ApplicationEvent事件机制源码分析
《spring扩展点之三:Spring 的监听事件 ApplicationListener 和 ApplicationEvent 用法,在spring启动后做些事情》
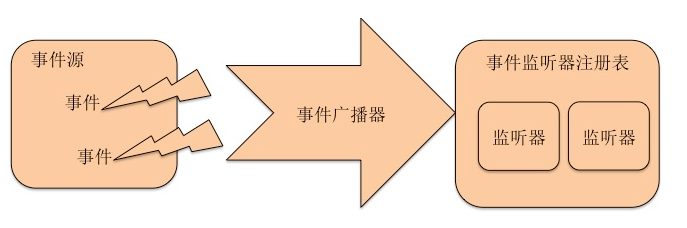
Spring中的监听器模式
1、Spring在事件处理机制中使用了监听器模式,其中的三个主要角色:
- 事件,ApplicationEvent,该抽象类继承了EventObject,EventObject是JDK中的类,并建议所有的事件都应该继承自EventObject。
- 事件监听器,ApplicationListener,是一个接口,该接口继承了EventListener接口。EventListener接口是JDK中的,建议所有的事件监听器都应该继承EventListener。监听器是用于接收事件,并触发事件的操作,这样说起来可能有点费解,简单的说就是,Listener是监听ApplicationContext.publishEvent,方法的调用,一旦调用publishEvent,就会执行ApplicaitonListener中的方法,下面这个是ApplicationContext的源码。
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener { /** * publishEvent触发该方方法 * 可以在该方法中写各种业务逻辑 */ void onApplicationEvent(E event); }
- 事件发布,ApplicationEventPublisher,ApplicationContext继承了该接口,在ApplicationContext的抽象实现类AbstractApplicationContext中做了实现。下面会详解。
2、Spring事件发布机制
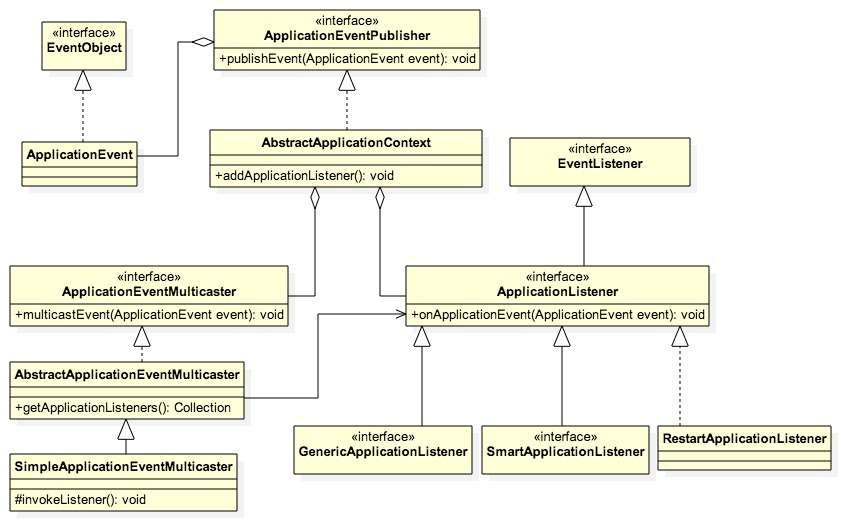
3、spring中的事件(异步)机制流程
Spring 中观察者模式的四个角色
- 事件:ApplicationEvent 是所有事件对象的父类。ApplicationEvent 继承自 jdk 的 EventObject, 所有的事件都需要继承 ApplicationEvent, 并且通过 source 得到事件源。
Spring 也为我们提供了很多内置事件,
ContextRefreshedEvent、ContextStartedEvent、ContextStoppedEvent、ContextClosedEvent、RequestHandledEvent。 - 事件监听器:ApplicationListener,也就是观察者,继承自 jdk 的 EventListener,该类中只有一个方法 onApplicationEvent。当监听的事件发生后该方法会被执行。
- 事件源:ApplicationContext,
ApplicationContext是 Spring 中的核心容器,在事件监听中 ApplicationContext 可以作为事件的发布者,也就是事件源。因为 ApplicationContext 继承自 ApplicationEventPublisher。在ApplicationEventPublisher中定义了事件发布的方法:publishEvent(Object event) - 事件管理:ApplicationEventMulticaster,用于事件监听器的注册和事件的广播。监听器的注册就是通过它来实现的,它的作用是把 Applicationcontext 发布的 Event 广播给它的监听器列表。
2.1、Spring事件源
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject { /** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L; /** System time when the event happened */ private final long timestamp; /** * Create a new ApplicationEvent. * @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null}) */ public ApplicationEvent(Object source) { super(source); this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } /** * Return the system time in milliseconds when the event happened. */ public final long getTimestamp() { return this.timestamp; } }
2.2、Spring事件监听器
spring-context-4.3.14.RELEASE-sources.jar中的ApplicationListener.java类类
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener { /** * Handle an application event. * @param event the event to respond to */ void onApplicationEvent(E event); }
jdk中的EventListener.java类是一个空接口
public interface EventListener { }
2.3、Spring事件发布
spring-context-4.3.14.RELEASE-sources.jar中的ApplicationEventPublisher.java类
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher { /** * Notify all <strong>matching</strong> listeners registered with this * application of an application event. Events may be framework events * (such as RequestHandledEvent) or application-specific events. * @param event the event to publish * @see org.springframework.web.context.support.RequestHandledEvent */ void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event); /** * Notify all <strong>matching</strong> listeners registered with this * application of an event. * <p>If the specified {@code event} is not an {@link ApplicationEvent}, * it is wrapped in a {@link PayloadApplicationEvent}. * @param event the event to publish * @since 4.2 * @see PayloadApplicationEvent */ void publishEvent(Object event); }
AbstractApplicationContext类中publishEvent方法实现:
protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) { Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null"); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event); } // Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary ApplicationEvent applicationEvent; if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) { applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event; } else { applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>(this, event); if (eventType == null) { eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType(); } } // Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) { this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent); } else { //事件委派给ApplicationEventMulticaster来执行
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType); } // Publish event via parent context as well... if (this.parent != null) { if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { ((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType); } else { this.parent.publishEvent(event); } } }
ApplicationEventMulticaster的multicastEvent方法的实现在SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类中:
@Override public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) { ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event)); //获得监听器集合,遍历监听器,可支持同步和异步的广播事件 for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { Executor executor = getTaskExecutor(); if (executor != null) { executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { invokeListener(listener, event); } }); } else { invokeListener(listener, event); } } }
invokeListener()方法:
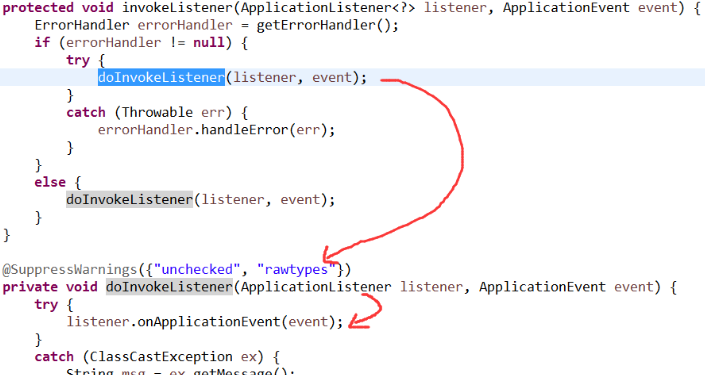
这就执行了ApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent方法,这里是事件发生的地方。
2.4、Spring如何根据事件找到事件对应的监听器
在Spring容器初始化的时候,也就是在AbstractApplicationContext.java在refresh()中:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { ...... try { ...... // Initialize event multicaster for this context. //初始化一个事件注册表 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); ...... // Check for listener beans and register them. //注册事件监听器 registerListeners(); ...... } } }
也就是在AbstractApplicationContext.java的initApplicationEventMulticaster方法初始化事件注册表
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { //获得beanFactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); //先查找BeanFactory中是否有ApplicationEventMulticaster if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { this.applicationEventMulticaster = beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); } else {//如果BeanFactory中不存在,就创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory); beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); } }
在SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster在父类AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster类中有如下属性:
//注册表 private final ListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new ListenerRetriever(false); //注册表的缓存 private final Map<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever> retrieverCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever>(64); private BeanFactory beanFactory;
ListenerRetriever.java是一个内部类,主要作用:助手类,它封装特定的目标侦听器集合,允许对预过滤的侦听器进行高效的检索。此助手的实例缓存每个事件类型和源类型。
ListenerRetriever.java的结构如下:
//用来存放监听事件 public final Set<ApplicationListener> applicationListeners; //存放监听事件的类名称 public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans; private final boolean preFiltered;
初始化注册表之后,就会把事件注册到注册表中,AbstractApplicationContext.registerListeners():
protected void registerListeners() { //获取所有的Listener,把事件的bean放到ApplicationEventMulticaster中 for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); //把事件的名称放到ApplicationListenerBean里去。 for (String lisName : listenerBeanNames) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(lisName); } }
Spring使用反射机制,通过方法getBeansOfType获取所有继承了ApplicationListener接口的监听器,然后把监听器放到注册表中,所以我们可以在Spring配置文件中配置自定义监听器,在Spring初始化的时候,会把监听器自动注册到注册表中去。
applicationContext.java中的getBeansOfType(Class<T> type)的实现在
@Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) throws BeansException { boolean isFactoryType = (type != null && FactoryBean.class.isAssignableFrom(type)); Map<String, T> matches = new LinkedHashMap<String, T>(); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : this.beans.entrySet()) { String beanName = entry.getKey(); Object beanInstance = entry.getValue(); // Is bean a FactoryBean? if (beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean && !isFactoryType) { // Match object created by FactoryBean. FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) beanInstance; Class<?> objectType = factory.getObjectType(); if ((includeNonSingletons || factory.isSingleton()) && objectType != null && (type == null || type.isAssignableFrom(objectType))) { matches.put(beanName, getBean(beanName, type)); } } else { if (type == null || type.isInstance(beanInstance)) { // If type to match is FactoryBean, return FactoryBean itself. // Else, return bean instance. if (isFactoryType) { beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName; } matches.put(beanName, (T) beanInstance); } } } return matches; }
反射的见《instanceof, isinstance,isAssignableFrom的区别》
ApplicationContext发布事件可以参考上面的内容。发布事件的时候的一个方法,getApplicationListeners:
protected Collection<ApplicationListener> getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent event) { //获取事件类型 Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType = event.getClass(); //或去事件源类型 Class sourceType = event.getSource().getClass(); ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType); //从缓存中查找ListenerRetriever ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey); //缓存中存在,直接返回对应的Listener if (retriever != null) { return retriever.getApplicationListeners(); } else {//缓存中不存在,就获取相应的Listener retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true); LinkedList<ApplicationListener> allListeners = new LinkedList<ApplicationListener>(); Set<ApplicationListener> listeners; Set<String> listenerBeans; synchronized (this.defaultRetriever) { listeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners); listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans); } //根据事件类型,事件源类型,获取所需要的监听事件 for (ApplicationListener listener : listeners) { if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) { retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener); allListeners.add(listener); } } if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) { BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) { ApplicationListener listener = beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class); if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) { retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName); allListeners.add(listener); } } } OrderComparator.sort(allListeners); this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever); return allListeners; } }
根据事件类型,事件源类型获取所需要的监听器supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType):
protected boolean supportsEvent(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, Class<?> sourceType) { GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ? (GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener)); return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType)); }
这里没有进行实际的处理,实际处理在smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType)和smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType)方法中。
smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType):
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) { Class typeArg = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(this.delegate.getClass(), ApplicationListener.class); if (typeArg == null || typeArg.equals(ApplicationEvent.class)) { Class targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(this.delegate); if (targetClass != this.delegate.getClass()) { typeArg = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(targetClass, ApplicationListener.class); } } return (typeArg == null || typeArg.isAssignableFrom(eventType)); }
该方法主要的逻辑就是根据事件类型判断是否和监听器参数泛型的类型是否一致。
smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType)方法的实现为:
public boolean supportsSourceType(Class<?> sourceType) { return true; }
定义自己的监听器要明确指定参数泛型,表明该监听器支持的事件,如果不指明具体的泛型,则没有监听器监听事件。
示例:
Spring 事件发布实现非常简单,只需要三个步骤:
- 定义一个继承ApplicationEvent事件
- 定义一个实现ApplicationListener的监听器或者使用 @EventListener 来监听事件
- 定义一个发送者,调用ApplicationContext直接发布或者使用 ApplicationEventPublisher 来发布自定义事件(@Autowired注入即可)
//1. 建立事件类,继承applicationEvent public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent { public MyEvent(Object source) { super(source); System.out.println("my Event"); } public void print(){ System.out.println("hello spring event[MyEvent]"); } } //2.建立监听类,实现ApplicationListener接口 public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener{ public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if(event instanceof MyEvent){ System.out.println("into My Listener"); MyEvent myEvent=(MyEvent)event; myEvent.print(); } } } //3.创建一个发布事件的类,该类实现ApplicationContextAware接口,得到ApplicationContext对象,使用该对象的publishEvent方法发布事件. public class MyPubisher implements ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext=applicationContext; } public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event){ System.out.println("into My Publisher's method"); applicationContext.publishEvent(event); } } //4.测试 public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/application-database.xml"); MyPubisher myPubisher=(MyPubisher) context.getBean("myPublisher"); myPubisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("1")); } }



