「基础算法」第5章 广度搜索课堂过关
目录
「基础算法」第5章 广度搜索课堂过关
A. 【例题1】走迷宫
题目
思路
广搜裸题,略
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
bool end;
const int f[4][2] = {0,1 , 0,-1 , 1,0 , -1,0};
int h[2] , t[2];
int q[2][500010][2];
int dis[1010][1010];
int n;
int sx , sy , ex , ey;
bool map[1010][1010];
inline int abs_(int x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;}
void bfs(int id) {
if(end)return;
int sig = (id ? -1 : 1);
int x = q[id][h[id]][0] , y = q[id][h[id]][1];
// cout << x << '\t' << y << endl;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) {
int gx = x + f[i][0] , gy = y + f[i][1];
if((gx == sx && gy == sy) || (gx == ex && gy == ey))continue;
if(gx <= 0 || gy <= 0 || gx > n || gy > n || !map[gx][gy])continue;
if(dis[gx][gy] != 0) {
if(dis[gx][gy] * dis[x][y] < 0) {
cout << abs_(-dis[gx][gy] + dis[x][y]) + 1 << endl;
end = true;
return;
}
else continue;
}
q[id][t[id]][0] = gx , q[id][t[id]][1] = gy;
dis[gx][gy] = sig + dis[x][y];
t[id]++;
}
h[id]++;
/* cout << endl;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) {
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++)
cout << dis[i][j] << '\t';
cout << endl;
}
cout <<endl;*/
}
void ctrl() {
h[0] = h[1] = 0;
t[0] = t[1] = 1;
q[0][0][0] = sx , q[0][0][1] = sy;
q[1][0][0] = ex , q[1][0][1] = ey;
while(!end)
bfs(t[0] > t[1] ? 1 : 0);
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++) {
char c = getchar();
while(c != '0' && c != '1') c = getchar();
map[i][j] = (c == '0' ? true : false);
}
cin >> sx >> sy >> ex >> ey;
ctrl();
/* cout << endl;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) {
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++)
cout << dis[i][j] << '\t';
cout << endl;
}*/
return 0;
}
B. 【例题2】山峰和山谷
题目
思路
广搜次裸题,略
代码
随机数据
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int random(int r , int l = 1) {
return (long long) rand() * rand() * rand() % (r - l + 1) + l;
}
int main() {
unsigned seed;
cin >> seed;
seed *= time(0);
srand(seed);
int n = random(100);
cout << n << endl;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) {
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++)
printf("%d " , random(n));
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#define nn 1010
using namespace std;
int read() {
int re = 0 , sig = 1;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') sig = -1;
c = getchar();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9')
re = (re << 1) + (re << 3) + c - '0',
c = getchar();
return re * sig;
}
int n , h[nn][nn];
bool vis[nn][nn];
const int f[8][2] = {0,1 , 0,-1 , 1,0 , -1,0 , 1,1 , -1,1 , -1,-1 , 1,-1};
int dfs(int x , int y) {
int ty = 0;
vis[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++) {
int gx = x + f[i][0] , gy = y + f[i][1];
if(gx <= 0 || gx > n || gy <= 0 || gy > n)
continue;
if(h[x][y] != h[gx][gy]) {
if(h[x][y] > h[gx][gy]) {
if(ty == 2) ty = -1;
else if(ty != -1) ty = 1;
}
else {
if(ty == 1) ty = -1;
else if(ty != -1) ty = 2;
}
continue;
}
if(vis[gx][gy]) continue;
int sty = dfs(gx , gy);
if(sty == 0) continue;
if(ty == 0) ty = sty;
else if(ty != sty) ty = -1;
}
return ty;
}
int ans1 , ans2;
int main() {
n = read();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++)
h[i][j] = read();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++) {
if(vis[i][j]) continue;
int ty = dfs(i , j);
if(ty == 1) {
ans1++;
}
else if(ty == 2) ans2++;
else if(ty == 0) {
ans1++ , ans2++;
}
}
cout << ans1 << ' ' << ans2;
return 0;
}
C. 【例题3】立体推箱子
题目
思路
其实木块可以直接看成三种状态:立着,横躺,竖躺,分别记为:S(stand),R(right),D(down) (英文不好别见怪)
#define R 0
#define D 1
#define S 2
用x,y表示是木块的坐标,s表示状态(当s=R时,(x,y)表示木块所处两个点中位于左边的点的坐标,s=D时,(x,y)表示木块所处两个点中位于下面的点的坐标)
写出一个check函数判断(x,y,s)是否合法:
inline bool check(int x , int y , int s) {//map[i][j]: 1硬地(或起点终点) 2易碎地面 3禁地
if(x <= 0 || y <= 0 || x > n || y > m)return false;
if(map[x][y] == 2) return false;
if(s == S) return map[x][y] == 1;
int gx , gy;
if(s == D) gx = x + 1 , gy = y;
if(s == R) gx = x, gy = y + 1;
if(gx <= 0 || gy <= 0 || gx > n || gy > m|| map[gx][gy] == 2) return false;
return true;
}
写出f数组:
const int f[3][4][3] = {//{delta_x , delta_y , s}
{{0,2,S} , {-1,0,R} , {1,0,R} , {0,-1,S}},//s=R时x,y,s对应的变化情况 (分别为向左滚动箱子,向下,向上,向右)
{{2,0,S} , {-1,0,S} , {0,-1,D} , {0,1,D}},//s=D同理
{{-2,0,D} , {1,0,D} , {0,-2,R} , {0,1,R}}//s=S同理
};
BFS代码就很简单啦
void bfs() {
memset(dis , -1 , sizeof(dis));//多组数据记得清空
q.clear();
q.push(sx , sy , ss);//起点入队
dis[sx][sy][ss] = 0;
while(!empty(q)) {
node p = q.front();
q.h++;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) {
int gx = p.x + f[p.s][i][0] , gy = p.y + f[p.s][i][1] , gs = f[p.s][i][2];//(gx,gy,gs)表示变化后的坐标和状态
if(!check(gx , gy , gs)) continue;
if(dis[gx][gy][gs] != -1) continue;
if(gx == ex && gy == ey && gs == S) {
cout << dis[p.x][p.y][p.s] + 1 << endl;
return;
}
dis[gx][gy][gs] = dis[p.x][p.y][p.s] + 1;
q.push(gx , gy , gs);
}
}
puts("Impossible");
}
完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define R 0
#define D 1
#define S 2
#define nn 510
struct node {
int x , y , s;
};
struct quenode {
int h , t;
node q[nn * nn * 3];
inline void push(int _x , int _y , int _s) {
node tmp;
tmp.x = _x , tmp.y = _y , tmp.s = _s;
q[t] = tmp;
++t;
}
inline node front() {
return q[h];
}
inline void clear() {
h = t = 0;
memset(q , 0 , sizeof(q));
}
}q;
#define empty(q) (q.h == q.t)
int n , m;
int sx , sy , ex , ey , ss;
int map[nn][nn];
int dis[nn][nn][5];
inline bool check(int x , int y , int s) {
if(x <= 0 || y <= 0 || x > n || y > m)return false;
if(map[x][y] == 2) return false;
if(s == S) return map[x][y] == 1;
int gx , gy;
if(s == D) gx = x + 1 , gy = y;
if(s == R) gx = x, gy = y + 1;
if(gx <= 0 || gy <= 0 || gx > n || gy > m|| map[gx][gy] == 2) return false;
return true;
}
const int f[3][4][3] = {//{delta_x , delta_y , s}
{{0,2,S} , {-1,0,R} , {1,0,R} , {0,-1,S}},//R
{{2,0,S} , {-1,0,S} , {0,-1,D} , {0,1,D}},//D
{{-2,0,D} , {1,0,D} , {0,-2,R} , {0,1,R}}//S
};
void bfs() {
memset(dis , -1 , sizeof(dis));
q.clear();
q.push(sx , sy , ss);
dis[sx][sy][ss] = 0;
while(!empty(q)) {
node p = q.front();
q.h++;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) {
int gx = p.x + f[p.s][i][0] , gy = p.y + f[p.s][i][1] , gs = f[p.s][i][2];
if(!check(gx , gy , gs)) continue;
if(dis[gx][gy][gs] != -1) continue;
if(gx == ex && gy == ey && gs == S) {
cout << dis[p.x][p.y][p.s] + 1 << endl;
return;
}
dis[gx][gy][gs] = dis[p.x][p.y][p.s] + 1;
q.push(gx , gy , gs);
}
}
puts("Impossible");
}
int main() {
while(1) {
cin >> n >> m;
if(n == 0 && m == 0)return 0;
bool readx = false;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j++) {
char c;
bool flag;
do {
c = getchar();
flag = true;
switch(c) {
case '.':
map[i][j] = 1;
break;
case 'E':
map[i][j] = 3;
break;
case '#':
map[i][j] = 2;
break;
case 'X':
if(readx) {
ss = (sx == i ? R : D);
}
else {
sx = i , sy = j;
ss = S;
readx = true;
}
map[i][j] = 1;
break;
case 'O':
map[i][j] = 1;
ex = i , ey = j;
break;
default :
flag = false;
break;
}
}while(!flag);
}
// cout << sx << '\t' << sy << endl;
bfs();
/*
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) {
for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j++) {
cout << map[i][j] <<' ';
}
cout << endl;
}*/
}
return 0;
}
D. 【例题4】荆轲刺秦王
待做(T_T)
E. 【例题5】电路维修
题目
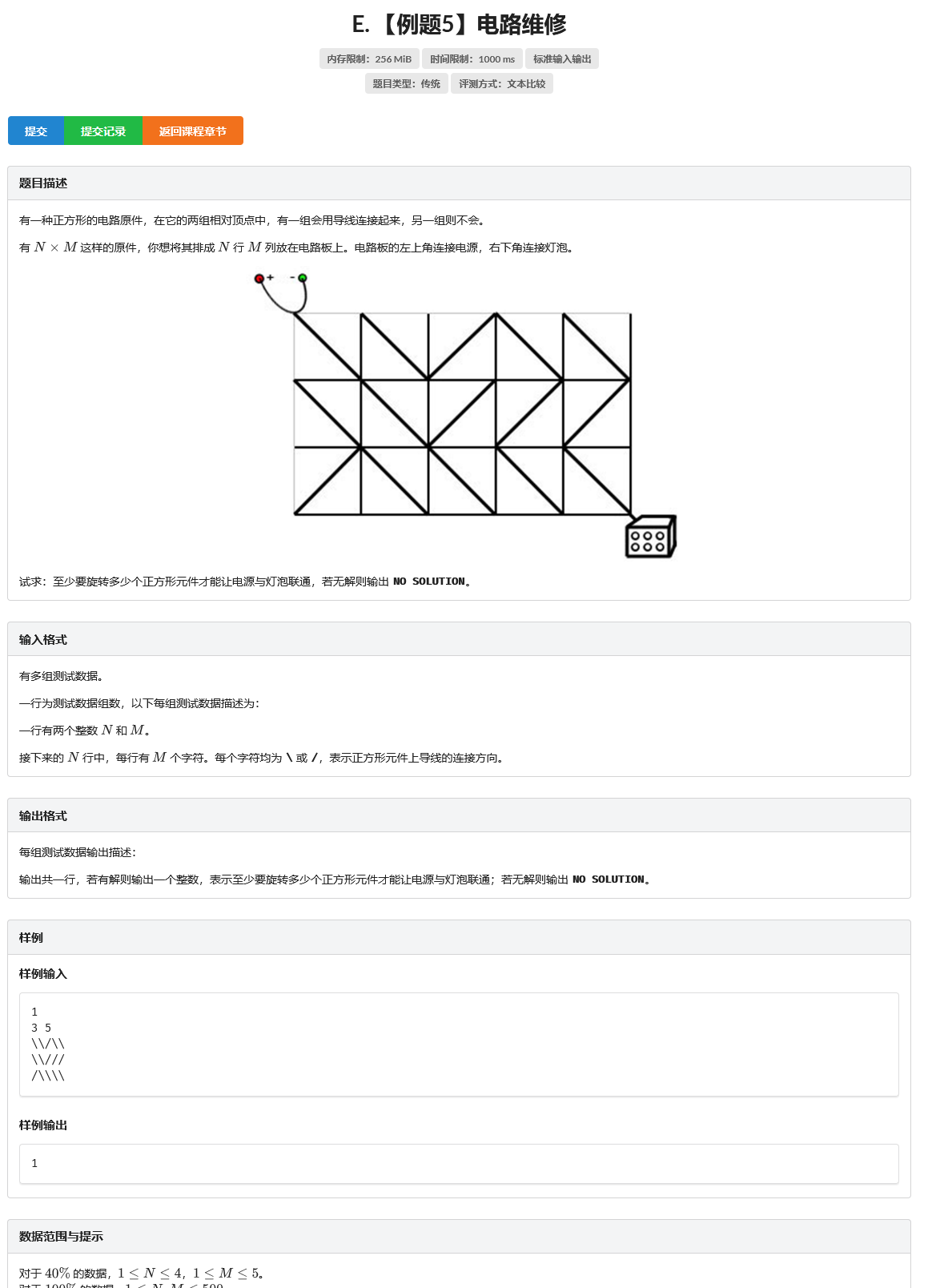
思路
对于每一个正方形元件,有四种情况:
连接电源的一端为:左上 右下 左下 右上,分别用1,2,3,4表示,向推箱子一样,先写出f数组:
const int stdf[10][4][3] = {//{delta_x , delta_y , st}
{{0}},
{{1,0,4} , {1,1,1} , {0,1,3} },
{{-1,0,3} , {-1,-1,2} , {0,-1,4} },
{{-1,1,3} , {-1,0,2} , {0,1,1} },
{{1,0,1} , {1,-1,4} , {0,-1,2} }
};
广搜:
注意下左上角的点状态一定要为“1”,右下角的状态也要为“1”
map[0][0] = 0;
q.push(mak(0,0,1,0));
while(!q.empty()) {
node t = q.top();
q.pop();
if(dis[t.x][t.y][t.st] != -1)continue;
// if(t.x == 1 && t.y == 1)
// cout << t.x << '\t' <<t.y << '\t' << t.st << '\t' << t.step << '\n';
if(t.x == n && t.y == m && t.st == 1) {
cout << t.step << endl;
return;
}
dis[t.x][t.y][t.st] = t.step;
int f[4][3];
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)
for(int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++)
f[i][j] = stdf[t.st][i][j];
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) {
int gx = f[i][0] + t.x , gy = f[i][1] + t.y , gt = f[i][2];
if(gx <= 0 || gy <= 0 || gx > n || gy > m) continue;
if(dis[gx][gy][gt] != -1) continue;
q.push(mak(gx , gy , gt , t.step + (map[gx][gy] == 0 ? (gt == 1 || gt == 2 ? 0 : 1) : (gt == 1 || gt == 2 ? 1 : 0) )) );
}
}
puts("NO SOLUTION");
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define nn 510
int n , m;
bool map[nn][nn];
int dis[nn][nn][5];
struct node {
int x , y , st;//st: 1:左上 2:右下 3: 左下 4: 右上(source)
int step;
bool operator < (const node &b) const {
return step > b.step;
}
};
node mak(int x , int y , int st , int step) {
node tmp;
tmp.x = x , tmp.y = y , tmp.st = st , tmp.step = step;
return tmp;
}
const int stdf[10][4][3] = {//{delta_x , delta_y , st}
{{0}},
{{1,0,4} , {1,1,1} , {0,1,3} },
{{-1,0,3} , {-1,-1,2} , {0,-1,4} },
{{-1,1,3} , {-1,0,2} , {0,1,1} },
{{1,0,1} , {1,-1,4} , {0,-1,2} }
};
void work () {
memset(map , 0 , sizeof(map));
memset(dis , -1 , sizeof(dis));
priority_queue <node> q;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
char c = getchar();
while (c != '\\' && c != '/') c = getchar();
map[i][j] = (c == '/' ? 1 : 0);
}
map[0][0] = 0;
q.push(mak(0,0,1,0));
while(!q.empty()) {
node t = q.top();
q.pop();
if(dis[t.x][t.y][t.st] != -1)continue;
// if(t.x == 1 && t.y == 1)
// cout << t.x << '\t' <<t.y << '\t' << t.st << '\t' << t.step << '\n';
if(t.x == n && t.y == m && t.st == 1) {
cout << t.step << endl;
return;
}
dis[t.x][t.y][t.st] = t.step;
int f[4][3];
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)
for(int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++)
f[i][j] = stdf[t.st][i][j];
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) {
int gx = f[i][0] + t.x , gy = f[i][1] + t.y , gt = f[i][2];
if(gx <= 0 || gy <= 0 || gx > n || gy > m) continue;
if(dis[gx][gy][gt] != -1) continue;
q.push(mak(gx , gy , gt , t.step + (map[gx][gy] == 0 ? (gt == 1 || gt == 2 ? 0 : 1) : (gt == 1 || gt == 2 ? 1 : 0) )) );
}
}
puts("NO SOLUTION");
}
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--) {
work();
}
return 0;
}
F. 【例题6】逃离噩梦
题目

思路
不难想但是有点难写的一道搜索题,简单点的做法就是直接从男生女生出发跑两遍BFS,算出距离,最后再枚举所有点得出答案,这里不详细展开
另外就是可以练下双向BFS,详细细节见下面代码
代码(双向BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define nn 1010
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1; char s = getchar();
while (s < '0' || s > '9') { if (s == '-') f = -f; s = getchar(); }
while (s >= '0' && s <= '9') { x = x * 10 + s - '0'; s = getchar(); }
return x * f;
}
struct point {
int x , y;
}man , gir , z1 , z2;
//队列
#define getp(p) (p.x = i , p.y = j)
#define empty_(q) (q.h == q.t)
#define pop_(q) (++q.h)
#define siz(q) (q.t - q.h)
#define head(q_) q_.q[q_.h]
struct que {
int h , t;
point q[nn * nn];
inline void push(int x , int y) {
q[t].x = x , q[t].y = y;
++t;
}
inline void push(point p) {
q[t++] = p;
}
inline void clear() {
memset(q , 0 , sizeof(q));
h = t = 0;
}
void print() {
for(int i = h ; i < t ; i++)
cout << q[i].x << ',' << q[i].y << '\t';
cout <<endl;
}
}q[3];
//==========队列END
int n , m;
int vis[nn][nn];//vis记录各个点到达距离,负数记录男生,正数记录女生
char map[nn][nn];//地图
//四向移动,两个数组是因为一开始对题意理解有误,可忽略
const int f[5][30][2] =
{
{{4 , 4}},
{{0,1} , {1,0} , {0 , -1} , {-1 , 0} },
{{0,1} , {1,0} , {0 , -1} , {-1 , 0} }
};
#define abs_(_) ((_) < 0 ? -(_) : (_))
inline int max_(int a , int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int bfs(int peo) {//搜索,peo==1表示男生,2表示女生
point p = head(q[peo]);
pop_(q[peo]);
int t = vis[p.x][p.y] + (peo == 1 ? -1 : 1);
if(t < 0) {//计算到达当前点时间
t = -t; t = t / 3 + (t % 3 == 0 ? 0 : 1);
}
if(abs_(p.x - z1.x) + abs_(p.y - z1.y) <= 2 * t || abs_(p.x - z2.x) + abs_(p.y - z2.y) <= 2 * t)//鬼已经扩展到当前点,舍去
return -1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 2 ; i++) {//BFS常规
for(int j = 0 ; j < f[0][0][i - 1] ; j++) {
int x = p.x + f[i][j][0] , y = p.y + f[i][j][1];
if(abs_(x - z1.x) + abs_(y - z1.y) <= 2 * t || abs_(x - z2.x) + abs_(y - z2.y) <= 2 * t)
continue;
if(map[x][y] == 'M' && peo == 2 || map[x][y] == 'G' &&peo == 1) return t;
if(x < 0 || x > n || y < 0 || y > m || map[x][y] != '.') continue;
if(vis[x][y] != 0) {
if((peo == 1 ? -1 : 1) * vis[x][y] >= 0) continue;
else {
int tmp = vis[p.x][p.y] + (peo == 1 ? -1 : 1);
return max_(t , vis[x][y] > 0 ? vis[x][y] : -(vis[x][y] % 3 == 0 ? vis[x][y] / 3 : vis[x][y] / 3 - 1));
}
}
vis[x][y] = vis[p.x][p.y] + (peo == 1 ? -1 : 1);
q[peo].push(x , y);
}
}
return -1;//暂时无法到达
}
int getans() {//搜索控制函数
q[1].push(man);
q[2].push(gir);
int tmp;
while(!empty_(q[1]) || !empty_(q[2])) {
int size = siz(q[1]);
//男生走3步
size = siz(q[1]);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= size ; i++)//这里需要保证男生女生两个队列中所有状态的时间同步,因此有这个循环
if(!empty_(q[1]))
if((tmp = bfs(1)) != -1) return tmp ;
size = siz(q[1]);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= size ; i++)//同理
if(!empty_(q[1]))
if((tmp = bfs(1)) != -1) return tmp ;
size = siz(q[1]);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= size ; i++)//
if(!empty_(q[1]))
if((tmp = bfs(1)) != -1) return tmp ;
//女生走一步
size = siz(q[2]);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= size ; i++)
if(!empty_(q[2]))
if((tmp = bfs(2)) != -1) return tmp ;
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int T = read();
while(T--) {
q[1].clear();//记得初始化
q[2].clear();
memset(vis , 0 , sizeof(vis));
memset(map , 0 , sizeof(map));
n = read() , m = read();
bool gz1 = false;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) //读入
for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j++){
char tmp = getchar();
while(tmp != 'X' && tmp != '.' && tmp != 'M' && tmp != 'G' && tmp != 'Z')
tmp = getchar();
map[i][j] = tmp;
if(tmp == 'M') getp(man);
if(tmp == 'G') getp(gir);
if(tmp == 'Z') {
if(gz1)
getp(z2);
else {
getp(z1);
gz1 = true;
}
}
}
cout << getans() << endl;
}
return 0;
}




