流程图渲染方式:Canvas vs SVG
我们是袋鼠云数栈 UED 团队,致力于打造优秀的一站式数据中台产品。我们始终保持工匠精神,探索前端道路,为社区积累并传播经验价值。
本文作者:霁明
背景
我们产品中会有一些流程图应用,例如审批中心的审批流程图:

我们数栈产品内的流程图,基本都是使用的 mxGraph 实现的,mxGraph 使用了SVG来渲染图形。
流程图组件库除了 mxGraph,还有其他一些流行的库,例如:ReactFlow、G6、X6等等,各个库的特点、具体实现原理各有不同,但图形渲染方式却主要都是这两种:Canvas 和 SVG。
本文会通过绘制流程图(只是简单绘制,不涉及图表库的实现),来介绍 Canvas 和 SVG 的使用方式、动画实现以及两者之间的一些差异。
Canvas
简介
MDN 对 Canvas 的介绍:
Canvas API 提供了一个通过 JavaScript 和 HTML的 <canvas>元素来绘制图形的方式。它可以用于动画、游戏画面、数据可视化、图片编辑以及实时视频处理等方面。
目前所有主流的浏览器都支持 Canvas。
使用
基本用法
创建蓝白红3个色块:
import { useEffect } from 'react';
function Page() {
useEffect(() => {
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas') as HTMLCanvasElement;
if (canvas?.getContext) {
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.fillStyle = '#002153';
ctx.fillRect(10, 10, 50, 100);
ctx.fillStyle = '#ffffff';
ctx.fillRect(60, 10, 50, 100);
ctx.fillStyle = '#d00922';
ctx.fillRect(110, 10, 50, 100);
}
}, []);
return <canvas id="canvas"></canvas>;
}
export default Page;
效果如下图:

绘制流程图
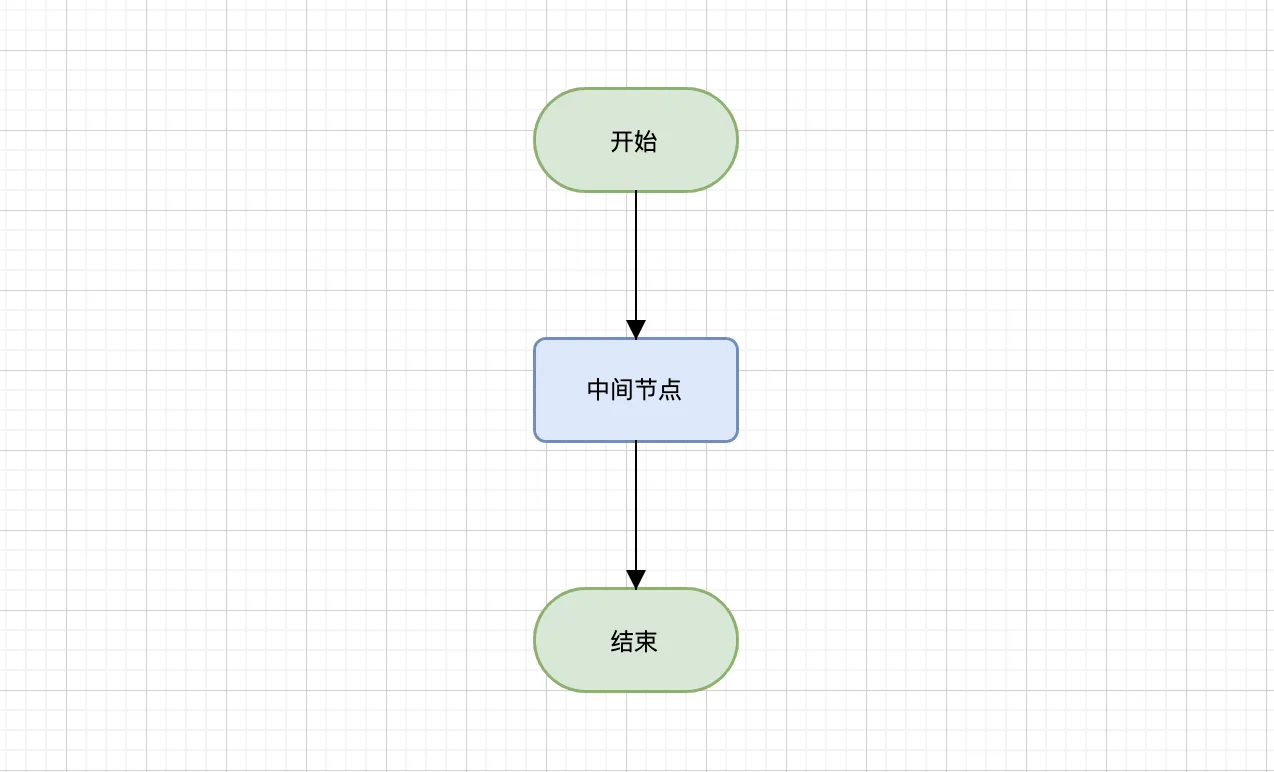
绘制一个开始节点、一个中间节点和一个结束节点,节点之间用有向线条进行连接,如下图:

前置知识:
devicePixelRatio:设备像素比,返回当前显示设备的物理像素分辨率与 _CSS _ 像素分辨率之比,它告诉浏览器应使用多少屏幕实际像素来绘制单个 CSS 像素。比如屏幕物理像素是2000px,css 像素是1000px,则设备像素比为2。
实现代码如下:
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import styles from '../../styles/canvas.module.css';
function Page() {
useEffect(() => {
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas') as HTMLCanvasElement;
if (canvas?.getContext) {
// 处理图像模糊问题
const ratio = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
const { width, height } = canvas;
canvas.width = Math.round(width * ratio);
canvas.height = Math.round(height * ratio);
canvas.style.width = `${width}px`;
canvas.style.height = `${height}px`;
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// 放大(处理图像模糊问题)
ctx.scale(ratio, ratio);
ctx.font = '12px sans-serif';
// 开始节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(300, 125, 25, Math.PI / 2, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左边框
ctx.lineTo(350, 100);
ctx.arc(350, 125, 25, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, (Math.PI * 5) / 2, false); // 右边框
ctx.lineTo(300, 150);
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#FFF';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('开始', 312, 130);
// 中间节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(280, 230, 5, Math.PI, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左上圆角
ctx.lineTo(370, 225);
ctx.arc(370, 230, 5, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, Math.PI * 2, false); // 右上圆角
ctx.lineTo(375, 270);
ctx.arc(370, 270, 5, 0, Math.PI / 2, false); // 右下圆角
ctx.lineTo(280, 275);
ctx.arc(280, 270, 5, Math.PI / 2, Math.PI, false); // 左下圆角
ctx.lineTo(275, 230);
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#FFF';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('中间节点', 300, 254);
// 结束节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(300, 400, 25, Math.PI / 2, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左边框
ctx.lineTo(350, 375);
ctx.arc(350, 400, 25, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, (Math.PI * 5) / 2, false); // 右边框
ctx.lineTo(300, 425);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#FFF';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('结束', 312, 405);
// 线条1
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(325, 150);
ctx.lineTo(325, 225);
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
ctx.stroke();
// 箭头1
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(320, 215);
ctx.lineTo(330, 215);
ctx.lineTo(325, 225);
ctx.fill();
// 线条2
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(325, 275);
ctx.lineTo(325, 375);
ctx.stroke();
// 箭头2
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(320, 365);
ctx.lineTo(330, 365);
ctx.lineTo(325, 375);
ctx.fill();
}
}, []);
return (
<div className={styles.container}>
<canvas id="canvas" width="800" height="600"></canvas>
</div>
);
}
export default Page;
绘制图形可以通过绘制矩形、绘制路径的方式来绘制图形,还可以使用 Path2D 对象来绘制,具体使用方法可以查看MDN。
样式和颜色
给节点加上样式,效果如下:
对比上一步,可以发现给节点内容和边框填充了颜色,以开始节点为例:
...
// 开始节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(300, 125, 25, Math.PI / 2, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左边框
ctx.lineTo(350, 100);
ctx.arc(350, 125, 25, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, (Math.PI * 5) / 2, false); // 右边框
ctx.lineTo(300, 150);
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#82b366';
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#d5e8d4';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('开始', 312, 130);
...
canvas 支持绘制许多样式,例如:颜色、透明度、线条样式、阴影等,具体使用可查看 MDN
动画实现
实现线条流动动画,实现效果如下图所示:

实现原理:将线条设置为虚线,然后设置偏移量,每间隔一定时间渲染一次,每次的偏移量都递增,便实现了线条流动的动画效果。
原理了解了,但在开发之前有两个点要考虑一下:
- 动画是有执行频率的,要控制的话用哪种方式好一点?
- 每次动画执行时,一般是整个画布都刷新,考虑到性能问题,是否可以局部刷新?
带着这两个问题,我们看下代码实现:
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import styles from '../../styles/page.module.css';
const rAFSetInterval = (handler: (timer: number) => void, timeout?: number) => {
let timer = null;
let startTime = Date.now();
const loop = () => {
let currentTime = Date.now();
if (currentTime - startTime >= timeout) {
startTime = currentTime;
handler(timer);
}
timer = requestAnimationFrame(loop);
};
loop();
return timer;
};
function Page() {
let canvas: HTMLCanvasElement;
let ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D;
let offset = 0;
useEffect(() => {
canvas = document.getElementById('canvas') as HTMLCanvasElement;
if (canvas) {
const ratio = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
const { width, height } = canvas;
canvas.width = Math.round(width * ratio);
canvas.height = Math.round(height * ratio);
canvas.style.width = `${width}px`;
canvas.style.height = `${height}px`;
ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.scale(ratio, ratio);
ctx.font = '12px sans-serif';
draw();
rAFSetInterval(run, 50);
}
}, []);
const run = () => {
offset++;
if (offset > 1000) {
offset = 0;
}
drawAnimateLine();
};
const draw = () => {
// 初始化
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
ctx.setLineDash([]);
ctx.lineDashOffset = 0;
// 开始节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(300, 125, 25, Math.PI / 2, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左边框
ctx.lineTo(350, 100);
ctx.arc(350, 125, 25, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, (Math.PI * 5) / 2, false); // 右边框
ctx.lineTo(300, 150);
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#82b366';
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#d5e8d4';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('开始', 312, 130);
// 中间节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(280, 230, 5, Math.PI, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左上圆角
ctx.lineTo(370, 225);
ctx.arc(370, 230, 5, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, Math.PI * 2, false); // 右上圆角
ctx.lineTo(375, 270);
ctx.arc(370, 270, 5, 0, Math.PI / 2, false); // 右下圆角
ctx.lineTo(280, 275);
ctx.arc(280, 270, 5, Math.PI / 2, Math.PI, false); // 左下圆角
ctx.lineTo(275, 230);
ctx.lineWidth = 3;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#6c8ebf';
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#dae8fc';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('中间节点', 300, 254);
// 结束节点
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(300, 375, 25, Math.PI / 2, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, false); // 左边框
ctx.lineTo(350, 350);
ctx.arc(350, 375, 25, (Math.PI * 3) / 2, (Math.PI * 5) / 2, false); // 右边框
ctx.lineTo(300, 400);
ctx.strokeStyle = '#82b366';
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillStyle = '#d5e8d4';
ctx.fill();
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';
ctx.fillText('结束', 312, 380);
// 线条1
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(325, 150);
ctx.lineTo(325, 223);
ctx.setLineDash([4, 4]);
ctx.lineDashOffset = -offset;
ctx.lineWidth = 1.5;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#000';
ctx.stroke();
// 箭头1
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(320, 215);
ctx.lineTo(325, 218);
ctx.lineTo(330, 215);
ctx.lineTo(325, 225);
ctx.fill();
// 线条2
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(325, 275);
ctx.lineTo(325, 348);
ctx.stroke();
// 箭头2
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(320, 340);
ctx.lineTo(325, 343);
ctx.lineTo(330, 340);
ctx.lineTo(325, 350);
ctx.fill();
};
const drawAnimateLine = () => {
// 清空线条
ctx.clearRect(324, 150, 2, 67);
ctx.clearRect(324, 275, 2, 67);
// 绘制线条1
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(325, 150);
ctx.lineTo(325, 223);
ctx.setLineDash([4, 4]);
ctx.lineDashOffset = -offset;
ctx.lineWidth = 1.5;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#000';
ctx.stroke();
// 绘制线条2
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(325, 275);
ctx.lineTo(325, 348);
ctx.stroke();
};
return (
<div className={styles.container}>
<canvas id="canvas" width="800" height="600"></canvas>
</div>
);
}
export default Page;
针对前面的两个问题,这里总结一下:
- 使用 requestAnimationFrame 实现一个 setInterval 方法,做到定时控制和性能兼顾
- 针对动画区域,通过坐标和区域宽高,进行 canvas 的局部刷新
SVG
简介
引用 MDN 对 SVG 的介绍:
可缩放矢量图形(Scalable Vector Graphics,SVG)基于 XML 标记语言,用于描述二维的矢量图形。
和传统的点阵图像模式(如 JPEG 和 PNG)不同的是,SVG 格式提供的是矢量图,这意味着它的图像能够被无限放大而不失真或降低质量,并且可以方便地修改内容,无需图形编辑器。通过使用合适的库进行配合,SVG 文件甚至可以随时进行本地化。
目前所有主流的浏览器都支持SVG(IE部分支持)。
使用
常用标签
流程图中主要用到的几种标签:
<svg>
SVG 容器元素,SVG 的代码都包裹在该元素下,可以作为根元素(一般是 svg 图片),也可以内嵌在HTML文档中。如果 svg 不是根元素,svg 元素可以用于在当前文档内嵌套一个独立的 svg 片段。这个独立片段拥有独立的视口和坐标系统。
<g>
元素 g 是用来组合对象的容器。添加到 g 元素上的变换会应用到其所有的子元素上。添加到 g 元素的属性会被其所有的子元素继承。
<rect>
rect元素是 SVG 的一个基本形状,用来创建矩形,基于一个角位置以及它的宽和高。它还可以用来创建圆角矩形。
<path>
path 元素是用来定义形状的通用元素。所有的基本形状都可以用 path 元素来创建。
<foreignObject>
foreignObject 元素允许包含来自不同的 XML 命名空间的元素。在浏览器的上下文中,很可能是 XHTML / HTML。在我们的流程图中,通过 HTML 渲染的节点一般都渲染在这个标签内。
基本用法
使用svg渲染图片
function Page() {
return (
<svg width="150" height="100">
<rect width="50" height="100" x="0" fill="#002153" />
<rect width="50" height="100" x="50" fill="#ffffff" />
<rect width="50" height="100" x="100" fill="#d00922" />
</svg>
);
}
export default Page;
上面代码渲染效果如下图:

绘制流程图
使用svg绘制流程图:

代码实现如下:
import styles from '../../styles/page.module.css';
function Page() {
return (
<svg width="800" height="600" className={styles.container}>
<g>
<path
d="M 320 110 C 286 110, 286 160, 320 160 L 370 160 C 404 160, 404 110, 370 110 Z"
stroke="#82b366"
strokeWidth="2"
fill="#d5e8d4"
/>
<text x="332" y="140" style={{ fontSize: 12 }}>
开始
</text>
</g>
<g>
<rect
x="295"
y="235"
width="100"
height="50"
rx="5"
fill="#dae8fc"
stroke="#6c8ebf"
strokeWidth="2"
></rect>
<text x="320" y="264" style={{ fontSize: 12 }}>
中间节点
</text>
</g>
<g>
<path
d="M 320 360 C 286 360, 286 410, 320 410 L 370 410 C 404 410, 404 360, 370 360 Z"
stroke="#82b366"
strokeWidth="2"
fill="#d5e8d4"
/>
<text x="332" y="390" style={{ fontSize: 12 }}>
结束
</text>
</g>
<g>
<path d="M 345 160 L 345 235" stroke="#000"></path>
<path d="M 340 225 L 345 228 L 350 225 L 345 235 Z" fill="#000"></path>
</g>
<g>
<path d="M 345 285 L 345 360" stroke="#000"></path>
<path d="M 340 350 L 345 353 L 350 350 L 345 360 Z" fill="#000"></path>
</g>
</svg>
);
}
export default Page;
以开始节点为例,主要看下path元素:
<path
d="M 320 110 C 286 110, 286 160, 320 160 L 370 160 C 404 160, 404 110, 370 110 Z"
stroke="#82b366"
strokeWidth="2"
fill="#d5e8d4"
/>
d 属性定义了要绘制的路径,路径定义是一个路径命令组成的列表,其中的每一个命令由命令字母和用于表示命令参数的数字组成。每个命令之间通过空格或逗号分隔。
M 表示 move to,即移动到某个坐标;L 表示 line to,即连线到某个坐标。
C 表示使用三次方贝塞尔曲线,后面跟随3个坐标点,分别是起始控制点、终点控制点、终点。
Z 表示 ClosePath,将从当前位置绘制一条直线到路径中的第一个点。上面只用到了4种命令,而命令总共有20种,具体可以查看MDN。
stroke、strokeWidth、fill 则分别指定了边框颜色、宽度,以及填充颜色。
动画实现
实现线条流动动画,实现效果如下图:

实现原理:先将线条设置为虚线,然后通过 css 动画,修改虚线的偏移量并无限循环,从而实现线条流动效果。
代码实现如下:
.animate-path {
stroke-dasharray: 5;
animation: dashdraw 0.5s linear infinite;
}
@keyframes dashdraw {
0% {
stroke-dashoffset: 10;
}
}
svg 可以通过 css、js 或者 animate 标签来实现动画,适用于需要高质量矢量图形、可缩放和交互性强的场景
对比
使用方式
Canvas 是比 SVG 更低级别的 API,绘制图形需要通过 JS 来操作。Canvas 提供了更大的灵活性,但复杂度也更高,理论上任何使用 SVG 绘制的图形,都可以通过 Canvas绘制出来。相反,由于 SVG 是比 Canvas 更高级别的 API,可以当作 HTML 元素去使用,也可以结合 JS、CSS 去操作,使用 SVG 创建一些复杂的图形会比使用 Canvas 更加简单。
交互性
SVG 位于 DOM 中,和普通 DOM 元素一样支持响应事件。Canvas 也可以响应交互事件,但需要额外的代码去实现。
性能
Canvas 和 SVG 性能的影响因素主要有两个:绘制图形的数量、绘制图形的大小。
下图是微软 MSDN 上给的一个对比图。

Canvas 的性能受画布尺寸影响更大,而 SVG 的性能受图形元素个数影响更大。网络上的对于性能及使用相关的建议是:如果绘制图像面积大或者绘制元素数量小时,建议使用SVG,如果绘制图像面积小或者绘制元素数量较大时,则建议使用 Canvas。
总结
本文介绍了 Canvas 和 SVG 的一些基本概念和使用方式,在我们日常开发中,有时会碰到需要绘制图形的场景,对于 Canvas 和 SVG,分别有其适合的场景:
- 需要绘制的图像简单、交互性强或者是矢量图(例如图标),建议使用 SVG。
- 需要支持像素级别的操作,或者复杂的动画和交互(例如数据可视化、交互式游戏),建议使用Canvas。
大多数流程图组件库都是使用 Canvas 或 SVG 来绘制图形,流程图一般图形简单,节点数量不多,会有一些简单的交互,因而大多数流程图组件库都使用 SVG 来进行渲染,例如 ReactFlow、draw.io、mxGraph、X6、XFlow 等,都是使用 svg 来进行渲染。
链接
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Canvas_API
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/SVG
最后
欢迎关注【袋鼠云数栈UED团队】~
袋鼠云数栈 UED 团队持续为广大开发者分享技术成果,相继参与开源了欢迎 star





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 实操Deepseek接入个人知识库
· CSnakes vs Python.NET:高效嵌入与灵活互通的跨语言方案对比
· 【.NET】调用本地 Deepseek 模型
· Plotly.NET 一个为 .NET 打造的强大开源交互式图表库
· 上周热点回顾(2.17-2.23)
2022-06-28 前端 Git-Hooks 工程化实践