一、Spring框架
Spring是一个基于IOC和AOP的结构J2EE系统的框架。
1、IOC反转控制是Spring的基础(Inversion Of Control)。也就是说创建对象由以前的程序员自己new构造方法来调用,变成了交给Spring创建对象。
2、DI依赖注入(Dependency Inject):就是拿到的对象的属性,已经被注入好相关值了,可以直接使用。
3、将lib.jar导入到新建的Spring项目的lib目录(类库)中。
导入jar包方法:右键project->properties->java build path->libaries->add external jars就行。
4、在src目录下,建立两个文件夹,一个pojo(放实体类),一个test(测试用)
准备pojo Product,用来测试IOC和DI

package com.demo.pojo; public class Product{ private int id; private String name; //属性的getter和setter方法 public int getId(){ return id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id=id; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } }
5、在src目录下新建一个applicationContext.xml文件
applicationContext.xml是Spring的核心配置文件,通过配置bean的属性,根据关键字product来获取Product对象,该对象获取的时候,被注入了字符串"Apple"到属性中。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema.context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <bean name="product" class="com.demo.pojo.Product"> <property name="name" value="Apple"/> </bean> </beans>
6、测试TestSpring
在test文件夹下,建立TestSpring

package com.demo.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.demo.pojo.Product; public class TestSpring{ public static void main(String[] args){ //加载applicationContext.xml配置文件 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext.xml"}); //根据ApplicationContext对象提供的getBean()方法,获取配置bean的name属性值。 Product product=(Product)context.getBean("product"); System.out.println(product.getName()); } }
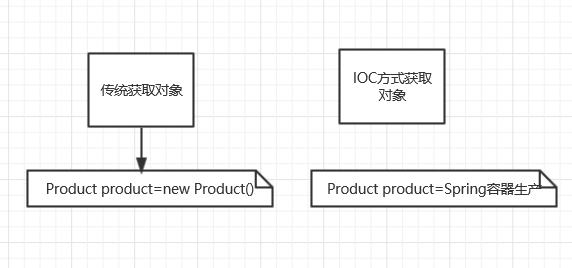
7、工作原理:
IOC方式获取对象方式:对象的生命周期交给Spring来管理,直接从Spring那里获取一个对象。
传统方式:通过new关键字主动创建一个对象。
二、注入对象
之前直接对Product的name属性注入"Apple"字符串,这一次我们注入一个Category分类对象。
1、首先修改Product.java实体类,新增一个Category属性。

package com.demo.pojo; public class Product{ private int id; private String name; private Category category;//类别属性 //属性的getter和setter方法 public int getId(){ return id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id=id; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public Category getCategory(){ return category; } pulic vodi setCategory(Category category){ this.category=category; } }
2、修改applicationContext.xml配置文件
在创建Product的时候注入一个Category对象,这里要使用ref来注入另一个对象。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema.context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <bean name="product" class="com.demo.pojo.Product"> <property name="name" value="Apple"/> <property name="category" ref="Category"/><!--将category对象注入到product--> </bean> <!--配置Category的bean--> <bean name="category" class="com.demo.pojo.Category"> <property name="name" value="Fruit"/> </bean> </beans>
3、TestSpring测试
通过Spring获取Product对象被注入的Category对象

package com.demo.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.demo.pojo.Product; public class TestSpring{ public static void main(String[] args){ //加载applicationContext.xml配置文件 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext.xml"}); //根据ApplicationContext对象提供的getBean()方法,获取配置bean的name属性值。 Product product=(Product)context.getBean("product"); System.out.println(product.getName());//Apple System.out.pringln(product.getCategory().getName());//Fruit } }
三、采用注解的方式进行IOC/DI
1、修改applicationContext.xml
添加配置:
<context:annotation-config/>
具体配置修改如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema.context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/ <bean name="product" class="com.demo.pojo.Product"> <property name="name" value="Apple"/> <!--<property name="category" ref="Category"/><!--将category对象注入到product--><!--注释掉刚才给Product注入的category属性,后面采用注解完成该操作--> </bean> <!--配置Category的bean--> <bean name="Category" class="com.demo.pojo.Category"> <property name="name" value="Fruit"/> </bean>
2、采用注解@Autowired
2.1、在Product.java的Category属性上面加上@Autowired注解

package com.demo.pojo; public class Product{ private int id; private String name; @Autowried//采用注解注入Category属性,不用在xml配置bean的Product引入Category private Category category;//类别属性 //属性的getter和setter方法 public int getId(){ return id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id=id; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public Category getCategory(){ return category; } pulic vodi setCategory(Category category){ this.category=category; } }
2.2、也可以在setCategory方法上面加上@Autowired注解,达到同样效果

package com.demo.pojo; public class Product{ private int id; private String name; //@Autowried//采用注解注入Category属性,不用在xml配置bean的Product引入Category private Category category;//类别属性 //属性的getter和setter方法 public int getId(){ return id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id=id; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public Category getCategory(){ return category; } @Autowried pulic void setCategory(Category category){ this.category=category; } }
2.3、还可以采用@Resource注解

package com.demo.pojo; import javax.annotation.Resource; public class Product{ private int id; private String name; //@Autowried//采用注解注入Category属性,不用在xml配置bean的Product引入Category @Resource(name="category") private Category category;//类别属性 //属性的getter和setter方法 public int getId(){ return id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id=id; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public Category getCategory(){ return category; } //@Autowried pulic void setCategory(Category category){ this.category=category; } }
3、TestSpring测试

package com.demo.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.demo.pojo.Product; public class TestSpring{ public static void main(String[] args){ //加载applicationContext.xml配置文件 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext.xml"}); //根据ApplicationContext对象提供的getBean()方法,获取配置bean的name属性值。 Product product=(Product)context.getBean("product"); System.out.println(product.getName());//Apple System.out.pringln(product.getCategory().getName());//Fruit } }
4、也可以不用再applicationContext.xml中一个一个配置bean。
配置bean属性的都去掉,直接加上:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.demo.pojo"/>
作用:告诉Spring,bean都放在com.demo.pojo包下
applicationContext.xml修改为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema.context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.demo.pojo"/> </beans>
4.1、使用@Component注解,为pojo加上注解,说明这个类是bean
Product.java:

package com.demo.pojo; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("product") public class Product{ private int id; private String name="Apple"; //@Autowried//采用注解注入Category属性,不用在xml配置bean的Product引入Category @Resource(name="category") private Category category;//类别属性 //属性的getter和setter方法 public int getId(){ return id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id=id; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public Category getCategory(){ return category; } //@Autowried pulic void setCategory(Category category){ this.category=category; } }
Category.java

package com.demo.pojo; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("category") public class Category { private int id; private String name="Fruit"; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
4.2、TestSpring测试

package com.demo.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.demo.pojo.Product; public class TestSpring{ public static void main(String[] args){ //加载applicationContext.xml配置文件 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext.xml"}); //根据ApplicationContext对象提供的getBean()方法,获取配置bean的name属性值。 Product product=(Product)context.getBean("product"); System.out.println(product.getName());//Apple System.out.pringln(product.getCategory().getName());//Fruit } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号