《CMU15-213课程——实验一》
《CMU15-213课程——实验一》
lab要求:
lab简述
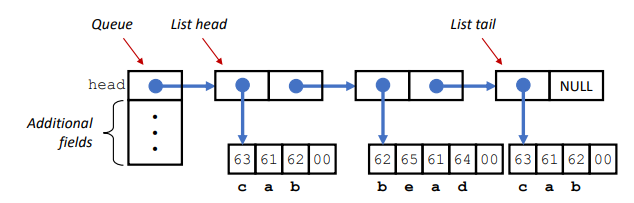
编写以单链表为主体的队列,其队列的元素由数据域和指针域,数据域为C风格字符串,指针域指向同类型的一个节点。
如图:
coding要求:
queue_new: Create a new, empty queue.
queue_free: Free all storage used by a queue.
queue_insert_head: Attempt to insert a new element at the head of the queue (LIFO discipline).
queue_insert_tail: Attempt to insert a new element at the tail of the queue (FIFO discipline).
queue_remove_head: Attempt to remove the element at the head of the queue.
queue_size: Compute the number of elements in the queue.
queue_reverse: Reorder the list so that the queue elements are reversed in order. This function should not allocate or free any list elements (either directly or via calls to other functions that allocate or free list elements.) Instead, it should rearrange the existing elements.
以上要求简述,能够对该队列进行创建,删除,头插节点,尾插节点,头部节点移除,队列长度查询,反转队列。
笔者注:
强烈建议英语不好的同学,学会适应看英文句子,因为很有帮助!!这不只是一小步,而是你迈向dream的一大步!!!并且遇到长时间解决不了的问题,可以学会放一放,idea会来的~~实验完成一定要独立!!!
实验总结
1.任何字符串使用都需要还是用堆空间动态开辟。
2.任何动态开辟空间,在malloc开辟失败时,都需要做出释放该空间操作,防止意外占用。
3.链表节点物理不连续(指针+节点数,可使指针指向对应的连续空间地址,但其空间对应变量存储的内容不一定是链表的节点,所以不能这样使用!!!)。
4.sizeof()用于检测数据大小(返回的是字节),strlen()返回字符串元素个数。也可以用sizeof()计算数组元素个数:sizeof(数组)/sizeof(元素的数据类型)。
5.写之前一定要考虑清楚,不然边运行边调试程序浪费时间。
源代码参考(仅放上需要更改的部分,仅供参考)
queue.h文件
typedef struct {
list_ele_t *head;
/*根据实验要求:队列除了头结点,还需要计算队列长度和尾结点
*/
list_ele_t *tail;
int length;
} queue_t;
queue.c文件
1.queue_new
queue_t *queue_new(void) {
queue_t *q = (queue_t*)malloc(sizeof(queue_t));
/* What if malloc returned NULL? */
/* create queue is failure */
if (q == NULL){//当创建队列为空时,直接返回为空
return NULL;
}
/* if the new queue was created successfully, these variable is initialization*/
//仅创建头结点
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->length = 0;
return q;
}
2.queue_free
需要考虑队列为空时的处理;对于非空队列的释放,需要将删除节点数据,再删除结点。
void queue_free(queue_t *q) {
/* How about freeing the list elements and the strings? */
/* Free queue structure */
//if queue is void , not do anything.
if (q == NULL){
return ;
}
//节点依次删除,节点数据->节点
//else queue's node data deleted successively
//单链表中的元素指针移动不能使用,指针+长度形式访问
//因为其物理上不连续
//对于非空队列的释放,依次从头部释放
if(q->length != 0){
for(;q->head ->next != NULL;){
list_ele_t *temp = q->head;//暂存需释放节点
q->head = q->head ->next;//头结点移动
free(temp->value);//释放
free(temp);
--q->length ;//长度减一
}
//最后释放头结点和队列
free(q->head ->value);
free(q->head);
}
free(q);
}
3.queue_insert_head
bool queue_insert_head(queue_t *q, const char *s) {
/* What should you do if the q is NULL? */
if(q == NULL){
return false;
}
list_ele_t *newh;
newh = (list_ele_t*)malloc(sizeof(list_ele_t));
/* Don't forget to allocate space for the string and copy it */
/* What if either call to malloc returns NULL? */
//如果malloc返回null值时,表明内存空间不足,我们应打印输出信息然后终止程序
if(newh == NULL){
free(newh);
return false;
}
//将c风格字符赋值给新节点
//第一种情况,赋值字符串为空
if(s == NULL){
return false;
}
else{//非空赋值字符串
newh->value = (char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
//但凡涉及到对开辟空间失败,我们都需要把开辟失败的空间释放
if(newh->value == NULL){
free(newh->value);
free(newh);
return false;
}
//成功开辟
strcpy(newh->value,s);
}
//把新节点插入头部
newh->next = q->head;
q->head = newh;
//当空队列第一次插入结点时,头部和尾部结点也需要赋值
if(q->length == 0){
q->tail = q->head;
}
++q->length;
return true;
}
4.queue_insert_tail
bool queue_insert_tail(queue_t *q, const char *s) {
/* You need to write the complete code for this function */
/* Remember: It should operate in O(1) time */
//如果队列为空,不进行任何操作
if(q == NULL){
return false;
}
list_ele_t *newt = (list_ele_t*)malloc( sizeof(list_ele_t));
//如果malloc返回null值时
if(newt == NULL){
free(newt);
return false;
}
//将新插入值赋于新节点数据位
newt->value = (char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
//如果结点数据的堆空间开辟失败
if(newt->value == NULL){
free(newt->value);
free(newt);
return false;
}
strcpy(newt->value,s);
newt->next = NULL;
//将新结点连接尾部结点,形成尾部,并移动尾部指针指向
q->tail ->next = newt;
q->tail = newt;
//当空队列第一次插入结点时,头部和尾部结点也需要赋值
if(q->length == 0){
q->tail = newt;
q->head = q->tail;
}
++q->length;
return true;
}
5.queue_remove_head
bool queue_remove_head(queue_t *q, char *buf, size_t bufsize) {
/* You need to fix up this code. */
//如果为空队列,或者不存在,直接返回
if(q == NULL || q->length == 0 ){
return false;
}
//将准备移除的头结点保存在temp中
list_ele_t *temp = q->head;
//移动头结点位置
q->head = q->head ->next;
if(bufsize != 0){
strncpy(buf,temp->value,bufsize-1);
buf[bufsize-1]='\0';
free(temp->value);
}
else{//rhq型删除头结点,也需要把对应的堆空间删除
free(temp->value);
}
//剔除头部节点,头部节点连接下一个结点
//将剔除结点删除
free(temp);
//队列长度减一
--q->length;
return true;
}
6.queue_size
size_t queue_size(queue_t *q) {
/* You need to write the code for this function */
/* Remember: It should operate in O(1) time */
if(q == NULL){
return false;
}
return (size_t)q->length;
}
7.queue_reverse
将队列元素反序,其实就相当于,交换头尾节点,然后将原前序结点依次插入在原尾结点后。
下段代码举例演示:
| temp_t | temp_h | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| temp_h | temp_t | ||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| temp_h | temp_t | ||
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| temp_h | temp_t | ||
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
void queue_reverse(queue_t *q) {
/* You need to write the code for this function */
//空队列直接返回
if(q == NULL || q->length == 1 || q->length ==0) return ;
//非空队列处理
//第一次交换,将头部与尾部相连
q->tail->next = q->head;
//原序的前序结点和尾序结点
list_ele_t *temp_h = q->head->next;
list_ele_t *temp_t = q->head;
//利用类似尾插法交换结点次序
// r -> q -> p -> t -> z
for(;temp_h != q->tail;){
//q -> r / p ->t -> z
//将当前的前序结点结点插入逆序的头部第二位置
q->tail -> next = temp_h;
//temp_h指针指向:由r到q
//移动指向的原序的前序结点
temp_h = temp_h ->next;
//q -> r -> p ->t -> z
//原序的尾序结点连接,完成当前需逆序结点的前后逆序相邻结点连接。
q->tail->next ->next= temp_t;
//temp_t指针指向: 由p到r
//移动动态的尾序结点
temp_t = q->tail->next;
}
//将原序的头部节点和尾部结点更改为逆序位置
list_ele_t *temp = q->tail;
q->head ->next = NULL;
q->tail = q->head;
q->head = temp;
return ;
}
实验测试命令
#make 构建文件
# ./qtest 可以自己进行测试队列
#make test 运行官方给出的测试cmd
本文作者:duuuuu17
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/duuuuu17/p/17410766.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步