SRv6 - Linux Kernel Implementation
To enable SRv6 support, at least CONFIG_IPV6 must be enabled. The default built-in SRv6 code supports elementary processing of SR-enabled packets. For extended features such as SR encapsulation or other advanced processing, enable CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_LWTUNNEL. The HMAC extension of SRv6 can be enabled through CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_HMAC. To use iptables to filter packets on their SRv6 header, enable CONFIG_IP6_NF_MATCH_SRH (available since kernel v4.18). Finally, the BPF network functions can be enabled through CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_BPF (available since kernel v4.18).
Today most of the recent distributions compile the kernel with CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_LWTUNNEL and CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_HMAC:
- Debian (since 10) - Fedora (since 24) - Raspbian (since 2018-04-18) - Ubuntu (since 18.04) - [...]
CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_BPF is enabled in:
- Debian (since 10) - Fedora (since 27)
Fedora (since 27) is the only one enabling CONFIG_IP6_NF_MATCH_SRH as well.
srext - a Linux kernel module for the SRv6 Network Programming model In parallel, the Networking Group from University of Rome Tor Vergata, Italy, is developing a new kernel module providing more advanced Segment Routing functions. This module is intended to be eventually fully compliant with the SRv6 Network Programming model defined in draft-filsfils-spring-srv6-network-programming. The srext module is available on GitHub. SR behaviors support The following tables show the availability in Linux of each SRv6 behavior defined in draft-filsfils-spring-srv6-network-programming. New entries will be added to these tables as more SRv6 behaviors are defined in IETF documents. Endpoint functions Endpoint functions are triggered when the IPv6 Destination Address of an incoming packet matches an entry in the My Local SIDs table of an SRv6-enabled node. Name Description Release End Endpoint function 4.10 (February 2017), srext End.X Endpoint function with Layer-3 cross-connect 4.10 (February 2017), srext End.T Endpoint function with specific IPv6 table lookup 4.14 (November 2017) End.DX2 Endpoint with decapsulation and Layer-2 cross-connect 4.14 (November 2017), srext End.DX6 Endpoint with decapsulation and IPv6 cross-connect 4.14 (November 2017), srext End.DX4 Endpoint with decapsulation and IPv4 cross-connect 4.14 (November 2017), srext End.DT6 Endpoint with decapsulation and IPv6 table lookup 4.14 (November 2017) End.DT4 Endpoint with decapsulation and IPv4 table lookup In development End.B6 Endpoint bound to an SRv6 policy 4.14 (November 2017) End.B6.Encaps Endpoint bound to an SRv6 encapsulation Policy 4.14 (November 2017) End.BM Endpoint bound to an SR-MPLS Policy In development End.S Endpoint in search of a target in table T In development End.AD Endpoint to SR-unaware APP via dynamic proxy srext End.AM Endpoint to SR-unaware APP via masquerading srext Transit behaviors Transit behaviors are triggered when an in-transit packet matches a steering rule on an SRv6-enabled node. Examples of steering rules are packets arriving on a specific incoming interface or whose Destination Address belongs in a given prefix. Name Description Release T.Insert Transit behavior with insertion of an SRv6 Policy 4.10 (February 2017) T.Encaps Transit behavior with encapsulation in an SRv6 policy 4.10 (February 2017) T.Encaps.L2 T.Encaps behavior of the received L2 frame 4.14 (November 2017)
ubuntu19.10-aarch64 [root@localhost uloop3]# cat boot/config-5.3.0-18-generic | grep IPV6_SEG6 CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_LWTUNNEL=y CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_HMAC=y CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_BPF=y [root@localhost uloop3]# cat boot/config-5.3.0-18-generic | grep MATCH_SRH CONFIG_IP6_NF_MATCH_SRH=m
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 route add 2001::2 encap seg6 mode inline segs abcd::1234 dev enp1s0
root@ubuntu:~# uname -a
Linux ubuntu 5.3.0-18-generic #19-Ubuntu SMP Tue Oct 8 20:14:34 UTC 2019 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/Linux
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 route del 2001::2 encap seg6 mode inline segs abcd::1234 dev enp1s0
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 r show
::1 dev lo proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
fe80::/64 dev enp1s0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 route add 2001::2 encap seg6 mode inline segs abcd::1234 dev enp1s0
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 r show
::1 dev lo proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
2001::2 encap seg6 mode inline segs 2 [ abcd::1234 :: ] dev enp1s0 metric 1024 pref medium
fe80::/64 dev enp1s0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 route del 2001::2 encap seg6 mode inline segs abcd::1234 dev enp1s0
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 r show
::1 dev lo proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
fe80::/64 dev enp1s0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# ip sr help
Usage: ip sr { COMMAND | help }
ip sr hmac show
ip sr hmac set KEYID ALGO
ip sr tunsrc show
ip sr tunsrc set ADDRESS
where ALGO := { sha1 | sha256 }
root@ubuntu:~# ip sr hmac show
root@ubuntu:~# ip sr tunsrc show
tunsrc addr 2001::1
root@ubuntu:~# ip -6 r show
::1 dev lo proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
2001::2 encap seg6 mode inline segs 2 [ abcd::1234 :: ] dev enp1s0 metric 1024 pref medium
2001::/64 dev enp1s0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
abcd::1234 via 2001::2 dev enp1s0 metric 1024 pref medium
fe80::/64 dev enp1s0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
centos8
[root@localhost ~]# uname -a Linux localhost.localdomain 4.18.0-147.3.1.el8_1.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Jan 3 23:55:26 UTC 2020 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux [root@localhost ~]# [root@localhost ~]# cat /boot/config-`uname -r` | grep grep IPV6_SEG6 grep: IPV6_SEG6: No such file or directory [root@localhost ~]# cat /boot/config-`uname -r` | grep IPV6_SEG6 # CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_LWTUNNEL is not set # CONFIG_IPV6_SEG6_HMAC is not set [root@localhost ~]# cat /boot/config-`uname -r` | grep MATCH_SRH # CONFIG_IP6_NF_MATCH_SRH is not set
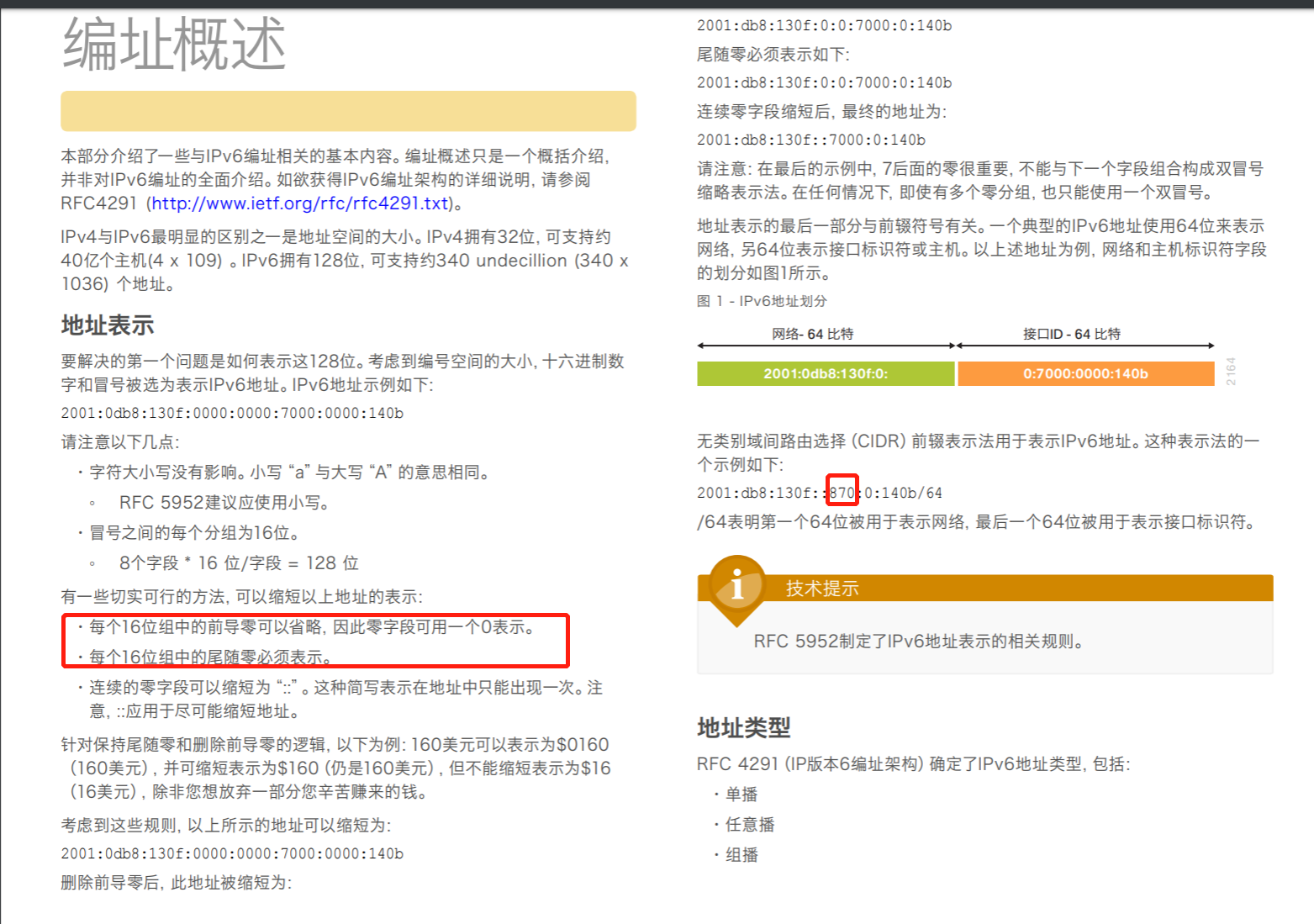
查看分配的 IPv6地址:ip -6 addr show ; 查看 IPv6 的路由表:ip -6 route,
ip -6 addr show dev
ip -6 n
ip -6 route list
ipv6 global & link-local 是共存的
ip -6 route show
ip -6 a ip -6 r ip -6 neigh ip n flush dev XXXX perf trace --no-syscalls --event 'net:*' ping6 xxxxxxxxxxx --------trace
添加IPV6地址 ip -6 addr add <ipv6address>/<prefixlength> dev <interface> ip -6 addr add 2001:0db8:0:f101::1/64 dev eth0 ifconfig <interface> inet6 add <ipv6address>/<prefixlength> ifconfig eth0 inet6 add 2001:0db8:0:f101::1/64 添加默认路由 ip -6 route add <ipv6network>/<prefixlength> via <ipv6address> ip -6 route add default via 2001:0db8:0:f101::1 route -A inet6 add <ipv6network>/<prefixlength> gw route -A inet6 add default gw 2001:0db8:0:f101::1 查看路由 ip -6 route show route -A 'inet6' route -6
ip6tables --list

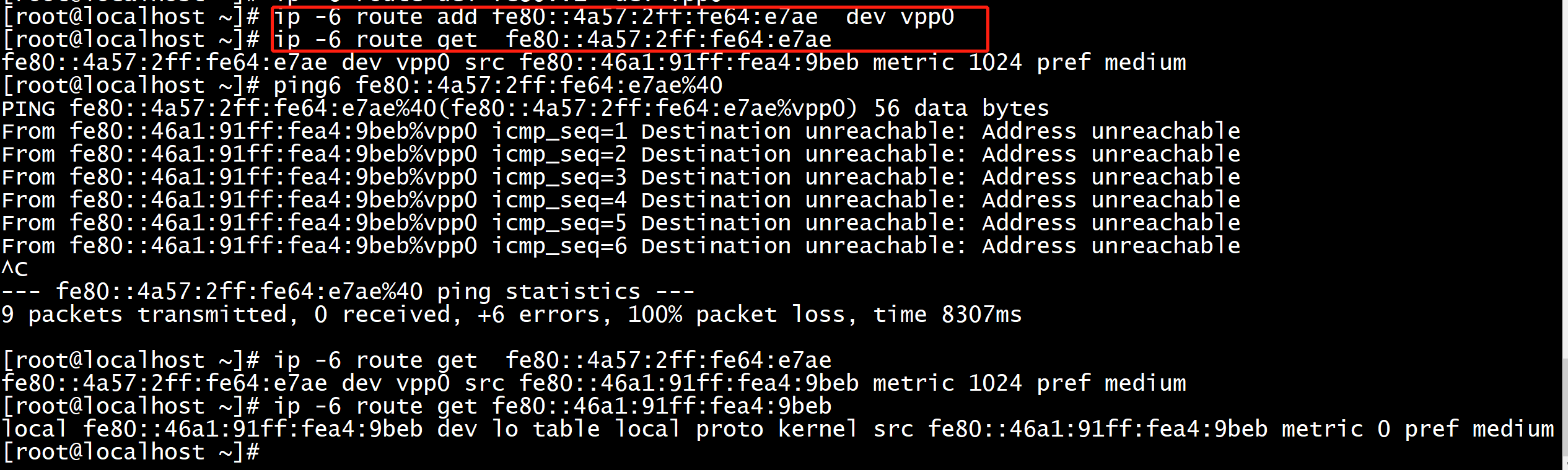
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1 sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.seg6_enabled=1 sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.seg6_enabled=1
net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1
root@ubuntu:~# sysctl -a | grep net.ipv6.conf | grep disable net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0 net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_policy = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_policy = 0 net.ipv6.conf.enp1s0.disable_ipv6 = 0 net.ipv6.conf.enp1s0.disable_policy = 0 net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 0 net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_policy = 0
root@ubuntu:~# sysctl -a | grep net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_defrtr = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_from_local = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_min_hop_limit = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_mtu = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_pinfo = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_rt_info_max_plen = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_rt_info_min_plen = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_rtr_pref = 1
root@ubuntu:~# ping6 2001::2 PING 2001::2(2001::2) 56 data bytes ^C --- 2001::2 ping statistics --- 341 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 374403ms root@ubuntu:~# ping6 2001::2%enp1s0 ping6: 2001::2%enp1s0: Name or service not known root@ubuntu:~# ping6 2001::2%2 PING 2001::2%2(2001::2%2) 56 data bytes
We setup a IPv6 network with two ubuntu systems and we make one PC as HOST and other as ROUTER(based on the concept of SLAAC). The host sent the "Router solicitation" message, but the router not respond with any "Router advertisement".
The corresponding configuration we done for router is
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.enp1s0.autoconf=1
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.enp1s0.accept_ra=2
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.enp1s0.forwarding=1





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律