python 控制语句
pyhton 控制语句
程序在一般情况下是按顺序执行的,编程语言提供了各种控制结构,允许复杂的执行路径。循环语句允许我们执行一个语句或语句多次
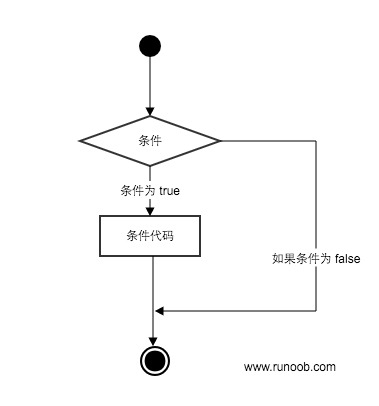
if 语句
Python条件语句是通过一条或多条语句的执行结果(True或者False)来决定执行的代码块,执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true
if True: print("Hello World") print("Goog Bye") ------------------------ Hello World Goog Bye if False: print("Hello Python") print("Goog Bye") ------------------------ Goog Bye
if ... else 语句
if False: print("No executed") else: print("Executed") ------------------------ Executed
if..elif...else
age = int(input("Please your age>>:")) if 0 < age and age <= 20: print("teenager") elif 20 < age and age <= 40: print("Man") elif 40 < age and age <= 60: print("Old") else: print("Died") ------------------------ Please your age>>:30 Man
if 嵌套
age = int(input("Please your age>>:")) if age >= 0: if 0 < age and age <= 20: print("teenager") elif 20 < age and age <= 40: print("Man") elif 40 < age and age <= 60: print("Old") else: print("Died") else: print("Your age error") ------------------------- Please your age>>:48 Old
while 循环语句
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。

Python中while语句的一般形式: while 判断条件: 语句

sum = 0 count = 0 while count <= 100: sum += count count += 1 print(sum) ------------------------- 5050
while无限循环,可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环 while True: print("无限循环")
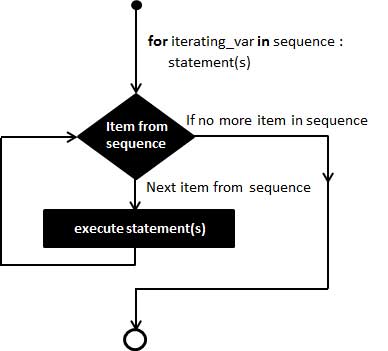
for 语句
for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目(一个列表或者一个字符串等)
for <variable> in <sequence>: <statements> else: <statements>

languages = ["C", "C++", "Perl", "Python"] for x in languages: print (x)

fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango','tomato','pelar'] for fruit in range(len(fruits)): print('fruit: ',fruits[fruit]) ------------------------------------------------ fruit: banana fruit: apple fruit: mango fruit: tomato fruit: pelar
break 语句
break 语句可以跳出 for 和 while 的循环体。若遇到break而使得 for 或 while 循环中终止而且 else 块将不执行

for megs in 'Hello Python': if megs == 'y': break print ('输出的当前字母为 :',megs) -------------------------------- 输出的当前字母为 : H 输出的当前字母为 : e 输出的当前字母为 : l 输出的当前字母为 : l 输出的当前字母为 : o 输出的当前字母为 : 输出的当前字母为 : P

counts = 0 while counts < 6: print("counts:" ,counts) if counts == 3: break counts += 1 --------------------------------- counts: 0 counts: 1 counts: 2 counts: 3
continue语句
continue语句被用来告诉Python跳过当前循环块中的剩余语句,然后继续进行下一轮循环

for megs in 'Hello Python': if megs == 'y': continue print ('输出的当前字母为 :',megs) -------------------------------- 输出的当前字母为 : H 输出的当前字母为 : e 输出的当前字母为 : l 输出的当前字母为 : l 输出的当前字母为 : o 输出的当前字母为 : 输出的当前字母为 : P 输出的当前字母为 : t 输出的当前字母为 : h 输出的当前字母为 : o 输出的当前字母为 : n

counts = 0 while counts < 6: counts += 1 if counts == 3: continue print("counts:", counts) -------------------------------- counts: 1 counts: 2 counts: 4 counts: 5 counts: 6
else子句
循环语句可以有 else 子句,它在穷尽列表(以for循环)或条件变为 false (以while循环)导致循环终止时被执行,但循环被break终止时不执行
for...else
for 循环中使用 break 语句,break 语句用于跳出当前循环体,且不执行else子句,否则执行else子句

sites = ["Baidu", "Google","UC","Taobao"] for site in sites: if site == "Baidu": print("李彦宏") break print("循环数据 " + site) else: print("没有循环数据!") print("完成循环!") -------------------------------- 李彦宏 完成循环!
while...else语句
while … else 在条件语句为 false 时执行则else 的语句块,若遇到break语句则不执行else子句

count = 0 while count < 10: print (count, " 小于 10") count = count + 1 else: print (count, " 大于或等于 10") ------------------------- 0 小于 10 1 小于 10 2 小于 10 3 小于 10 4 小于 10 5 小于 10 6 小于 10 7 小于 10 8 小于 10 9 小于 10 10 大于或等于 10
pass语句
Python pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性。pass 不做任何事情,一般用做占位语句

for char in "Hello World": if char == 'W': pass print("执行pass语句") print("char: " ,char) ------------------------------ char: H char: e char: l char: l char: o char: 执行pass语句 char: W char: o char: r char: l char: d
简单示例
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- ''' 用户登录、注销、注册 ''' import json user_dict = {} cmd_list = ['ls','move','cd','mkdir','rm','touch'] def login(): while True: user_name = input("please enter login user name >>: ") with open('data.json','r') as f: data = f.read() user_dict = json.loads(data) if user_name in user_dict: while True: user_pawd = input("please enter login user pawd >>: ") if user_pawd == user_dict[user_name]: while True: cmd = input("please enter command >>>: ") if cmd in cmd_list: print("Run command %s" %cmd) elif cmd == "quit": break else: print("please cmd error,please enter again!") break else: print("Enter login user pawd error,please enter again!") break else: print("Enter login user name error,please enter again!") def registered(): while True: with open('data.json','r') as f: data = f.read() user_dict = json.loads(data) user_name = input("please enter user name >>>: ") if user_name not in user_dict: user_pawd = input("please enter user pawd >>>: ") user_dict[user_name] = user_pawd data = json.dumps(user_dict) with open('data.json','w') as f: f.write(data) break else: print("Enter user name existed !")
def logout(): while True: user_name = input("please enter delete user name >>: ") with open('data.json','r') as f: data = f.read() user_dict = json.loads(data) if user_name in user_dict: del user_dict[user_name] data = json.dumps(user_dict) with open('data.json','w') as f: f.write(data) break else: print("user name not existed!")
if __name__ == '__main__': while True: choice = input(" login \n regist \n quit \n logout \n >>:") if choice == "login": login() elif choice == "regist": registered() elif choice == "logout": logout() elif choice == "quit": break else: print("choice error!")





