Hystrix实现ThreadLocal上下文的传递 转
springcloud微服务中, 服务间传输全局类参数,如session信息等。
Feign调用过程中,传递请求头:
public class ForwardHeaderFeignRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor { public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ForwardHeaderFeignRequestInterceptor.class); @Override public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) { ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); if(null != attributes) { HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest(); Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames(); if (headerNames != null) { while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) { String name = headerNames.nextElement(); String values = request.getHeader(name); requestTemplate.header(name, values); } } } if(logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.info("feign interceptor headers:{}", GsonUtils.toJson(requestTemplate.headers())); } } }
当Feign开启的Hystrix时,RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();是 null 。
原因在于,Hystrix的默认隔离策略是THREAD 。而 RequestContextHolder 源码中,使用了两个血淋淋的ThreadLocal 。
一、问题背景
Hystrix有2个隔离策略:THREAD以及SEMAPHORE,当隔离策略为 THREAD 时,是没办法拿到 ThreadLocal 中的值的。
Hystrix提供了基于信号量和线程两种隔离模式,通过在Hystrix基础章节中已经验证过,通过@HystrixCommand注解的方法体将在新的线程中执行,这样会带来些什么意想不到的意外呢,先来看一个示例:
1、定义一个webapi,通过RequestContextHolder设定一个当前线程的上下文:
@GetMapping(value = "/getServerInfo/{serviceName}")
public String getServer1Info(@PathVariable(value = "serviceName") String serviceName) {
LOGGER.info("当前线程ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "当前线程Name" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().setAttribute("context", "main-thread-context", SCOPE_REQUEST);
return consumeService.getServerInfo(serviceName);
}
2、在@HystrixCommand注解的方法中再次通过RequestContextHolder获取当前上下文设定的value值:
@Override @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "getServerInfoFallback", commandProperties = {@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.strategy", value = "THREAD")}, commandKey = "cust2GetServerInfo", threadPoolKey = "cust2ThreadPool", groupKey = "cust2") public String getServerInfo(String serviceName) { LOGGER.info(RibbonFilterContextHolder.getCurrentContext().get("TAG")); LOGGER.info(RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("context", SCOPE_REQUEST).toString()); //如果是service1则需要添加http认证头,service1暂时添加了认证机制;反之service2不需要认证直接发出请求即可 if ("service1".equals(serviceName)) { HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders()); ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange("http://" + serviceName + "/getServerInfo?userName=shuaishuai", HttpMethod.GET, requestEntity, String.class); return responseEntity.getBody(); } else return restTemplate.getForObject("http://" + serviceName + "/getServerInfo?userName=shuaishuai", String.class); } public String getServerInfoFallback(String serviceName, Throwable e) { if (e != null) { LOGGER.error(e.getMessage()); } return "Maybe the server named " + serviceName + " is not normal running"; }
3、启动服务请求1中定义的API:
可以看到上图中上下文的赋值与取值在不同的线程中执行,TAG信息被正常获取,而RequestContextHolder设定的上线文信息获取失败,并进入回退方法并打印出了对应的异常信息,首先来看下为何TAG信息被正常获取,在RibbonFilterContextHolder中定义变量如下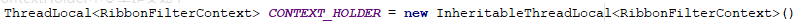
而在RequestContextHolder中变量定义如下
其区别在于是采用ThreadLocal与InheritableThreadLocal的差异,InheritableThreadLocal能够在子线程中继续传播父线程的上线文,而ThreadLocal只能在保存在当前线程中,但事实上我们不可能所有的应用均采用InheritableThreadLocal,尽管他是一个不错的选择,但如何让ThreadLocal也实现在Hystrix应用场景下实现线程上下文的传播呢。这就是本章的重点了。
二、解决方案
方案一:调整格隔离策略:
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.strategy: SEMAPHORE
这样配置后,Feign可以正常工作。
但该方案不是特别好。原因是Hystrix官方强烈建议使用THREAD作为隔离策略! 可以参考官方文档说明。
方案二:自定义策略
记得之前在研究zipkin日志追踪的时候,看到过Sleuth有自己的熔断机制,用来在thread之间传递Trace信息,Sleuth是可以拿到自己上下文信息的,查看源码找到了
资料搜索
既然遇到了问题,就到springcloud的官方文档先检索下,找到如下对应的描述
您还可以选择设置hystrix。shareSecurityContext属性为真。这样做将自动配置一个Hystrix并发策略插件钩子,它将把SecurityContext从主线程转移到Hystrix命令使用的线程。Hystrix不允许注册多个Hystrix并发策略,因此可以通过将自己的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy声明为Spring bean来使用扩展机制。Spring Cloud将在Spring上下文中查找您的实现,并将其封装在自己的插件中。
红色框部分主要意思是,我们可以声明一个定制化的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy实例,并通过HystrixPlugins注册。先找到HystrixConcurrencyStrategy类,其有下面一段类注释
/** * Abstract class for defining different behavior or implementations for concurrency related aspects of the system with default implementations. * <p> * For example, every {@link Callable} executed by {@link HystrixCommand} will call {@link #wrapCallable(Callable)} to give a chance for custom implementations to decorate the {@link Callable} with * additional behavior. * <p> * When you implement a concrete {@link HystrixConcurrencyStrategy}, you should make the strategy idempotent w.r.t ThreadLocals. * Since the usage of threads by Hystrix is internal, Hystrix does not attempt to apply the strategy in an idempotent way. * Instead, you should write your strategy to work idempotently. See https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/issues/351 for a more detailed discussion. * <p> * See {@link HystrixPlugins} or the Hystrix GitHub Wiki for information on configuring plugins: <a * href="https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki/Plugins">https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki/Plugins</a>. */ public abstract class HystrixConcurrencyStrategy {
被@HystrixCommand注解的方法,其执行源Callable可以通过wrapCallable方法进行定制化装饰,加入附加的行为,继续来看看wrapCallable方法的定义
/** * Provides an opportunity to wrap/decorate a {@code Callable<T>} before execution. * <p> * This can be used to inject additional behavior such as copying of thread state (such as {@link ThreadLocal}). * <p> * <b>Default Implementation</b> * <p> * Pass-thru that does no wrapping. * * @param callable * {@code Callable<T>} to be executed via a {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} * @return {@code Callable<T>} either as a pass-thru or wrapping the one given */ public <T> Callable<T> wrapCallable(Callable<T> callable) { return callable; }
其同样提供了非常详细的注释,该方法提供了在方法被执行前进行装饰的机会,可以用来复制线程状态等附加行为,这个貌似就是我们需要的,很合意。
同样在Hystrix官方文档提供了更加详细的说明(https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki/Plugins#concurrency-strategy),Concurrency Strategy作为了Plugin的一种类别,描述如下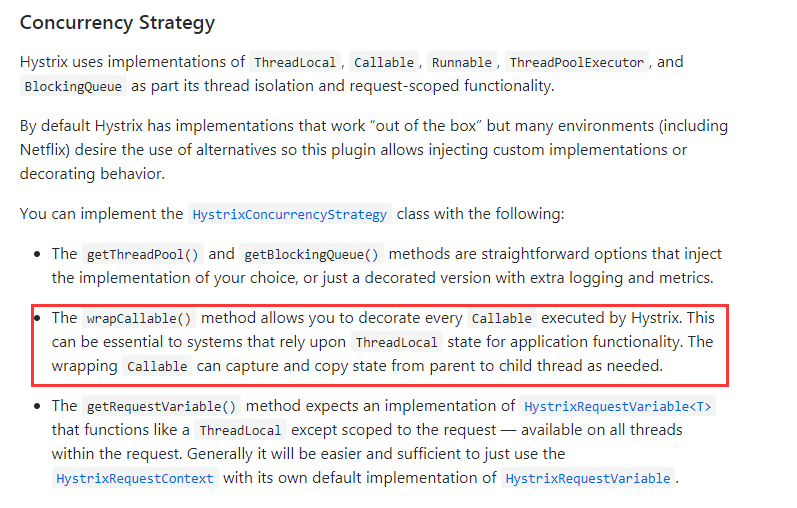
可以看到红色框中的重点描述,其已经说了非常明确,可以从父线程复制线程状态至子线程。自定义的Plugin如何被HystrixCommand应用呢,继续查看官方的描述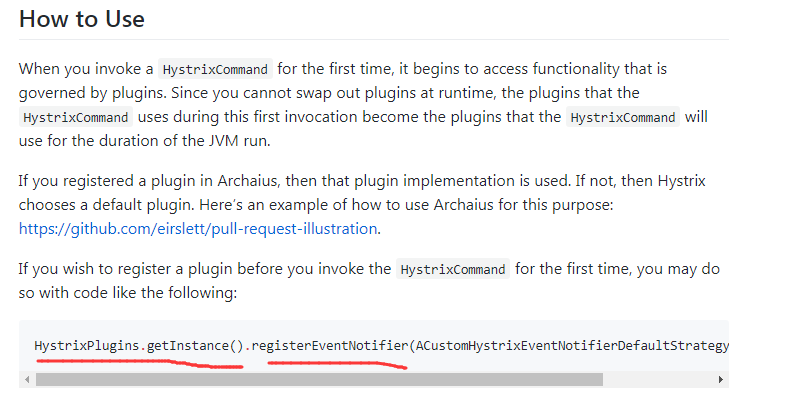
其提供了HystrixPlugins帮助我们注册自定义的Plugin,除了我们本章节重点关注的Concurrency Strategy类别plugin,还有如下类别以及对应的抽象实现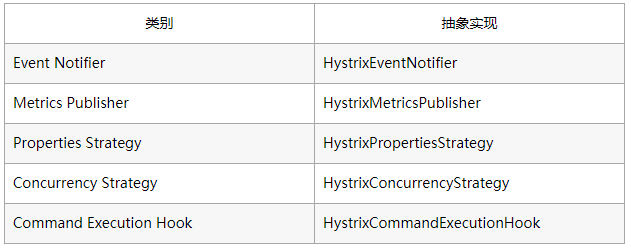
源码分析
在springcloud中还有如下一段话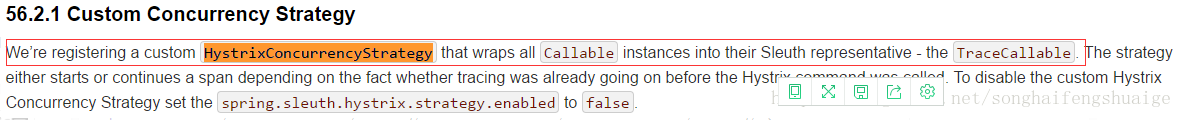
既然提高了定制化的实现,不如来看看官方已经提供了哪些默认实现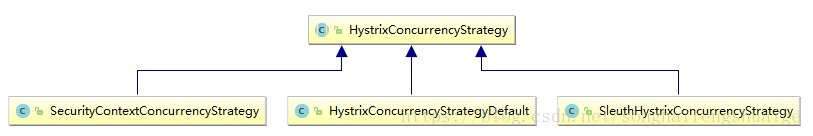
首先来看看HystrixConcurrencyStrategyDefault,
public class HystrixConcurrencyStrategyDefault extends HystrixConcurrencyStrategy { private static HystrixConcurrencyStrategyDefault INSTANCE = new HystrixConcurrencyStrategyDefault(); public static HystrixConcurrencyStrategy getInstance() { return INSTANCE; } private HystrixConcurrencyStrategyDefault() { } }
很精简的一段代码,并没有任何方法重写,其作为了一个标准提供默认实现。继续来看看SecurityContextConcurrencyStrategy实现,直接找到wrapCallable方法
@Override public <T> Callable<T> wrapCallable(Callable<T> callable) { return existingConcurrencyStrategy != null ? existingConcurrencyStrategy .wrapCallable(new DelegatingSecurityContextCallable<T>(callable)) : super.wrapCallable(new DelegatingSecurityContextCallable<T>(callable)); }
其对Callabe进行了二次包装,继续跟进来看看DelegatingSecurityContextCallable的定义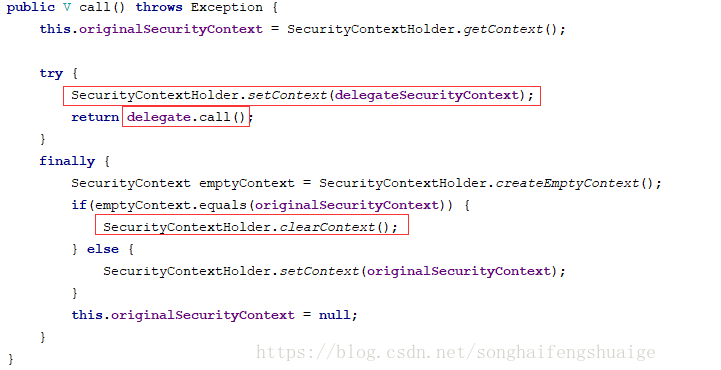
其主要实现均在call方法中,红色框中标出了重点,在调用call方法前,我们可以将当前上下文信息放入SecurityContextHolder中,在执行完成后清空SecurityContextHolder对应的设置。再来看看SecurityContextConcurrencyStrategy是如何被应用的,在HystrixSecurityAutoConfiguration中有如下代码段
@Configuration @Conditional(HystrixSecurityCondition.class) @ConditionalOnClass({ Hystrix.class, SecurityContext.class }) public class HystrixSecurityAutoConfiguration { @Autowired(required = false) private HystrixConcurrencyStrategy existingConcurrencyStrategy; @PostConstruct public void init() { // Keeps references of existing Hystrix plugins. HystrixEventNotifier eventNotifier = HystrixPlugins.getInstance() .getEventNotifier(); HystrixMetricsPublisher metricsPublisher = HystrixPlugins.getInstance() .getMetricsPublisher(); HystrixPropertiesStrategy propertiesStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance() .getPropertiesStrategy(); HystrixCommandExecutionHook commandExecutionHook = HystrixPlugins.getInstance() .getCommandExecutionHook(); HystrixPlugins.reset(); // Registers existing plugins excepts the Concurrent Strategy plugin. HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerConcurrencyStrategy( new SecurityContextConcurrencyStrategy(existingConcurrencyStrategy)); HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerEventNotifier(eventNotifier); HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerMetricsPublisher(metricsPublisher); HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerPropertiesStrategy(propertiesStrategy); HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerCommandExecutionHook(commandExecutionHook); } static class HystrixSecurityCondition extends AllNestedConditions { public HystrixSecurityCondition() { super(ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN); } @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "hystrix.shareSecurityContext") static class ShareSecurityContext { } } }
在启动注册配置过程中机会通过HystrixPlugins注册当前扩展的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy实现。
小节:自定义扩展类实现Callable接口,并传入当前Callable变量delegate,在delegate执行call方法前后进行线程上线文的操作即可实现线程状态在父线程与子线程间的传播。
扩展HystrixConcurrencyStrategy解决前言中的意外
通过源码部分的解读,基本了解springcloud是如何实现扩展的,又是如何被应用的,照葫芦画瓢下。
1、定义一个RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy实现HystrixConcurrencyStrategy接口,并重写其wrapCallable方法:
public class RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy extends HystrixConcurrencyStrategy { @Override public <T> Callable<T> wrapCallable(Callable<T> callable) { return new RequestAttributeAwareCallable<>(callable, RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()); } static class RequestAttributeAwareCallable<T> implements Callable<T> { private final Callable<T> delegate; private final RequestAttributes requestAttributes; public RequestAttributeAwareCallable(Callable<T> callable, RequestAttributes requestAttributes) { this.delegate = callable; this.requestAttributes = requestAttributes; } @Override public T call() throws Exception { try { RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes); return delegate.call(); } finally { RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes(); } } } }
其中定义RequestAttributeAwareCallable装饰类,通过构造函数传入当前待执行Callable代理和当前待传播的RequestAttributes值,并在delegate的call方法执行前对RequestContextHolder的RequestAttributes赋值,在finally块中重置。
2、同样在任意配置类中添加如下代码段即可,通过HystrixPlugins注册RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy:
@PostConstruct public void init() { HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerConcurrencyStrategy(new RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy()); }
3、启动服务验证,子线程取值成功:
小节:以上参考SecurityContextConcurrencyStrategy的实现,完成了Hystrix中RequestContextHolder上下文信息传播。
提高HystrixConcurrencyStrategy包装扩展性
上一个小节介绍了如果在Hystrix线程隔离场景下实现ThreadLocal定义的上下文传播,根据示例,在实际应用过程中如果我们有多个类似RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy策略,需要将每个自定义HystrixConcurrencyStrategy示例注册至HystrixPlugins中,这在扩展性方面显然是缺失的,借鉴spring的实践,我们可以定义对Callable的包装接口HystrixCallableWrapper,根据实际的业务只需要对HystrixCallableWrapper进行实现,并注册对应的实现bean即可。具体实现如下:
1、定义用于包装hystrix中Callable实例的接口:
public interface HystrixCallableWrapper { /** * 包装Callable实例 * * @param callable 待包装实例 * @param <T> 返回类型 * @return 包装后的实例 */ <T> Callable<T> wrap(Callable<T> callable); }
2、通过之前的源码阅读与实践,基本已经发现实现线程上线文传播的核心在于对Callable进行包装,通过多次对Callable包装即实现了一个链式包装过程,如下扩展HystrixConcurrencyStrategy接口实现RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy,其中定义CallableWrapperChain类对所有注入的HystrixCallableWrapper包装实现进行装配:
public class RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy extends HystrixConcurrencyStrategy { private final Collection<HystrixCallableWrapper> wrappers; public RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy(Collection<HystrixCallableWrapper> wrappers) { this.wrappers = wrappers; } @Override public <T> Callable<T> wrapCallable(Callable<T> callable) { return new CallableWrapperChain(callable, wrappers.iterator()).wrapCallable(); } private static class CallableWrapperChain<T> { private final Callable<T> callable; private final Iterator<HystrixCallableWrapper> wrappers; CallableWrapperChain(Callable<T> callable, Iterator<HystrixCallableWrapper> wrappers) { this.callable = callable; this.wrappers = wrappers; } Callable<T> wrapCallable() { Callable<T> delegate = callable; while (wrappers.hasNext()) { delegate = wrappers.next().wrap(delegate); } return delegate; } } }
3、实现HystrixCallableWrapper接口,定义一个包装RequestContextHolder上下文处理的实现类:
public final class RequestAttributeAwareCallableWrapper implements HystrixCallableWrapper { @Override public <T> Callable<T> wrap(Callable<T> callable) { return new RequestAttributeAwareCallable(callable, RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()); } static class RequestAttributeAwareCallable<T> implements Callable<T> { private final Callable<T> delegate; private final RequestAttributes requestAttributes; RequestAttributeAwareCallable(Callable<T> callable, RequestAttributes requestAttributes) { this.delegate = callable; this.requestAttributes = requestAttributes; } @Override public T call() throws Exception { try { RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes); return delegate.call(); } finally { RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes(); } } } }
4、实现HystrixCallableWrapper接口,定义一个包装Mdc日志处理上下文的实现类:
public class MdcAwareCallableWrapper implements HystrixCallableWrapper { @Override public <T> Callable<T> wrap(Callable<T> callable) { return new MdcAwareCallable<>(callable, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()); } private class MdcAwareCallable<T> implements Callable<T> { private final Callable<T> delegate; private final Map<String, String> contextMap; public MdcAwareCallable(Callable<T> callable, Map<String, String> contextMap) { this.delegate = callable; this.contextMap = contextMap != null ? contextMap : new HashMap(); } @Override public T call() throws Exception { try { MDC.setContextMap(contextMap); return delegate.call(); } finally { MDC.clear(); } } } }
5、最后通过在Configuration配置类中注册如下HystrixCallableWrapper 实现类的bean实例,并通过HystrixPlugins注册扩展包装实现:
@Bean public HystrixCallableWrapper requestAttributeAwareCallableWrapper() { return new RequestAttributeAwareCallableWrapper(); } @Bean public HystrixCallableWrapper mdcAwareCallableWrapper(){ return new MdcAwareCallableWrapper(); } @Autowired(required = false) private List<HystrixCallableWrapper> wrappers = new ArrayList<>(); @PostConstruct public void init() { HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerConcurrencyStrategy(new RequestContextHystrixConcurrencyStrategy(wrappers)); }
总结
本章从官方网站与源码出发,逐步实现了hystrix中如何进行线程上下文的传播。同时为了更好的扩展性,提供了基于自定义接口并注入实现的方式。
---------------------
作者:帅天下
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/songhaifengshuaige/article/details/80345012
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号