基于注解的声明式事务的实现原理
我们知道,基于注解的声明式事务要想生效,必不可少的一步是在容器配置类上加@EnableTransactionManagement注解,开启事务,所以就从这个注解开始分析。
1. @EnableTransactionManagement注解通过导入方式,在容器中注册了两个重要组件:
AutoProxyRegistrar——相当于一个自定义组件注册器,在容器中注册了一个后置处理器;
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration——是一个容器配置类,在其中注册了事务增强器。
以下是@EnableTransactionManagement注解的源码,注意@Import中的那个类,实现了ImportsSelector接口,正是通过这个ImportSelector导入了上述两个组件。关于ImportsSelector的用法https://www.cnblogs.com/dubhlinn/p/10662763.html中有过记录。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class) public @interface EnableTransactionManagement { /** * Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created ({@code true}) as * opposed to standard Java interface-based proxies ({@code false}). The default is * {@code false}. <strong>Applicable only if {@link #mode()} is set to * {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}</strong>. * <p>Note that setting this attribute to {@code true} will affect <em>all</em> * Spring-managed beans requiring proxying, not just those marked with * {@code @Transactional}. For example, other beans marked with Spring's * {@code @Async} annotation will be upgraded to subclass proxying at the same * time. This approach has no negative impact in practice unless one is explicitly * expecting one type of proxy vs another, e.g. in tests. */ boolean proxyTargetClass() default false; /** * Indicate how transactional advice should be applied. * <p><b>The default is {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}.</b> * Please note that proxy mode allows for interception of calls through the proxy * only. Local calls within the same class cannot get intercepted that way; an * {@link Transactional} annotation on such a method within a local call will be * ignored since Spring's interceptor does not even kick in for such a runtime * scenario. For a more advanced mode of interception, consider switching this to * {@link AdviceMode#ASPECTJ}. */ AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY; /** * Indicate the ordering of the execution of the transaction advisor * when multiple advices are applied at a specific joinpoint. * <p>The default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE}. */ int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; }
2. AutoProxyRegistrar组件
首先看spring源码
public class AutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); /** * Register, escalate, and configure the standard auto proxy creator (APC) against the * given registry. Works by finding the nearest annotation declared on the importing * {@code @Configuration} class that has both {@code mode} and {@code proxyTargetClass} * attributes. If {@code mode} is set to {@code PROXY}, the APC is registered; if * {@code proxyTargetClass} is set to {@code true}, then the APC is forced to use * subclass (CGLIB) proxying. * <p>Several {@code @Enable*} annotations expose both {@code mode} and * {@code proxyTargetClass} attributes. It is important to note that most of these * capabilities end up sharing a {@linkplain AopConfigUtils#AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME * single APC}. For this reason, this implementation doesn't "care" exactly which * annotation it finds -- as long as it exposes the right {@code mode} and * {@code proxyTargetClass} attributes, the APC can be registered and configured all * the same. */ @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { boolean candidateFound = false; Set<String> annoTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes(); for (String annoType : annoTypes) { AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annoType); if (candidate == null) { continue; } Object mode = candidate.get("mode"); Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass"); if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() && Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) { candidateFound = true; if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) { AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry); if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry); return; } } } } if (!candidateFound && logger.isInfoEnabled()) { String name = getClass().getSimpleName(); logger.info(String.format("%s was imported but no annotations were found " + "having both 'mode' and 'proxyTargetClass' attributes of type " + "AdviceMode and boolean respectively. This means that auto proxy " + "creator registration and configuration may not have occurred as " + "intended, and components may not be proxied as expected. Check to " + "ensure that %s has been @Import'ed on the same class where these " + "annotations are declared; otherwise remove the import of %s " + "altogether.", name, name, name)); } } }
重点是它实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,它跟上述ImportsSelector一样,都是导入方式注册bean时可以选用的接口,那么它在容器中注册了什么组件呢?跟进源码中的粉色粗体语句,会发现它会调用AopConfigUtils的这个方法
@Nullable
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
也就是说,它会在容器中注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,这是个什么东西?来看一下它的继承关系图
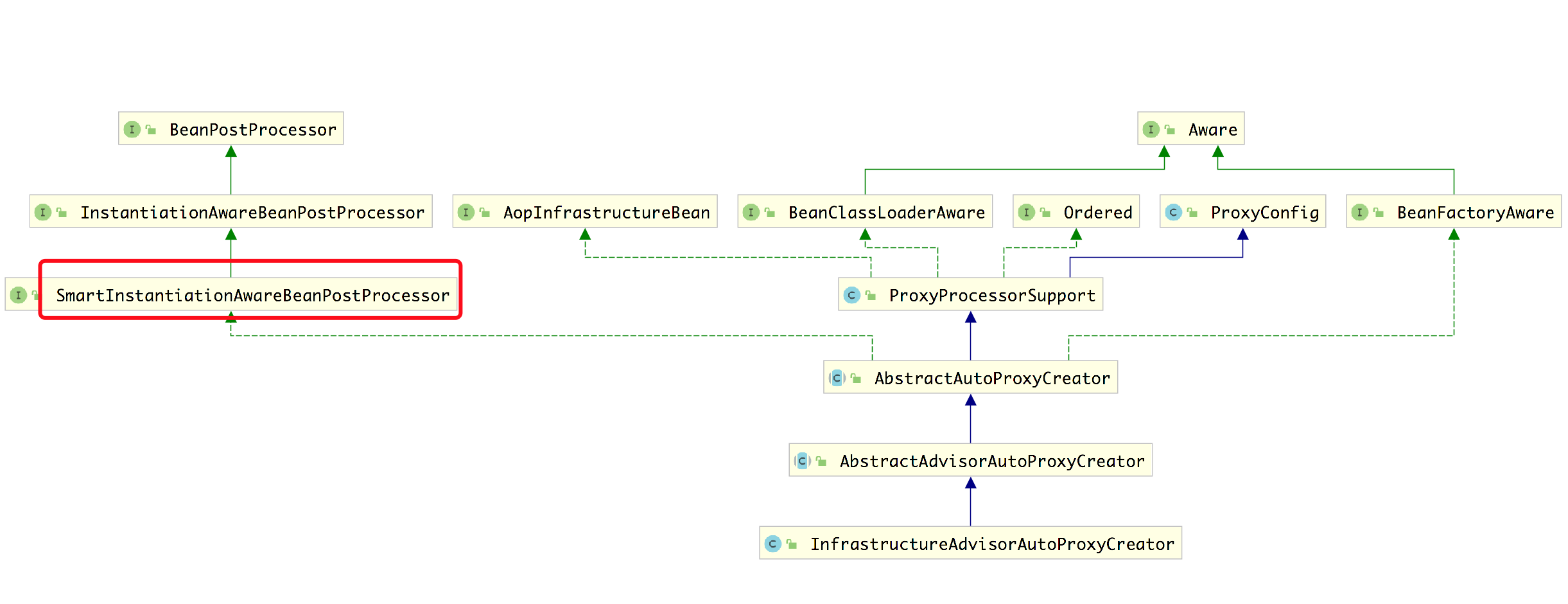
它实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,说明这是一个后置处理器,而且跟springAOP开启@EnableAspectJAutoProxy时注册的AnnotationAwareAspectJProxyCreator实现的是同一个接口(见https://www.cnblogs.com/dubhlinn/p/10708454.html),所以说,声明式事务是springAOP思想的一种应用。
3. ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration组件
先看spring源码
@Configuration public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration { @Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME) @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() { BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor(); advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource()); //① advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor()); //② if (this.enableTx != null) { advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order")); } return advisor; } @Bean @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() { return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(); } @Bean @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() { TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor(); interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource()); if (this.txManager != null) { interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager); } return interceptor; } }
从源码中可以看出,ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration是一个容器配置类,它注册了一个组件transactionAdvisor,我们称为事务增强器;
然后在这个事务增强器中又注入了两个属性:
①:transactionAttributeSource,即属性解析器;
②:transactionInterceptor,即事务拦截器。
首先来看属性解析器,截取一段源码
public class AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource extends AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource implements Serializable { private static final boolean jta12Present; private static final boolean ejb3Present; static { ClassLoader classLoader = AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.class.getClassLoader(); jta12Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", classLoader); ejb3Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute", classLoader); } private final boolean publicMethodsOnly; private final Set<TransactionAnnotationParser> annotationParsers; /** * Create a default AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource, supporting * public methods that carry the {@code Transactional} annotation * or the EJB3 {@link javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute} annotation. */ public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource() { this(true); } /** * Create a custom AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource, supporting * public methods that carry the {@code Transactional} annotation * or the EJB3 {@link javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute} annotation. * @param publicMethodsOnly whether to support public methods that carry * the {@code Transactional} annotation only (typically for use * with proxy-based AOP), or protected/private methods as well * (typically used with AspectJ class weaving) */ public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) { this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly; if (jta12Present || ejb3Present) { this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4); this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser()); if (jta12Present) { this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser()); } if (ejb3Present) { this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser()); } } else { this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser()); } } }
属性解析器有一个成员变量是annotationParsers,是一个集合,可以添加多种注解解析器(TransactionAnnotationParser),例如spring的、jta的、ejb的,现在我们只看spring的注解解析器源码:
public class SpringTransactionAnnotationParser implements TransactionAnnotationParser, Serializable { protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) { RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute(); Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation"); rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value()); Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation"); rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value()); rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue()); rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly")); rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value")); List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>(); for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) { rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) { rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) { rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) { rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules); return rbta; } }
注意粉色粗体部分,全都是@Transactional注解的属性,所以属性解析器的作用之一就是用来解析@Transaction注解的。
然后来看一下事务拦截器,还是截取一段spring源码
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { /** * Create a new TransactionInterceptor. * <p>Transaction manager and transaction attributes still need to be set. * @see #setTransactionManager * @see #setTransactionAttributes(java.util.Properties) * @see #setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource) */ public TransactionInterceptor() { }/** * Create a new TransactionInterceptor. * @param ptm the default transaction manager to perform the actual transaction management * @param tas the attribute source to be used to find transaction attributes * @see #setTransactionManager * @see #setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource) */ public TransactionInterceptor(PlatformTransactionManager ptm, TransactionAttributeSource tas) { setTransactionManager(ptm); setTransactionAttributeSource(tas); } @Override @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { // Work out the target class: may be {@code null}. // The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class // as well as the method, which may be from an interface. Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); // Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction... return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed); } }
需要注意的两点:
① 事务拦截器实现了MethodInterceptor接口,这又是在springAOP中提到的拦截器链(https://www.cnblogs.com/dubhlinn/p/10708454.html),追溯一下上面提到的InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator后置处理器,它会在代理对象执行目标方法的时候获取其拦截器链,而拦截器链就是这个TransactionInterceptor,这就把这两个组件联系起来了;
② 构造方法传入PlatformTransactionManager(事务管理器)、TransactionAttributeSource(属性解析器),但是追溯一下上面贴的ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration的源码,在注册事务拦截器的时候并没有调用这个带参构造方法,而是调用的无参构造方法,然后再调用set方法注入这两个属性,效果也是一样的。
然后我们继续跟进粉色粗体的invokeWithinTransaction方法的源码,看看触发的方法里面执行了什么
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); //①
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); //②
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); //③
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); //④
return retVal;
}
else {
...
}
}
重点看粉色粗体的4个语句
① 获取属性解析器,即在ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration容器配置类中注册事务拦截器时注入的;
② 获取事务管理器,跟进一下源码
protected PlatformTransactionManager determineTransactionManager(@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
// Do not attempt to lookup tx manager if no tx attributes are set
if (txAttr == null || this.beanFactory == null) {
return getTransactionManager();
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, qualifier);
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.transactionManagerBeanName)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, this.transactionManagerBeanName);
}
else {
PlatformTransactionManager defaultTransactionManager = getTransactionManager();
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY);
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.beanFactory.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(
DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY, defaultTransactionManager);
}
}
return defaultTransactionManager;
}
}
spring会先根据qualifier,即@Transactional注解的value属性去获取,但是这个我们一般都不配置,我们只要看到粉色粗体部分就放心了,只要在容器中有注册过PlatformTransactionManager类型的事务管理器,就可以直接通过类型来获取;
③ 如果目标方法抛异常,会执行completeTransactionAfterThrowing,跟进一下源码:
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
核心是粉色粗体语句——拿到事务管理器、执行回滚;
④ 如果目标方法正常运行,则会执行commitTransactionAfterReturning,同样跟进一下源码:
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
粉色粗体部分——拿到事务管理器、执行提交。
总结一下基于注解的声明式事务的原理:
1. 在容器配置类上使用@EnableTransactionManagement注解,该注解在容器中注册了两大组件——AutoProxyRegistrar、ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration;
2. AutoProxyRegistrar通过导入方式在容器中注册了InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,这是一个后置处理器;
3. ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration本身就是一个容器配置类,它注册了transactionAdvisor(事务增强器),然后又在这个事务增强器中注入了两个属性transactionAttributeSource、transactionInterceptor;
4. transactionAttributeSource用于解析@Transactional注解的各种属性;
5. transactionInterceptor实现了MethodInterceptor,是一个拦截器链,这个拦截器链会从容器中获取事务管理器,利用事务管理器,在目标方法发生异常时执行回滚,在目标发生正常完成后提交事务;
6. 第2步的InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator后置处理器,会在目标对象创建完成之后将其包装为代理对象,代理对象在执行目标方法时会首先获取拦截器链,这个拦截器链就是第5步的transactionInterceptor。






