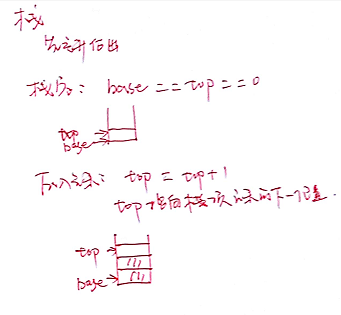
一、栈
栈顶(top) 栈底(bottom)
先进后出,从栈顶插入,从栈顶删除
顺序栈:用一组地址连续的存储单元一次存储自栈底到栈顶的元素,同时附设top栈顶指针
初始化:先分配一个指定大小的空间,空间不足时,再逐段扩大
base 栈底指针,始终指向栈底
top 栈顶指针,始终指向栈顶元素的下一位置
base = top 表示栈空
base == null 表示栈结构不存在
二、队列
先进先出
从队头(front)删除,从队尾(rear)插入
双端队列,限定输入和输出可以在两端(或者某一端)进行
链队列,用链表表示,头指针、尾指针
头指针指向队头元素,尾指针指向队尾元素的下一位置
队列空,队头指针和队尾指针指向同一元素
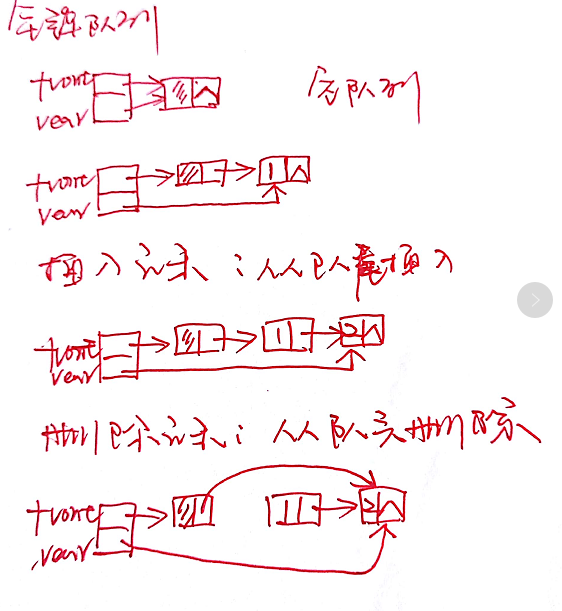
循环队列:地址连续的存储单元

1.用两个栈实现一个队列
//用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的出队和入队操作。 Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); public void add(int node) { stack1.push(node);// } public int remove() { if(stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty()){ System.out.println("队列为空"); return 0; }else{ if(stack2.isEmpty()){ while(! stack1.isEmpty()){ stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } return stack2.pop(); }else{ return stack2.pop(); } } }
2.用两个队列实现一个栈
//用两个队列来实现一个栈,弯成栈的出栈和入栈操作 Queue<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>(); Queue<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>(); public int pop(){ //在出栈时,每一次出栈都应该将一个队列中的除最后一个元素移到另一个队列中,因此,任一时刻,都有一个队列是空的 if(queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()){ //两个队列都是空 System.out.println("栈为空"); return 0; }else{ Queue<Integer> queueEmpty = queue1.isEmpty()?queue1:queue2;//记录空的那个队列 Queue<Integer> queueNotEmpty = queue2.isEmpty()?queue1:queue2;//记录非空的那个队列 while(!queueNotEmpty.isEmpty()){ int key = queueNotEmpty.poll();//从队列头部删除一个元素 //删除之后,判断队列是不是空,如果是空,证明这是队列的最后一个元素,即此次栈需要弹出的元素 if(queueNotEmpty.isEmpty()){ return key; }else{ queueEmpty.add(key); } } return 0; } } public void push(int key){ queue1.add(key); }



