P6587 超超的序列 加强(详解)
题目
思路
作为一道蓝题,这题并不难想,就是细节有点多
真的挺好的一道题,把线段树和trie很好地融合到一起
以样例为例,建一棵如下的01trie,其中,红色数字就是输入进来的a,根到该数字的路径形成的数字就是该数字下标的二进制表示(从低位到高位)
例如,4这个数字:根到4的路径为0->0->1,4的下标为(100)2(这个表示二进制),即4
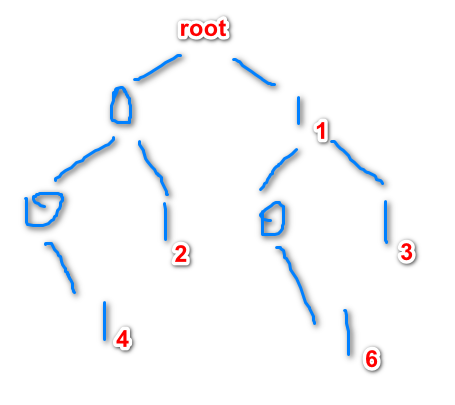
观察每一个询问,
2 x y:询问所有 ai 的和,其中 i≡y(mod 2^x)。
我们直接先令y%=2^x
以x=2,y=1为例,求的就是所有的a[i]的和,其中i满足二进制下最后x位等于y,即最后两位为01,还是看图

被圈起来的这棵子树的所有数字肯定都是要计算的(因为对应的i在二进制下必以01结尾),我们直接用自底向上的前缀和维护即可
特别地,"1"这个数字也要计算,这需要特判一下,这就是这道题麻烦的地方
修改操作同理
不觉得这很像线段树了吗?每一次的操作都是对一整个子树进行的,不同的是:有时候还会对根到这棵子树的路径上的某些点操作,但是这不影响大局
所以,我们考虑用懒标记优化,做法与线段树类似,这里不细讲,具体看代码
另外,值得注意的是:每一个红色的数字都是在树的"1"结点上的,也就是说,每一次修改或查询最多涉及到一个目标子树外的结点(按照上面x=2,y=1的例子,目标子树就是图中被圈起来的子树),这里仔细思考一下,不理解也没关系,这个不是很重要,我也是AC之后才意识到的,但是有助于加深对这道题的理解以及简化代码
最后,一定要开long long,否则0分(亲测)
代码(附对拍程序)
注意:使用对拍的时候需要将强制在线关掉,见下:
op = read();
op = (op + lastans) % 2 + 1;
变为:
op = read();
// op = (op + lastans) % 2 + 1;
另外,std程序可以找一个标程,但建议自己写暴力(毕竟比赛没有标程)
我的AC代码(tested.cpp)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define nn 1000010
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int read() {
int re = 0;
bool sig = false;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-')
sig = true;
c = getchar();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9')
re = (re << 1) + (re << 3) + c - '0',
c = getchar();
return sig ? -re : re;
}
int trie[nn][3] , num[nn];
ll a[nn] , tag[nn] , dat[nn];
int n , m;
void build() {
int top = 1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) {
int tmp = i;
int p = 1;
while(tmp != 0) {
if(trie[p][tmp & 1] == 0)
trie[p][tmp & 1] = ++top;
p = trie[p][tmp & 1];
tmp >>= 1;
}
a[p] = dat[p] = read();
num[p]++;
}
}
void dfs(int p) {
if(p == 0)return;
dfs(trie[p][0]);
dfs(trie[p][1]);
dat[p] += dat[trie[p][0]] + dat[trie[p][1]];
num[p] += num[trie[p][0]] + num[trie[p][1]];
tag[p] = 0;
}
inline void spread(int p) {//懒标记下传
if(p == 0) {
tag[p] = 0;
return;
}
if(tag[p] != 0) {
tag[trie[p][0]] += tag[p];
dat[trie[p][0]] += num[trie[p][0]] * tag[p];
if(a[trie[p][0]] != -1)
a[trie[p][0]] += tag[p];
tag[trie[p][1]] += tag[p];
dat[trie[p][1]] += num[trie[p][1]] * tag[p];
if(a[trie[p][1]] != -1)
a[trie[p][1]] += tag[p];
}
tag[p] = 0;
}
void change(int x , int y , ll v , int p) {//修改,使用递归的方式,有助于更新dat值
if(x == 0) {
if(a[p] != -1)
a[p] += v;
dat[p] += v * num[p];
tag[p] += v;
return;
}
spread(p);
change(x - 1 , y >> 1 , v , trie[p][y & 1]);
if(y == 0 && a[p] != -1) {
a[p] += v;
}
dat[p] = dat[trie[p][0]] + dat[trie[p][1]];
if(a[p] != -1)
dat[p] += a[p];
}
int query() {//查询
int x = read() , y = read();
ll res = 0;
int p = 1;
y %= (1 << x);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= x ; i++) {
spread(p);
if(y == 0)
res += dat[p] - dat[trie[p][0]] - dat[trie[p][1]];
p = trie[p][y & 1];
y >>= 1;
}
res += dat[p];
printf("%lld\n" , res);
return res;
}
int main() {
memset(a , -1 , sizeof(a));//值为-1代表该结点没有数字
n = read(); m = read();
build();
dfs(1);
ll lastans = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i++) {
int op;
op = read();
op = (op + lastans) % 2 + 1;
if(op == 1) {
int x , y , v;
x = read(); y = read(); v = read();
change(x , y % (1 << x) , (ll)v , 1);
}
else
lastans = query();
}
return 0;
}
随机数据生成(random.cpp)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int random(int r , int l = 1) {
if(l == r)return l;
return (long long)rand() * rand() % (r - l) + l;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned) time(0));
int n = 100 , m = 100;
printf("%d %d\n" , n , m);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
printf("%d " , random(20));
putchar('\n');
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i++) {
int op = rand() % 2 + 1;
int tmp = log(n) / log(2);
int x = random(tmp * 3 / 2 , tmp / 2) , y = random(1024) , v = random(1000);
printf("%d " , op);
if(op == 1)
printf("%d %d %d\n" , x , y , v);
else
printf("%d %d\n" , x , y);
}
return 0;
}
对拍控制(compare.cpp)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
while(true) {
system("random.exe > input.txt");
puts("random");
system("tested.exe < input.txt > output1.txt");
puts("tested");
system("std.exe < input.txt > output2.txt");
puts("std");
if(system("fc output1.txt output2.txt")) {
cout << "WA";
system("start input.txt");
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}




