springBoot数据校验与统一异常处理
概念
异常,在程序中经常发生,如果发生异常怎样给用户一个良好的反馈体验就是我们需要处理的问题。以前处理异常信息,经常都是给前端一个统一的响应,如数据错误,程序崩溃等等。没办法指出哪里出错了,这是一种对用户很不友好的体验。我们应该根据自己的业务给予信息提示
异常类
定义一个全局的异常类,有异常信息,都交到这边来。它像一个污水处理厂,汇集所有的工业污水,然后分门别类进行污水净化。要现实这种功能就要用到springBoot的@ControllerAdvice注解,它的作用是控制器增加,应用到有以下的注解的函数或类@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder,@ModelAttribute。
创建一个异常类
package com.xmlxy.exception;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class CommonExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(Exception e)
{
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
result.put("code","9999");
result.put("msg","异常被捕获了");
return result;
}
}
写个接口测试一下
@RequestMapping(value = "test",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test()
{
int i = 1 / 0;
return "test接口";
}
我们都知道这会让控制台抛出一个除数不能为零的异常信息。调用接口,会发现控制台并没有异常信息,页面输出
{"msg":"除数不能为零","code":"9999"}
然后前端根据我们约定的code,或弹出窗,或跳转页面。但是这样是远远不够的,因为异常信息很多,我上文中,因为贪图省事,直接用Exception捕获并没有给予详细的异常捕捉。如果多余的不同异常,需要进行不同的异常处理,就可以编写多个exceptionHandler方法,可以指定处理异常类。
@ExceptionHandler(FileNotFoundException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(FileNotFoundException e)
{
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code","8888");
result.put("msg","文件不存在");
return result;
}
自定义异常
现有的异常有时并没有满足我们业务需求,就得自定义自己的专属异常类,举一个前几次讲的登录接口demo,用户可能没输密码直接点登录,是进行密码错误提示,还是反馈密码为空哪种体验比较好,很明显是后一种。
自定义异常,继承Exception接口
package com.xmlxy.exception;
public class FistSpringBootException extends Exception
{
private String code;
private FistSpringBootException(String code)
{
super();
this.code = code;
}
public FistSpringBootException(String code,String message)
{
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
封装一个数据效验类
package com.xmlxy.exception;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
public class ParamUtil
{
/*验证是否是数字*/
public static int isNumber(String args,String name) throws FistSpringBootException {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(args) && !name.matches("^[0-9]*$"))
{
throw new FistSpringBootException("1111",name + "参数不合法");
}
return Integer.parseInt(args);
}
/*验证参数是否为空*/
public static String isEmpty(String args,String name) throws FistSpringBootException {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(args))
{
throw new FistSpringBootException("2222",name + "参数不能为空");
}
return String.valueOf(args);
}
}
登录接口
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping(value = "login",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String login(HttpServletRequest request) throws FistSpringBootException {
String user = ParamUtil.isEmpty(request.getParameter("user"),"user");
String pwd = ParamUtil.isEmpty(request.getParameter("pwd"),"pwd");
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if ("admin".equals(user) && "admin".equals(pwd))
{
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUser(user);
user1.setPwd(pwd);
session.setAttribute("user",user1);
return "登录成功";
}
return "密码错误,登录失败";
}
}
进行异常捕获
package com.xmlxy.exception;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class CommonExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(Exception e)
{
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
result.put("code","9999");
result.put("msg","除数不能为零");
return result;
}
@ExceptionHandler(FileNotFoundException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(FileNotFoundException e)
{
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code","8888");
result.put("msg","文件不存在");
return result;
}
@ExceptionHandler(FistSpringBootException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(FistSpringBootException e)
{
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
result.put("code","1111");
result.put("msg",e.getMessage());
return result;
}
}
demo写完,直接测试一下,访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/login?user=&pwd=
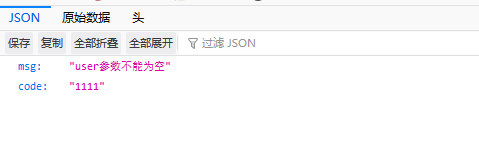
是否会发现自己还得效验数据有点费劲,没事,springBoot已经帮我们想好了,很简单,只要加上注解。
User类
package com.xmlxy.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
@Component
@Data
public class User {
@NotBlank(message = "user不能为空")
private String user;
@NotBlank(message = "pwd不能为空")
private String pwd;
}
异常全局配置
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(BindException e)
{
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
result.put("code","1111");
result.put("msg","参数不合法");
return result;
}
登录接口
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping(value = "login",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String login(@Valid User user, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if ("admin".equals(user.getUser()) && "admin".equals(user.getPwd()))
{
session.setAttribute("user",user);
return "登录成功";
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "密码错误,登录失败";
}
}
再次访问,会发现已经帮你效验了
{"msg":"参数不合法","code":"1111"}
还有很多的数据效验注解,比如@Email注解,接收参数必须是email地址,还有限制长度的@Length注解,以下是常用的校验注解
@Null 被注释的元素必须为 null
@NotNull 被注释的元素必须不为 null
@AssertTrue 被注释的元素必须为 true
@AssertFalse 被注释的元素必须为 false
@Min(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@Max(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@DecimalMin(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@DecimalMax(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@Size(max=, min=) 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
@Digits (integer, fraction) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内
@Past 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期
@Future 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期
@Pattern(regex=,flag=) 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
Hibernate Validator提供的校验注解:
@NotBlank(message =) 验证字符串非null,且长度必须大于0
@Email 被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址
@Length(min=,max=) 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内
@NotEmpty 被注释的字符串的必须非空
@Range(min=,max=,message=) 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号