使用HttpMessageConverter实现HTTP的序列化和反序列化
对象的序列化/反序列化大家应该都比较熟悉:序列化就是将object转化为可以传输的二进制,反序列化就是将二进制转化为程序内部的对象。序列化/反序列化主要体现在程序I/O这个过程中,包括网络I/O和磁盘I/O。
那么什么是http序列化和反序列化呢?
在使用springmvc/SpringBoot时,我们经常会这样写:
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody public String test(@RequestBody String param) {
return "param '" + param + "'";
}
@RestController中有@ResponseBody,可以帮我们把User序列化到resp.body中。@RequestBody可以帮我们把req.body的内容转化为User对象。如果是开发Web应用,一般这两个注解对应的就是Json序列化和反序列化的操作。这里实际上已经体现了Http序列化/反序列化这个过程,只不过和普通的对象序列化有些不一样,Http序列化/反序列化的层次更高,属于一种Object2Object之间的转换。
有过Netty使用经验的对这个应该比较了解,Netty中的Decoder和Encoder就有两种基本层次,层次低的一种是Byte <—> Message,二进制与程序内部消息对象之间的转换,就是常见的序列化/反序列化;另外一种是 Message <—> Message,程序内部对象之间的转换,比较高层次的序列化/反序列化。
Http协议的处理过程,TCP字节流 <—> HttpRequest/HttpResponse <—> 内部对象,就涉及这两种序列化。在springmvc中第一步已经由Servlet容器(tomcat等等)帮我们处理了,第二步则主要由框架帮我们处理。上面所说的Http序列化/反序列化就是指的这第二个步骤,它是controller层框架的核心功能之一,有了这个功能,就能大大减少代码量,让controller的逻辑更简洁清晰,就像上面示意的代码那样,方法中只有一行代码。spirngmvc进行第二步操作,也就是Http序列化和反序列化的核心是HttpMessageConverter。
HttpMessageConverter
Http请求响应报文其实都是字符串,当请求报文到java程序会被封装为一个ServletInputStream流,开发人员再读取报文,响应报文则通过ServletOutputStream流,来输出响应报文。
从流中只能读取到原始的字符串报文,同样输出流也是。那么在报文到达SpringMVC / SpringBoot和从SpringMVC / SpringBoot出去,都存在一个字符串到java对象的转化问题。这一过程,在SpringMVC / SpringBoot中,是通过HttpMessageConverter来解决的。HttpMessageConverter接口源码:
package org.springframework.http.converter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage; import org.springframework.http.HttpOutputMessage; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> { boolean canRead(Class<?> var1, @Nullable MediaType var2); boolean canWrite(Class<?> var1, @Nullable MediaType var2); List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes(); T read(Class<? extends T> var1, HttpInputMessage var2) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException; void write(T var1, @Nullable MediaType var2, HttpOutputMessage var3) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException; }
以上面的代码为例子来说明一下:在请求进入test方法前,会根据@RequestBody注解选择对应的HttpMessageConverter实现类来将请求参数解析到param变量中,因为这里的参数是String类型的,所以这里是使用了StringHttpMessageConverter类,它的canRead()方法返回true,然后read()方法会从请求中读出请求参数,绑定到test()方法的param变量中。
同理当执行test方法后,由于返回值标识了@ResponseBody,SpringMVC / SpringBoot将使用StringHttpMessageConverter的write()方法,将结果作为String值写入响应报文,当然,此时canWrite()方法返回true。
借用下图简单描述整个过程:
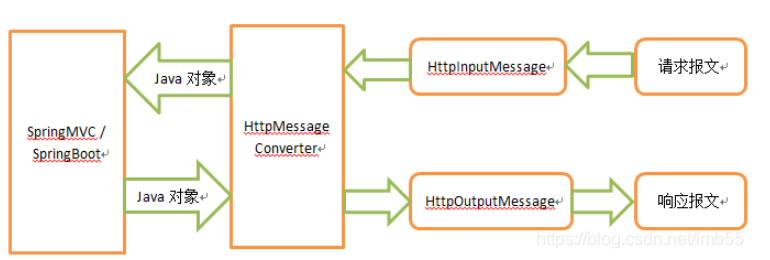
在Spring的处理过程中,一次请求报文和一次响应报文,分别被抽象为一个请求消息HttpInputMessage和一个响应消息HttpOutputMessage。处理请求时,由合适的消息转换器将请求报文绑定为方法中的形参对象,在这里同一个对象就有可能出现多种不同的消息形式,如json、xml。同样响应请求也是同样道理。在Spring中,针对不同的消息形式,有不同的HttpMessageConverter实现类来处理各种消息形式,至于各种消息解析实现的不同,则在不同的HttpMessageConverter实现类中。
替换@ResponseBody默认的HttpMessageConverter
1、springboot框架默认的使用jackson进行json转化
public class User { private String username; private Integer age; private Integer phone; private String email; public User(String username, Integer age) { super(); this.username = username; this.age = age; } }
@Controller @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/testt") @ResponseBody public User testt() { User user = new User("name", 18); return user; } }
浏览器访问/user/testt请求结果如下:
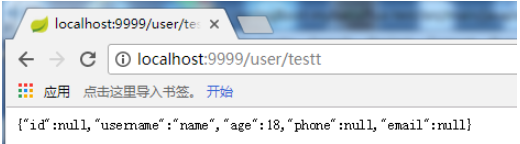
这就是使用Jackson解析的结果,没有传值的字段默认被解析成了null。现在来改成使用fastjson解析对象,这里就是替换默认的HttpMessageConverter,就是将其改成使用FastJsonHttpMessageConverter来处理Java对象与HttpInputMessage/HttpOutputMessage间的转化。
2、使用fastjson替代默认的jackson转化方式
增加Fastjson的maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.47</version>
</dependency>
Springboot配置FastJsonHttpMessageConverter有两种方法:
方法一:启动类继承extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter,然后覆盖方法configureMessageConverters
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature; import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig; import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConverters; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** springboot以fastjon方式转化json数据 */ @SpringBootApplication public class Application extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(Application.class); @Override public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) { super.configureMessageConverters(converters); //1.需要定义一个convert转换消息的对象; FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastJsonHttpMessageConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); //2.添加fastJson的配置信息,比如:是否要格式化返回的json数据; FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig(); SerializerFeature[] serializerFeatures = new SerializerFeature[]{ // 输出key是包含双引号 // SerializerFeature.QuoteFieldNames, // 是否输出为null的字段,若为null 则显示该字段 // SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, // 数值字段如果为null,则输出为0 SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero, // List字段如果为null,输出为[],而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty, // 字符类型字段如果为null,输出为"",而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty, // Boolean字段如果为null,输出为false,而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse, // Date的日期转换器 SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat, // 循环引用 SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect, }; fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(serializerFeatures); //3处理中文乱码问题 List<MediaType> fastMediaTypes = new ArrayList<>(); fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8); //4.在convert中添加配置信息. fastJsonHttpMessageConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(fastMediaTypes); fastJsonHttpMessageConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig); //5.将convert添加到converters当中. converters.add(fastJsonHttpMessageConverter); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args); logger.info("=====spring boot start success===="); } }
方法二:添加配置类来注入Bean:HttpMessageConverters
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature; import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig; import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConverters; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter; import java.nio.charset.Charset; @Configuration public class HttpMessageConverterConfig { //引入Fastjson解析json,不使用默认的jackson //必须在pom.xml引入fastjson的jar包,并且版必须大于1.2.10 @Bean public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonHttpMessageConverters() { //1、定义一个convert转换消息的对象 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); //2、添加fastjson的配置信息 FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig(); SerializerFeature[] serializerFeatures = new SerializerFeature[]{ // 输出key是包含双引号 // SerializerFeature.QuoteFieldNames, // 是否输出为null的字段,若为null 则显示该字段 // SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, // 数值字段如果为null,则输出为0 SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero, // List字段如果为null,输出为[],而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty, // 字符类型字段如果为null,输出为"",而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty, // Boolean字段如果为null,输出为false,而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse, // Date的日期转换器 SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat, // 循环引用 SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect, }; fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(serializerFeatures); fastJsonConfig.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); //3、在convert中添加配置信息 fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig); //4、将convert添加到converters中 HttpMessageConverter<?> converter = fastConverter; return new HttpMessageConverters(converter); } }
浏览器发起请求,得到的结果如下:
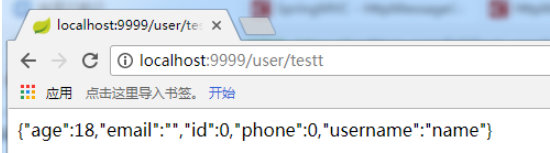
未传值的字符串类型的属性被解析为””,未传值的数值类型的属性被解析为0。
参考资料:
1、【Spring】HttpMessageConverter的作用及替换
2、springboot学习(三)——使用HttpMessageConverter进行http序列化和反序列化
3、SpringBoot-扩展FastJsonHttpMessageConverter对返回的json对象进行扩展
4、fastjson SerializerFeature详解
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lmb55/article/details/90676823



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号