DRF之请求执行流程和APIView源码分析
【一】路由入口
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from book import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
# 原来的路由写法
# path('test_http/', views.TestHttpResponse),
# 现在的路由写法
path('test/', views.TestView.as_view()),
path('test_http/', views.TestHttpResponse.as_view()),
]
- 在视图类中我们继承了
APIView - 在路由中我们由原来的继承
View的视图函数TestHttpResponse变成了 继承APIView的视图函数TestView,并使用了写的路由写法,即TestView.as_view() - 因此我们的入口就是在
as_view()方法上
【二】视图分析
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class TestView(APIView):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
print(request)
print(type(request))
print(dir(request))
return Response('ok')
【三】APIView源码分析
【1】执行流程入口
- 当请求过来时 会触发
path('test/', views.TestView.as_view())
-
执行 视图函数
TestView的as_view方法 -
那我们就从
as_view进去
【2】路由中的 as_view()
class APIView(View):
# The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view.
# 设置用于渲染响应的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES。
renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
# 设置用于解析请求内容的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES。
parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
# 设置用于认证用户身份的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES。
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
# throttle_classes:设置用于限制API访问频率的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES。
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
# 设置用于确定用户权限的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES。
permission_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES
# 设置用于协商内容的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS。
content_negotiation_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS
# 设置用于处理元数据的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS。
metadata_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS
# 设置用于API版本控制的类,默认使用api_settings.DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS。
versioning_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS
# Allow dependency injection of other settings to make testing easier.
# 允许依赖注入其他设置以方便测试,允许在配置文件中自定义配置并使用自定义配置
settings = api_settings
# 引用了DefaultSchema,表示默认的API模式类
schema = DefaultSchema()
# 包装成静态方法
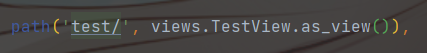
@classmethod
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs):
"""
# 将原始类存储在视图函数中
Store the original class on the view function.
# 这允许我们在执行URL时发现有关视图的信息反向查找
This allows us to discover information about the view when we do URL
reverse lookups. Used for breadcrumb generation.
"""
# 判断获取到的属性值是否为models.query.QuerySet类型
# cls 视图类 去视图类中反射,是否存在 queryset 对象
# getattr(cls, 'queryset', None)
if isinstance(getattr(cls, 'queryset', None), models.query.QuerySet):
# 作用是在直接访问.queryset属性时触发一个运行时错误
def force_evaluation():
# 不要直接评估.queryset属性,因为结果会被缓存并在请求之间重用
# 应该使用.all()方法或调用.get_queryset()方法来获取数据集。
raise RuntimeError(
'Do not evaluate the `.queryset` attribute directly, '
'as the result will be cached and reused between requests. '
'Use `.all()` or call `.get_queryset()` instead.'
)
# 将force_evaluation()函数赋值给cls.queryset._fetch_all
# 当外部代码直接访问.queryset属性时,会抛出RuntimeError异常
# 提醒开发者按照建议的方式来获取数据集。
cls.queryset._fetch_all = force_evaluation
# 调用父类的 as_view 方法
view = super().as_view(**initkwargs)
# 将当前视图类 添加 给 view 方法
view.cls = cls
# 将所有传入的参数 添加给 view 方法
view.initkwargs = initkwargs
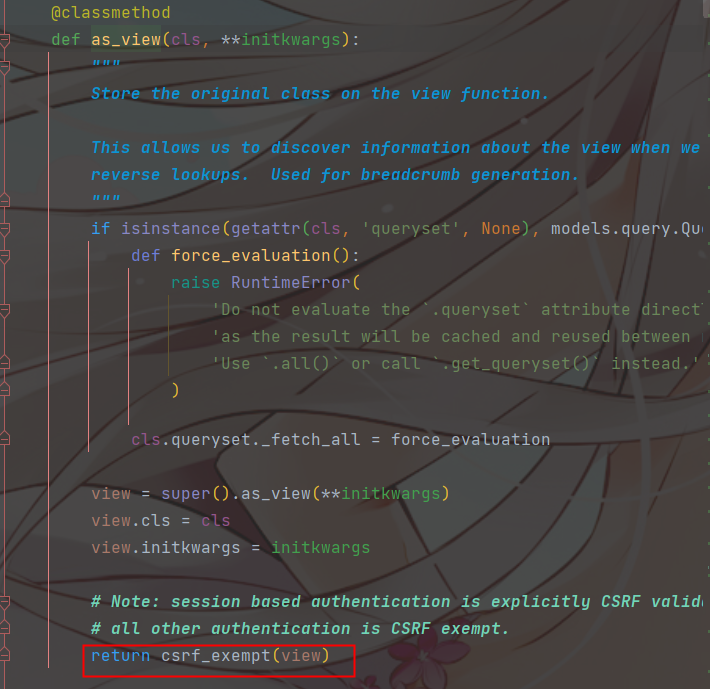
# 基于会话的身份验证是显式CSRF验证的
# Note: session based authentication is explicitly CSRF validated,
# 所有其他认证都是免除CSRF的
# all other authentication is CSRF exempt.
# 用 csrf_exempt 包装了 view 方法,去除了 csrf 认证
# 这里返回出去的去除了 csrf 认证的 view 对象就是我们上面的as_view
# 而我们在上面执行了 as_view() 方法其实就是 这个 view() 方法 对到相应的视图函数就是 get(request,*args,**kwargs)
return csrf_exempt(view)
【3】父类 View 的 as_view 方法
class View:
"""
# 为所有视图创建简单的父类。仅实现按方法调度和简单的健全性检查。
Intentionally simple parent class for all views. Only implements
dispatch-by-method and simple sanity checking.
"""
# 定义允许请求的请求方式
http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace']
# 定义初始化方法
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
"""
#在URLconf中调用;可以包含有用的额外关键字参数和其他内容。
Constructor. Called in the URLconf; can contain helpful extra
keyword arguments, and other things.
"""
# Go through keyword arguments, and either save their values to our
# instance, or raise an error.
# 遍历传入的所有参数
for key, value in kwargs.items():
# 将遍历得到的键和值,全部添加到 self 对象中
setattr(self, key, value)
# 包装成静态方法
@classonlymethod
# 允许传入视图类和其他参数
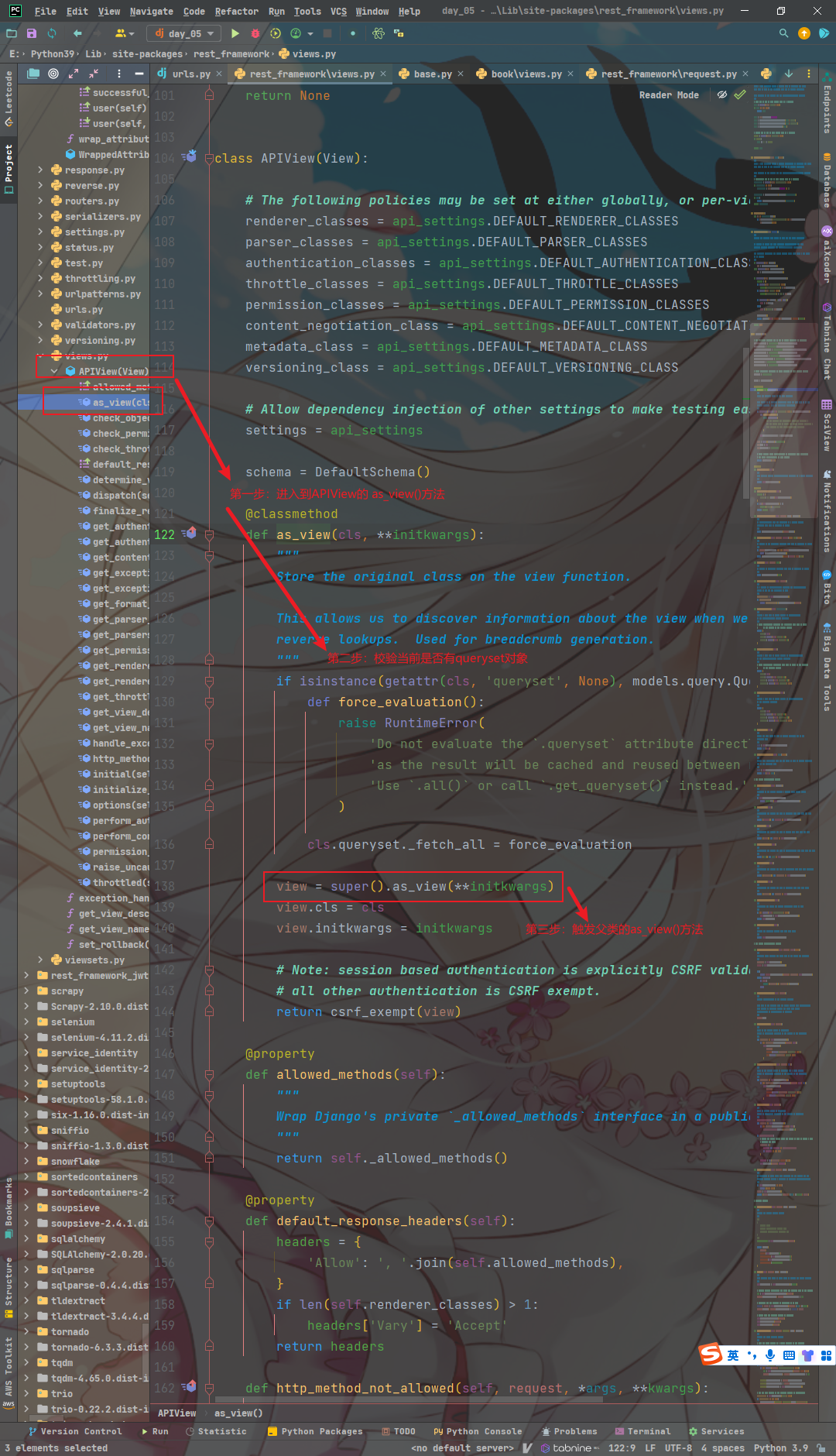
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs):
# 请求-响应过程的主要入口点
"""Main entry point for a request-response process."""
# 遍历 initkwargs 传入的参数的键
for key in initkwargs:
# 判断当前请求方式是否在上述请求方式列表中存在
if key in cls.http_method_names:
# 抛出异常
# 方法名称 不被接受为关键字参数
raise TypeError(
'The method name %s is not accepted as a keyword argument '
'to %s().' % (key, cls.__name__)
)
# 判断如果当前视图类中没有写当前请求方式
if not hasattr(cls, key):
# 抛出异常
# 只能接收存在的请求当时
raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r. as_view "
"only accepts arguments that are already "
"attributes of the class." % (cls.__name__, key))
# 闭包函数
def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
# 实例化得到对象,并将参数传入
self = cls(**initkwargs)
# 调用启动方法,初识化公共类属性
self.setup(request, *args, **kwargs)
# 判断当前对象是否存在 request 属性
if not hasattr(self, 'request'):
# 不存在则抛出异常
raise AttributeError(
# 不存在 request 属性,必须提供
"%s instance has no 'request' attribute. Did you override "
"setup() and forget to call super()?" % cls.__name__
)
# 返回 dispatch 方法,并将所有参数传入
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
# 将 当前类 添加给 view 对象
view.view_class = cls
# 将所有参数 添加给 view 对象
view.view_initkwargs = initkwargs
# take name and docstring from class
# 从类中获取名称和文档字符串
update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=())
# and possible attributes set by decorators
# like csrf_exempt from dispatch
# 是否存在装饰器,例如 csrf认证
update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=())
# 将 view 对象返回
return view
setup
def setup(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 初始化所有视图方法共享的属性
"""Initialize attributes shared by all view methods."""
# 判断当前类对象中存在get方法,并且没有 head 方法
if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'):
# 将自身的 head 方法替换成 get 方法
self.head = self.get
# 将传入的 request 赋值给当前对象
self.request = request
# 将传入的 位置参数 赋值给当前对象
self.args = args
# 将传入的 关键字参数 赋值给当前对象
self.kwargs = kwargs
【4】APIView 的 dispatch 方法
- 通过上面分析,我们发现在APIView中调用了父类的 as_view()方法
- 在父类 View 中,又调用了 dispatch 方法
- 因为我们是又 APIView 进到的 View ,所以我们当前的 self 其实是 APIView
- 那 self.dispatch() ,理所应当的就要从自己找,就是在下面所示的 APIView 中的 dispatch
- 源码解析
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
# 大致意识是和 APIView相似但是添加了新的功能
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
# 初识化参数,将 位置参数 添加给 self 对象
self.args = args
# 初识化参数,将 关键字参数 添加给 self 对象
self.kwargs = kwargs
# 初始化传入的请求对象,将其封装为符合Django规范的请求对象
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
# 保存了初始化后的请求对象
self.request = request
# 保存了默认的响应头部信息
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate?
try:
# 进行的初始化操作,例如验证用户身份等
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
# Get the appropriate handler method
# 获取适当的处理程序方法
# 将 请求方式小写 ,并判断当前请求方式是否在允许的请求方式类表内
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
# handler : 当前的请求当时,获取到当前请求方式
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
# 如果请求方法不存在,则会调用self.http_method_not_allowed方法,返回不允许的HTTP方法的响应
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
# 调用选择的处理方法,将请求对象和参数传递给它,并获取返回的响应对象
response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
except Exception as exc:
# 如果在处理请求过程中发生任何异常,异常处理方法可以根据实际需求进行自定义,可以返回适当的错误响应。
response = self.handle_exception(exc)
# 对响应进行最后的处理,例如添加额外的响应头部信息、修改响应内容等。
self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
# 返回处理好的最终响应对象
return self.response
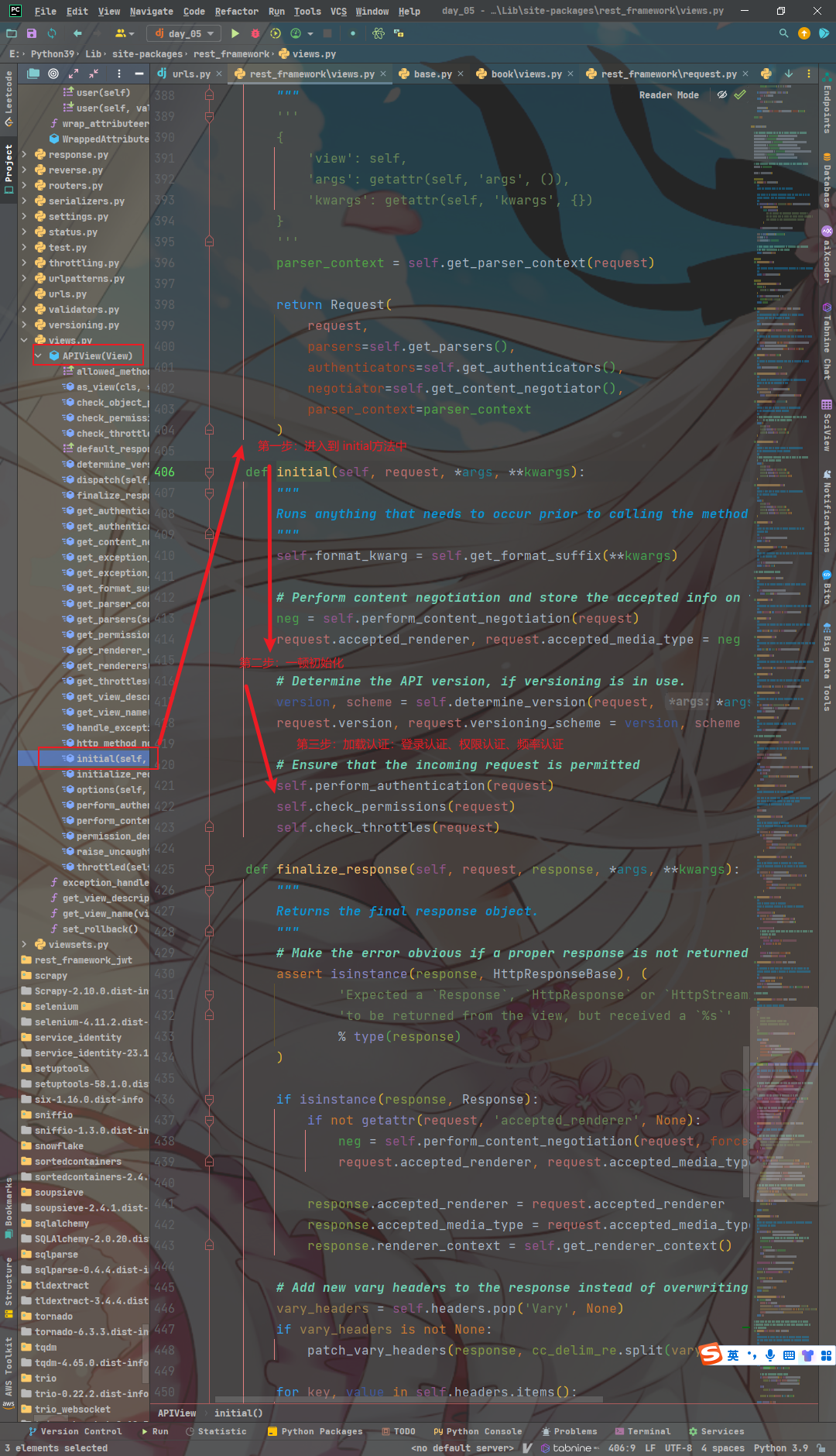
initialize_request
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
# 返回一个实例化的 request 对象
Returns the initial request object.
"""
# 拿到解析后的数据字典
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request)
# 返回实例化后的Request对象
return Request(
# 当前 request 对象
request,
# 解析器
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
# 认证用户
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
# 解析后的数据
parser_context=parser_context
)
get_parser_context
def get_parser_context(self, http_request):
"""
# 返回一个被解析器解析过得数据字典
Returns a dict that is passed through to Parser.parse(),
as the `parser_context` keyword argument.
"""
# Note: Additionally `request` and `encoding` will also be added
# to the context by the Request object.
# 返回了 类 对象本身
return {
'view': self,
# 将 位置参数 返回,无则为空
'args': getattr(self, 'args', ()),
# 将 关键字参数 返回,无则为空
'kwargs': getattr(self, 'kwargs', {})
}
initial
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
# 在调用方法处理程序之前运行任何需要发生的事情。
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
# 通过get_format_suffix方法获取到的格式后缀保存在实例变量self.format_kwarg中
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
# Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
# 调用了perform_content_negotiation方法,并将请求对象request作为参数传递进去
# 执行内容协商,并返回一个包含可接受的渲染器和媒体类型的元组
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
# 将内容协商结果中的渲染器和媒体类型保存在请求对象request的accepted_renderer和accepted_media_type属性中
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
# Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
# 调用了determine_version方法,并将请求对象request以及其他参数传递进去。
# 该方法用于确定API的版本和版本控制方案,并返回一个包含版本和版本控制方案的元组。
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
# 将确定的API版本和版本控制方案保存在请求对象request的version和versioning_scheme属性中
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# 确保允许传入请求
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
# 登录认证:调用了perform_authentication方法,并将请求对象request作为参数传递进去。
# 该方法用于执行身份验证,确保传入的请求是合法的。
self.perform_authentication(request)
# 权限认证:调用了check_permissions方法,并将请求对象request作为参数传递进去。
# 该方法用于检查权限,确保用户有权访问该资源
self.check_permissions(request)
# 频率认证:调用了check_throttles方法,并将请求对象request作为参数传递进去。
# 该方法用于检查限流,确保请求没有超过预定的频率限制。
self.check_throttles(request)
get_format_suffix
def get_format_suffix(self, **kwargs):
"""
# 确定请求是否包含“.json”样式的格式后缀
Determine if the request includes a '.json' style format suffix
"""
if self.settings.FORMAT_SUFFIX_KWARG:
return kwargs.get(self.settings.FORMAT_SUFFIX_KWARG)
【四】总结
【1】请求过来的完整执行流程
- 当请求过来时,触发路由中的
TestView.as_view()方法- 也就是
TestView.as_view()(request)
- 也就是
- 在
APIView中触发了self.as_view()- 但是
APIView没有as_view() - 于是调用了父类中的
as_view()方法
- 但是
- 在父类的
as_view()方法又触发了dispatch方法- 于是又回到了
APIView的dispatch方法
- 于是又回到了
- 在
APIView的dispatch方法中对数据进行处理
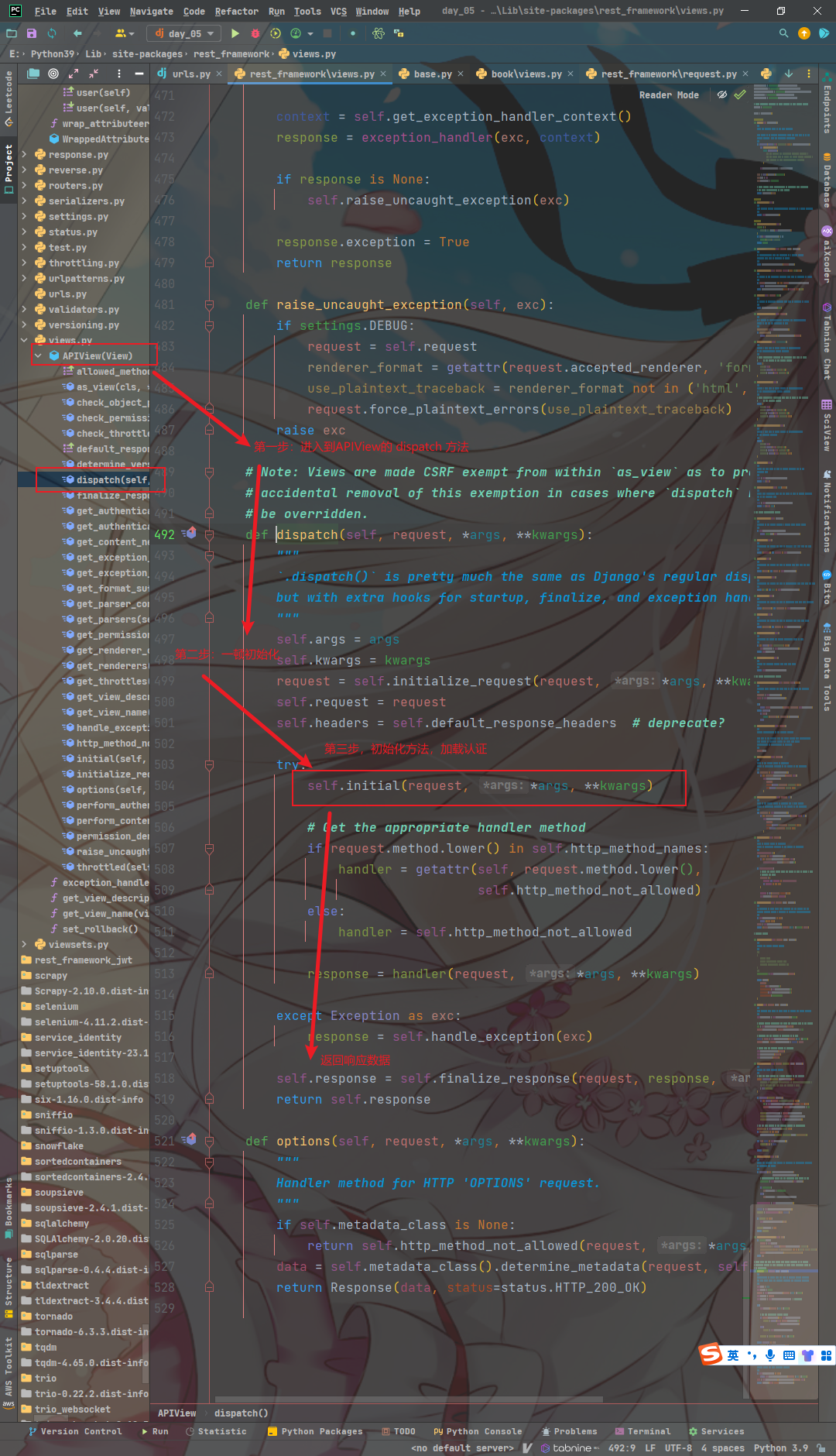
- 在
dispatch方法中有一个initial方法,这个方法完成了三大认证- 即 登陆、权限、频率认证
- 三大认证完成后,执行 handler
- 先到视图类中映射视图函数,然后执行视图函数,获得响应数据,并返回

-
所有数据都处理完后接着向下走
-
对返回的 view 对象去除的 csrf 认证
【2】APIView相较View的大变化
- 以后只要继承APIView的所有视图类的方法,都没有csrf的校验了
- 以后只要继承APIView的所有视图类的方法 中的request是新的request了
- 在执行视图类的方法之前,执行了三大认证(认证,权限,频率)
- 期间除了各种错误,都会被异常捕获,统一处理
本文来自博客园,作者:Chimengmeng,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/dream-ze/p/17700731.html


