ribbon 详解
ribbon 详解
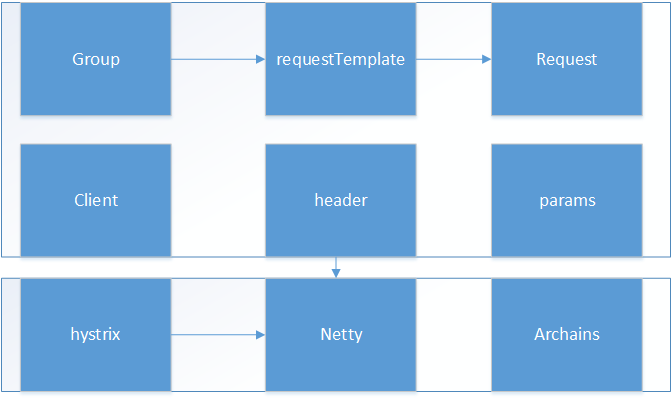
1. 顶层架构
2. 简单的示例:使用ResourceTemplate方式
@Test
public void testGroup(){
HttpResourceGroup httpResourceGroup = Ribbon.createHttpResourceGroup("test",
ClientOptions.create().withMaxAutoRetries(3).
withConfigurationBasedServerList("localhost:8081,localhost:8080"));
HttpRequestTemplate<ByteBuf> recommendationsByUserIdTemplate = httpResourceGroup.newTemplateBuilder("recommendationsByUserId", ByteBuf.class)
.withMethod("GET")
.withUriTemplate("/aa/index")
.withHeader("X-Auth-Token", "abc")
//.withFallbackProvider(new RecommendationServiceFallbackHandler())
//.withResponseValidator(new RecommendationServiceResponseValidator())
.build();
RibbonRequest<ByteBuf> request = recommendationsByUserIdTemplate.requestBuilder()
.withRequestProperty("userId", "test")
.build();
ByteBuf buf = request.execute();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.capacity()];
buf.readBytes(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
3.实现:
3.1 关键对象
public interface RibbonRequest<T> {
/**
* Blocking API that returns a single (or last element if there is a sequence of objects from the execution) element
*/
public T execute();
/**
* Non blocking API that returns a {@link Future}, where its {@link Future#get()} method is blocking and returns a
* single (or last element if there is a sequence of objects from the execution) element
*/
public Future<T> queue();
/**
* Non blocking API that returns an {@link Observable} while the execution is started asynchronously.
* Subscribing to the returned {@link Observable} is guaranteed to get the complete sequence from
* the beginning, which might be replayed by the framework. Use this API for "fire and forget".
*/
public Observable<T> observe();
/**
* Non blocking API that returns an Observable. The execution is not started until the returned Observable is subscribed to.
*/
public Observable<T> toObservable();
/**
* Create a decorated {@link RequestWithMetaData} where you can call its similar blocking or non blocking
* APIs to get {@link RibbonResponse}, which in turn contains returned object(s) and
* some meta data from Hystrix execution.
*/
public RequestWithMetaData<T> withMetadata();
}
明显,最终生成的关键对象RibbonRequest,使用的时观察者模式,底层实现肯定会使用RxJava或者Hystrix。
3.2 关键实现:HystrixObservableCommandChain
HystrixObservableCommandChain<T> createHystrixCommandChain() {
List<HystrixObservableCommand<T>> commands = new ArrayList<HystrixObservableCommand<T>>(2);
if (cacheProvider != null) {
commands.add(new CacheObservableCommand<T>(cacheProvider.getCacheProvider(), cacheProvider.getKey(), cacheHystrixCacheKey,
requestProperties, template.cacheHystrixProperties()));
}
commands.add(new HttpResourceObservableCommand<T>(client, httpRequest, hystrixCacheKey, requestProperties, template.fallbackHandler(),
template.responseValidator(), template.getClassType(), template.hystrixProperties()));
return new HystrixObservableCommandChain<T>(commands);
}
在HystrixObservableCommandChain执行toObservable的时候,会依次便利集合中所有的HystrixObservableCommand,知道其toObservable不为null。
所以,如果cacheProvider不为null会调用CacheObservableCommand的toObservable,如果cacheProvider为null,则直接调用HttpResourceObservableCommand的toObservable.
3.3 http请求:
Observable<HttpClientResponse<ByteBuf>> httpResponseObservable = httpClient.submit(httpRequest);
Observable<T> o =
(server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
@Override
// Called for each server being selected
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
context.setServer(server);
final ServerStats stats = loadBalancerContext.getServerStats(server);
// Called for each attempt and retry
Observable<T> o = Observable
.just(server)
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
...
});
if (maxRetrysSame > 0)
o = o.retry(retryPolicy(maxRetrysSame, true));
return o;
}
}
if (maxRetrysSame > 0)
o = o.retry(retryPolicy(maxRetrysSame, true));
return o;
会调用统一服务器n次,后调用下一个服务器m次(n,m为设定的最大调用次数)。
4.简单示例:使用注解方式
public interface AAIndex {
@Http( method = Http.HttpMethod.GET,
uri = "http://localhost:8080/aa/index")
RibbonRequest<ByteBuf> index();
}
@Test
public void testRibbonAnnotation(){
AAIndex aaIndex = Ribbon.from(AAIndex.class);
ByteBuf buf = aaIndex.index().execute();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.capacity()];
buf.readBytes(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
5.实现:
5.1 动态代理:
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
new Class[]{clientInterface, ProxyLifeCycle.class},
new RibbonDynamicProxy<T>(clientInterface, resourceGroupFactory, configFactory, transportFactory, processors)
);
使用JDK自带的代理类实现,代理了client接口,和ProxyLifeCycle,其实现具体类为RibbonDynamicProxy。
5.2 支持的注解:
static void registerAnnotationProcessors(AnnotationProcessorsProvider processors) {
processors.register(new HttpAnnotationProcessor());
processors.register(new HystrixAnnotationProcessor());
processors.register(new CacheProviderAnnotationProcessor());
processors.register(new ClientPropertiesProcessor());
}
最终的实现跟非注解方式的实现是一致的。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <O> RibbonRequest<O> executeFromTemplate(Object[] args) {
HttpRequestBuilder<?> requestBuilder = httpRequestTemplateBuilder.build().requestBuilder();
withParameters(requestBuilder, args);
withContent(requestBuilder, args);
return (RibbonRequest<O>) requestBuilder.build();
}
没有智能的代码,源码面前了无秘密

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号