C# 线程的常用方法与生命周期管理
一、Thread的基本使用
1、Start
不带参数
static void Main(string[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(OneTest); thread.Name = "Test"; thread.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void OneTest() { Thread thisTHread = Thread.CurrentThread; Console.WriteLine("线程标识:" + thisTHread.Name); Console.WriteLine("当前地域:" + thisTHread.CurrentCulture.Name); // 当前地域 Console.WriteLine("线程执行状态:" + thisTHread.IsAlive); Console.WriteLine("是否为后台线程:" + thisTHread.IsBackground); Console.WriteLine("是否为线程池线程"+thisTHread.IsThreadPoolThread); }
带参数
static void Main(string[] args) { string myParam = "abcdef"; ParameterizedThreadStart parameterized = new ParameterizedThreadStart(OneTest); Thread thread = new Thread(parameterized); thread.Start(myParam); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void OneTest(object obj) { string str = obj as string; if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str)) return; Console.WriteLine("新的线程已经启动"); Console.WriteLine(str); }
使用静态变量或类成员变量
class Program { private string A = "成员变量"; public static string B = "静态变量"; static void Main(string[] args) { // 创建一个类 Program p = new Program(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(p.OneTest1); thread1.Name = "Test1"; thread1.Start(); Thread thread2 = new Thread(OneTest2); thread2.Name = "Test2"; thread2.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } public void OneTest1() { Console.WriteLine("新的线程已经启动"); Console.WriteLine(A); // 本身对象的其它成员 } public static void OneTest2() { Console.WriteLine("新的线程已经启动"); Console.WriteLine(B); // 全局静态变量 } }
优点:不需要装箱拆箱,多线程可以共享空间;
缺点:变量是大家都可以访问,此种方式在多线程竞价时,可能会导致多种问题(可以加锁解决)。
二、委托与Lambda
public delegate void ThreadStart();
使用委托
static void Main(string[] args) { System.Threading.ThreadStart start = DelegateThread; Thread thread = new Thread(start); thread.Name = "Test"; thread.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void DelegateThread() { OneTest("a", "b", 666, new Program()); } public static void OneTest(string a, string b, int c, Program p) { Console.WriteLine("新的线程已经启动"); }
使用Lambda
static void Main(string[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(() => { OneTest("a", "b", 666, new Program()); }); thread.Name = "Test"; thread.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void OneTest(string a, string b, int c, Program p) { Console.WriteLine("新的线程已经启动"); }
三、暂停与阻塞
Thread.Sleep() 方法可以将当前线程挂起一段时间,Thread.Join() 方法可以阻塞当前线程一直等待另一个线程运行至结束。
在等待线程 Sleep() 或 Join() 的过程中,线程是阻塞的(Blocket)。
什么是阻塞?
当线程由于特点原因暂停执行,那么它就是阻塞的。
如果线程处于阻塞状态,线程就会交出他的 CPU 时间片,并且不会消耗 CPU 时间,直至阻塞结束。
阻塞会发生上下文切换。
static void Main(string[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(OneTest); thread.Name = "小弟弟"; Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now}:大家在吃饭,吃完饭后要带小弟弟逛街"); Console.WriteLine("吃完饭了"); Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now}:小弟弟开始玩游戏"); thread.Start(); // 化妆 5 s Console.WriteLine("不管他,大姐姐化妆先"); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)); Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now}:化完妆,等小弟弟打完游戏"); thread.Join(); Console.WriteLine("打完游戏了嘛?" + (!thread.IsAlive ? "true" : "false")); Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now}:走,逛街去"); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void OneTest() { Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + "开始打游戏"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now}:第几局:" + i); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); // 休眠 2 秒 } Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + "打完了"); }
Join() 也可以实现简单的线程同步,即一个线程等待另一个线程完成。
四、线程终止
Thread.Abort() 方法不能在 .NET Core 上使用,不然会出现 System.PlatformNotSupportedException:“Thread abort is not supported on this platform.” 。
五、线程的不确定性
线程的不确定性是指几个并行运行的线程,不确定在下一刻 CPU 时间片会分配给谁(当然,分配有优先级)。
对我们来说,多线程是同时运行的,但一般 CPU 没有那么多核,不可能在同一时刻执行所有的线程。CPU 会决定某个时刻将时间片分配给多个线程中的一个线程,这就出现了 CPU 的时间片分配调度。
执行下面的代码示例,你可以看到,两个线程打印的顺序是不确定的,而且每次运行结果都不同。
CPU 有一套公式确定下一次时间片分配给谁,但是比较复杂,需要学习计算机组成原理和操作系统。
static void Main(string[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(Test1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(Test2); thread1.Start(); thread2.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void Test1() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine("Test1:" + i); } } public static void Test2() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine("Test2:" + i); } }
六、线程优先级、前台线程和后台线程
Thread.Priority 属性用于设置线程的优先级,Priority 是一个 ThreadPriority 枚举,其枚举类型如下:
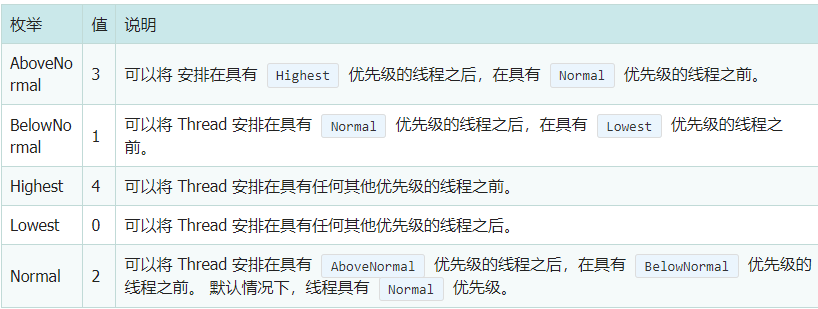
先级排序:Highest > AboveNormal > Normal > BelowNormal > Lowest。
Thread.IsBackgroundThread 可以设置线程是否为后台线程。
前台线程的优先级大于后台线程,并且程序需要等待所有前台线程执行完毕后才能关闭;而当程序关闭是,无论后台线程是否在执行,都会强制退出。


