【11.0】Vue之状态管理器(Vuex)的使用
vuex
【一】介绍
vuex :状态管理器---》存数据(变量)的地方,所有组件都可以操作
在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信
- Vuex是一个用于集中式状态管理的Vue插件。
- 在Vue应用中,组件间共享的数据通常需要通过props逐级传递,但对于较深层级的组件或跨组件的通信,这种方式可能会导致代码冗余和不易维护。
- 而使用Vuex,我们可以将共享的状态集中存储在一个地方,并允许任何组件以可预测的方式进行读取和修改。
【二】何时使用
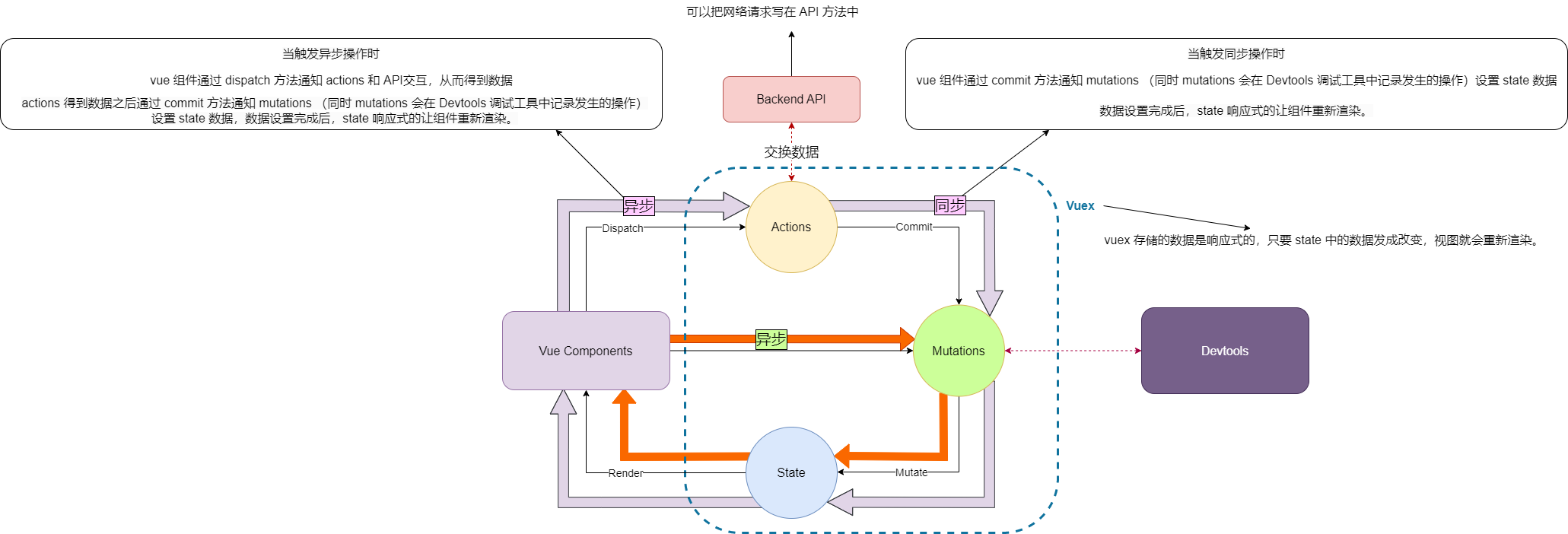
【1】Vuex图解
-
vuex 对象中通过 state 来存储状态
- 除了 state 以外还有用来操作 state 中数据的方法集
- 以及当我们需要对 state 中的数据需要加工的方法集等等成员。
-
成员列表:
-
state:存放状态(全局状态数据) 必填项
-
mutations:对于 state 成员进行同步修改操作(也可以支持异步操作)
-
getters:获取 state 中的数据,类似于组件中的计算属性
-
actions:进行异步操作,异步得到结果后通知 mutation 修改 state 成员
-
modules:模块化状态管理,多状态文件管理时使用,开发项目时多为多模块项目
-
-
在多模块 vuex 中会有配置namespaced:true开启命名空间。
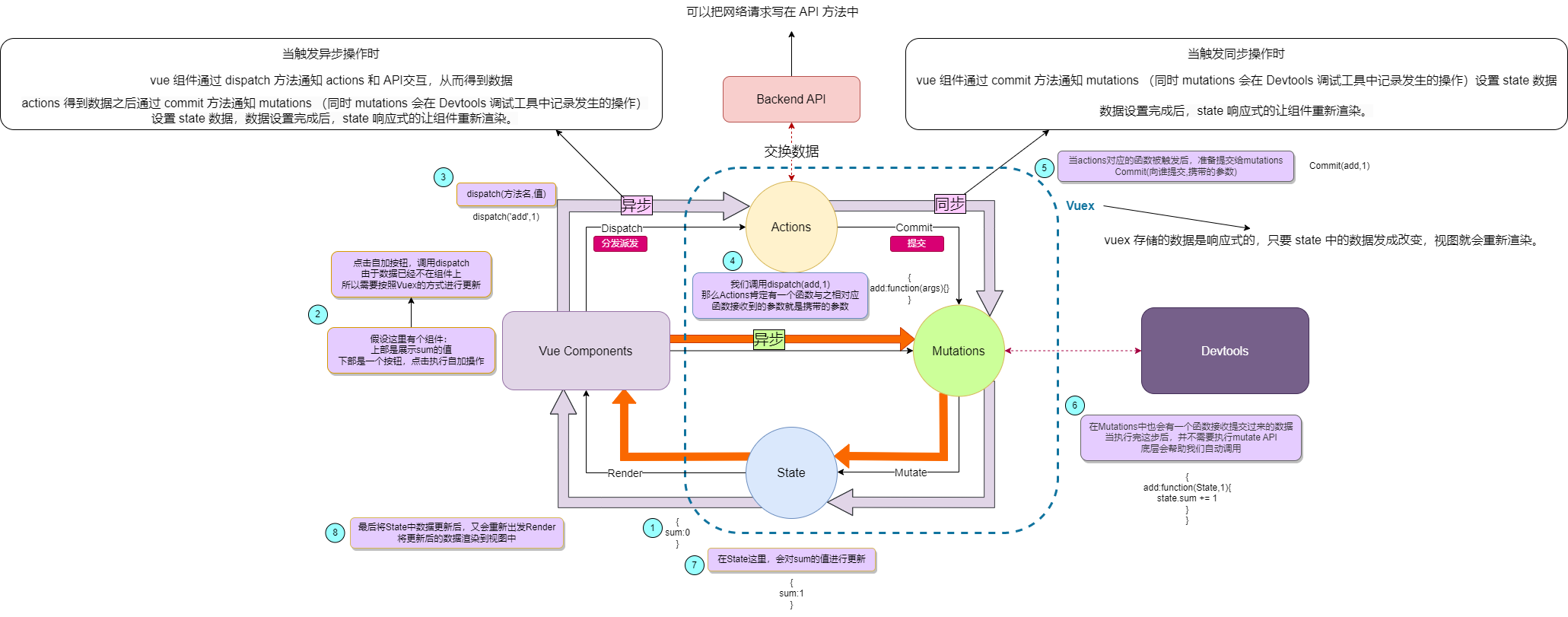
【2】Vuex执行流程
-
vue 组件会从 vuex 的 state 中获取数据,当组件修改数据时,会经过以下流程:
- 当触发同步操作时:
- vue 组件通过 commit 方法通知 mutations (同时 mutations 会在 Devtools 调试工具中记录发生的操作)设置 state 数据,数据设置完成后,state 响应式的让组件重新渲染。
注意:vuex 存储的数据是响应式的,只要 state 中的数据发成改变,视图就会重新渲染。
- 当触发同步操作时:
-
当触发异步操作时:
-
vue 组件通过 dispatch 方法通知 actions 和 API交互,从而得到数据,actions 得到数据之后通过 commit 方法通知 mutations (同时 mutations 会在 Devtools 调试工具中记录发生的操作)设置 state 数据,数据设置完成后,state 响应式的让组件重新渲染。
-
这里可以看出,在 vuex 中,我们可以把网络请求写在 API 方法中。
-
- 扩展:
- 早期 mutations 只允许同步操作,如果要进行异步操作需要按照上述流程
- 原因是早期的 Devtools 监听不到异步操作。
- 但是现在调试工具经过升级后,已经能够监听到异步操作了,
- 也就是说现在的 mutations 也支持异步操作
- 但是在方文档中还是只允许同步操作。
【三】基本使用(操作state的数据)
【顾客-服务员-厨师-上菜】
- 通过 dispatch 触发 actions 再调用 mutations 中的函数
rc\views\HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>Vuex的使用</h1>
<h3>使用Vuex中的store内的 number</h3>
购物车商品数量:{{ this.$store.state.number }}
<hr>
<button @click="clickAdd">点我购物车 +1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
clickAdd() {
// (1) 直接操作
// this.$store.state.number += 1
// (2) 经过Vuex,通过 dispatch 触发 actions
// 'add' : 必须是 actions 中存在的函数
this.$store.dispatch('add', 1)
}
}
}
</script>
src\store\index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
number: 10
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
// 至少要有参数 state : 上面 的 state 对象
Add(state, args) {
state.number += args
}
},
actions: {
// 至少要有参数 context : 上下文对象,触发 mutations中的函数执行,或者直接修改 state 中的数据
// args : 接收到的传入的参数
add(context, args) {
// 使用 Commit 触发 mutations 中的函数
context.commit('Add', args) // 会触发 mutations 中的Add的执行
}
},
modules: {}
})
【顾客-厨师-上菜】
- 直接操作 mutations 执行相应的函数
rc\views\HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>Vuex的使用</h1>
<h3>使用Vuex中的store内的 number</h3>
购物车商品数量:{{ this.$store.state.number }}
<hr>
<button @click="clickAdd">点我购物车 +1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
clickAdd() {
// (1) 直接操作
// this.$store.state.number += 1
// (2) 经过Vuex,通过 dispatch 触发 actions
// 'add' : 必须是 actions 中存在的函数
// this.$store.dispatch('add', 1)
// (3) 直接操作 mutations
this.$store.commit('Add', 1)
}
}
}
</script>
src\store\index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
number: 10
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
// 至少要有参数 state : 上面 的 state 对象
Add(state, args) {
state.number += args
}
},
actions: {
// 至少要有参数 context : 上下文对象,触发 mutations中的函数执行,或者直接修改 state 中的数据
// args : 接收到的传入的参数
add(context, args) {
// 使用 Commit 触发 mutations 中的函数
context.commit('Add', args) // 会触发 mutations 中的Add的执行
}
},
modules: {}
})
【四】基本使用(组件间通信)
src\components\ShoppingCar.vue- 局部组件
<script setup>
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h4>购物车商品数量</h4>
{{ this.$store.state.goods }}
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
src\views\HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>Vuex的使用</h1>
<h3>使用Vuex中的store内的 number</h3>
购物车商品数量:{{ this.$store.state.number }}
<hr>
<button @click="clickAdd">点我购物车 +1</button>
<h3>使用Vuex组件间通信</h3>
<ul>
<li>智力
<button @click="add('智力')">+</button>
</li>
<li>力量
<button @click="add('力量')">+</button>
</li>
</ul>
<br>
<ShoppingCar></ShoppingCar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ShoppingCar from "@/components/ShoppingCar.vue";
// @ is an alias to /src
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {
ShoppingCar,
},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
clickAdd() {
// (1) 直接操作
// this.$store.state.number += 1
// (2) 经过Vuex,通过 dispatch 触发 actions
// 'add' : 必须是 actions 中存在的函数
// this.$store.dispatch('add', 1)
// (3) 直接操作 mutations
this.$store.commit('Add', 1)
},
add(args) {
// 直接操作 mutations
// this.$store.state.goods.push(args)
// 经过Vuex,通过 dispatch 触发 actions
this.$store.dispatch('AddGoods', args)
}
}
}
</script>
src\store\index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
number: 10,
goods: []
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
// 至少要有参数 state : 上面 的 state 对象
Add(state, args) {
state.number += args
},
AddGoods(state, args) {
state.goods.push(args)
}
},
actions: {
// 至少要有参数 context : 上下文对象,触发 mutations中的函数执行,或者直接修改 state 中的数据
// args : 接收到的传入的参数
add(context, args) {
// 使用 Commit 触发 mutations 中的函数
context.commit('Add', args) // 会触发 mutations 中的Add的执行
},
AddGoods(context, args) {
// 可以在这里发送 Ajax请求,检查内存是否足够
context.commit('AddGoods', args) // 会触发 mutations 中的Add的执行
// 假设库存不够,不能将数据进行更改
// alert('库存不足')
// return
}
},
modules: {}
})
【】Vuex案例
- 假设我们有一个购物车应用,有以下几个组件:
ProductList(商品列表)Cart(购物车)CartItem(购物车中的商品项)。
- 首先
- 在安装了Vue和Vuex之后
- 在Vue根实例中调用
Vue.use(Vuex)以启用Vuex插件。
- 在Vue根实例中调用
- 在安装了Vue和Vuex之后
- 然后
- 我们创建一个
store对象来存储我们的共享状态。 - 在该对象中,我们定义了一个
state属性来存储购物车中的商品列表,以及一些操作(如添加商品到购物车、从购物车删除商品等)来修改该状态。
- 我们创建一个
// main.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import App from './App';
// 导入其他模块的store,如果有
import store from './store';
Vue.use(Vuex);
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store, // 使用store
render: h => h(App)
});
// store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
cartItems: [] // 购物车商品列表
},
mutations: {
addToCart(state, product) {
state.cartItems.push(product);
},
removeFromCart(state, product) {
const index = state.cartItems.indexOf(product);
if (index !== -1) {
state.cartItems.splice(index, 1);
}
}
},
actions: {
addToCart({ commit }, product) {
commit('addToCart', product);
},
removeFromCart({ commit }, product) {
commit('removeFromCart', product);
}
},
getters: {
cartItemCount(state) {
return state.cartItems.length;
}
}
});
export default store;
- 在上述代码中
- 我们定义了一个名为
cartItems的状态,在mutations中定义了两个操作来修改该状态:addToCart用于添加商品到购物车,removeFromCart用于从购物车中删除商品。actions则是包装了对应的mutations操作,可以进行异步操作或触发其他mutations操作。getters用于计算衍生的状态,例如计算购物车中商品的数量。
- 我们定义了一个名为
- 现在
- 我们可以在任何组件中使用
this.$store来访问store对象,以读取或修改状态。 - 例如,在
ProductList组件中点击"Add to Cart"按钮时,可以通过调用this.$store.dispatch('addToCart', product)来将商品添加到购物车。
- 我们可以在任何组件中使用
- 在
Cart组件中- 可以使用
this.$store.state.cartItems来获取购物车商品列表,并在CartItem组件中通过遍历该列表渲染每个商品项。
- 可以使用
- 这样,我们就实现了组件间共享状态的集中管理,并且避免了繁琐的props传递和事件监听。
本文来自博客园,作者:Chimengmeng,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/dream-ze/p/17610526.html


