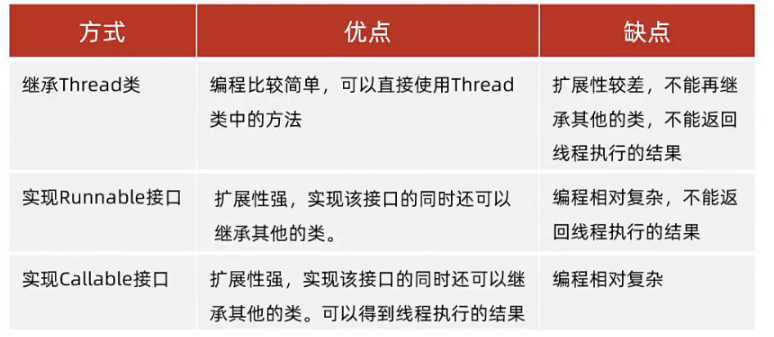
1 // 方式一:继承Thread类
2 public class Thread{
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 Thread t = new MyThread();
5 t.start();
6
7 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
8 System.out.println("主线程:" + i);
9 }
10 }
11 }
12
13 public class MyThread extends Thread {
14 @Override
15 public void run(){
16 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
17 System.out.println("子线程:" + i);
18 }
19 }
20 }
1 /*
2 创建线程方式二、实现 Runnable接口
3 */
4 public class ThreadDemo2 {
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 Runnable r = new MyRunnable();
7 Thread t = new Thread(r);
8 t.start();
9 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
10 System.out.println("主线程:" + i);
11 }
12 }
13 }
14
15 public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
16 @Override
17 public void run() {
18 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
19 System.out.println("任务线程:" + i);
20 }
21 }
22 }
public class ThreadDemo2_mini {
/*
线程创建方式二 、实现Runnable接口(匿名内部类方式)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程1:" + i);
}
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
// 同上简化
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程2:" + i);
}
}
}).start();
// 同上简化
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程3:" + i);
}
}).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程:" + i);
}
}
}
/*
方式三:实现Collable接口
*/
public class ThreadDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 Callable 任务对象
// 线程1
Callable<String> call = new MyCallable(50);
// 把 Callable 任务对象 交给 FutureTask 对象
// FutureTask 对象作用 1:是 Runnable 的对象 (实现了 Runnable 接口),可以交给 Thread
// FutureTask 对象作用 2: 可以在线程执行完毕之后通过调用 get 方法得到线程执行完成的结果
FutureTask<String> task = new FutureTask<>(call);
// 交给线程
Thread t = new Thread(task);
// 启动线程
t.start();
// 线程 2
Callable<String> call2 = new MyCallable(100);
FutureTask<String> task2 = new FutureTask<>(call2);
Thread t2 = new Thread(task2);
t2.start();
// 获取线程执行完的结果
try {
// 如果任务没有执行完毕这里会先等待,等任务执行完之后在提取结果
String s = task.get();
System.out.println("线程1:" + s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
// 如果任务没有执行完毕这里会先等待,等任务执行完之后在提取结果
String s2 = task2.get();
System.out.println("线程2:" + s2);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
/*
定义一个任务类、实现 Callable 接口、应申明线程结束后的结果类型
*/
private int n;
public MyCallable(int n){
this.n = n;
}
// 重写 call 方法
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return "子线程结果是:" + sum;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号