元素到队列时,把头元素重新添加到尾部即可。
代码:
class MyStack { Queue<Integer> queue1; // 和栈中保持一样元素的队列 Queue<Integer> queue2; // 辅助队列 /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyStack() { queue1 = new LinkedList<>(); queue2 = new LinkedList<>(); } /** Push element x onto stack. */ public void push(int x) { queue2.offer(x); // 先放在辅助队列中 while (!queue1.isEmpty()){ queue2.offer(queue1.poll()); } Queue<Integer> queueTemp; queueTemp = queue1; queue1 = queue2; queue2 = queueTemp; // 最后交换queue1和queue2,将元素都放到queue1中 } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ public int pop() { return queue1.poll(); // 因为queue1中的元素和栈中的保持一致,所以这个和下面两个的操作只看queue1即可 } /** Get the top element. */ public int top() { return queue1.peek(); } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return queue1.isEmpty(); } } 使用两个 Deque 实现 class MyStack { // Deque 接口继承了 Queue 接口 // 所以 Queue 中的 add、poll、peek等效于 Deque 中的 addLast、pollFirst、peekFirst Deque<Integer> que1; // 和栈中保持一样元素的队列 Deque<Integer> que2; // 辅助队列 /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyStack() { que1 = new ArrayDeque<>(); que2 = new ArrayDeque<>(); } /** Push element x onto stack. */ public void push(int x) { que1.addLast(x); } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ public int pop() { int size = que1.size(); size--; // 将 que1 导入 que2 ,但留下最后一个值 while (size-- > 0) { que2.addLast(que1.peekFirst()); que1.pollFirst(); } int res = que1.pollFirst(); // 将 que2 对象的引用赋给了 que1 ,此时 que1,que2 指向同一个队列 que1 = que2; // 如果直接操作 que2,que1 也会受到影响,所以为 que2 分配一个新的空间 que2 = new ArrayDeque<>(); return res; } /** Get the top element. */ public int top() { return que1.peekLast(); } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return que1.isEmpty(); } } 优化,使用一个 Deque 实现 class MyStack { // Deque 接口继承了 Queue 接口 // 所以 Queue 中的 add、poll、peek等效于 Deque 中的 addLast、pollFirst、peekFirst Deque<Integer> que1; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyStack() { que1 = new ArrayDeque<>(); } /** Push element x onto stack. */ public void push(int x) { que1.addLast(x); } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ public int pop() { int size = que1.size(); size--; // 将 que1 导入 que2 ,但留下最后一个值 while (size-- > 0) { que1.addLast(que1.peekFirst()); que1.pollFirst(); } int res = que1.pollFirst(); return res; } /** Get the top element. */ public int top() { return que1.peekLast(); } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return que1.isEmpty(); } } 优化,使用一个 Queue 实现 class MyStack { Queue<Integer> queue; public MyStack() { queue = new LinkedList<>(); } //每 offer 一个数(A)进来,都重新排列,把这个数(A)放到队列的队首 public void push(int x) { queue.offer(x); int size = queue.size(); //移动除了 A 的其它数 while (size-- > 1) queue.offer(queue.poll()); } public int pop() { return queue.poll(); } public int top() { return queue.peek(); } public boolean empty() { return queue.isEmpty(); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!