概述
Redis除了RDB方式提供持久化外,还提供了AOF的方式,和RDB保存数据库的键值对不同,AOF是记录数据库执行的命令来记录数据库状态的。当AOF开始时,Redis服务器加载时,会先检查AOF文件是否存在,如果存在,则加载AOF,否则加载RDB文件。本章主要分为:
1.AOF实现
2.AOF文件载入与还原
3.AOF重写及实现
AOF实现
AOF持久化功能的实现可以分为命令追加、文件写入、文件同步三个步骤。
命令追加
当AOF持久化功能处于打开状态时,服务器在执行完一个写命令之后,会以协议格式将被执行的写命令追加到AOF_BUF缓冲区的末尾,可以看下redisServer的数据库数据结构中,有包含这一属性:
/* AOF persistence */ int aof_state; /* REDIS_AOF_(ON|OFF|WAIT_REWRITE) */ int aof_fsync; /* Kind of fsync() policy */ char *aof_filename; /* Name of the AOF file */ int aof_no_fsync_on_rewrite; /* Don't fsync if a rewrite is in prog. */ int aof_rewrite_perc; /* Rewrite AOF if % growth is > M and... */ off_t aof_rewrite_min_size; /* the AOF file is at least N bytes. */ off_t aof_rewrite_base_size; /* AOF size on latest startup or rewrite. */ off_t aof_current_size; /* AOF current size. */ int aof_rewrite_scheduled; /* Rewrite once BGSAVE terminates. */ pid_t aof_child_pid; /* PID if rewriting process */ list *aof_rewrite_buf_blocks; /* Hold changes during an AOF rewrite. */ sds aof_buf; /* AOF buffer, written before entering the event loop ,且类型为SDS*/ int aof_fd; /* File descriptor of currently selected AOF file */ int aof_selected_db; /* Currently selected DB in AOF */
比如在客户端执行命令,set key value,服务器执行完这个命令后,会将命令转换为以下格式追加到缓冲区末尾:
![]()
文件写入与同步
Redis服务器就是一个事件循环,这个循环中的文件事件复杂客户端的请求以及回复,而时间事件就是执行像serverCron这样需要定时执行的函数。
在服务器处理文件事件时,可能会执行写命令,会有一些写命令被追加到AOF缓冲区。所以在服务器结束一个文件事件前,会调用flushAppendOnlyFile函数还判断是否需要到缓冲区的内容进行保存到AOF文件,函数的源码如下:
void flushAppendOnlyFile(int force) { ssize_t nwritten; int sync_in_progress = 0; mstime_t latency; if (sdslen(server.aof_buf) == 0) return; //判断缓冲区大小 if (server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC) //判断AOF配置 sync_in_progress = bioPendingJobsOfType(REDIS_BIO_AOF_FSYNC) != 0; if (server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC && !force) { /* With this append fsync policy we do background fsyncing. * If the fsync is still in progress we can try to delay * the write for a couple of seconds. */ if (sync_in_progress) { if (server.aof_flush_postponed_start == 0) { /* No previous write postponing, remember that we are * postponing the flush and return. */ server.aof_flush_postponed_start = server.unixtime; return; } else if (server.unixtime - server.aof_flush_postponed_start < 2) { /* We were already waiting for fsync to finish, but for less * than two seconds this is still ok. Postpone again. */ return; } /* Otherwise fall trough, and go write since we can't wait * over two seconds. */ server.aof_delayed_fsync++; redisLog(REDIS_NOTICE,"Asynchronous AOF fsync is taking too long (disk is busy?). Writing the AOF buffer without waiting for fsync to complete, this may slow down Redis."); } }
append_fsync有三种选项,默认为AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC:

AOF文件的载入
生成AOF文件后,会启动服务器时,会优先加载AOF文件,怎么去加载呢?
首先,Redis server会fork一个无网络连接的伪客户端(因为redis命令只能从客户端执行,前面讲了AOF文件保存的是执行的命令),接下来就是从AOF文件中读取并解析一行命令,并通过伪客户端来执行该命令。然后循环读取文件、解析、执行。具体过程如下:
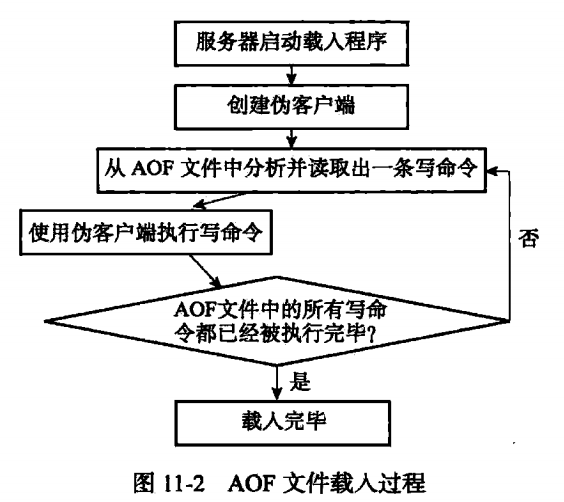
AOF重写
前面有讲到,AOF文件保存的是执行的命令,比如先在Redis客户端执行了四条命令,set msg 1,set msg 2,set msg 3,set msg 4,这样四条命令,其实最后msg的值为4,我们只需要保存最后一条命令即可,但是如果按照之前的实现,我们需要保存4条命令。正是由于这种机制,所以AOF文件会越来越大,而且会有很多类似这种情况的命令。体积过大不仅可能影响主机,更加会影响到载入及还原的时间,所以我们需要对AOF文件进行重写,以减少体积。类似上面这种情况,在AOF重写后,只需要有一条命令就够了。那AOF是怎么实现的呢?
实现
虽然Redis中这个功能叫做AOF重写,但是并没有对现有的AOF文件进行任何读取,分析,写入操作,这个功能实际上是通过读取服务器当前的数据库状态实现的。
还是拿上面的set msg的几条命令来举例,保存到AOF时,会有4条命令,这时候最快的速度不是去分析AOF文件,而且直接从数据库中取出msg的内容为4,再通过命令set msg 4保存到新的AOF文件中。其他类型的list,hash等都是类似的操作。所以AOF重写后只有一条命令。源码如下:

int rewriteAppendOnlyFile(char *filename) { dictIterator *di = NULL; dictEntry *de; rio aof; FILE *fp; char tmpfile[256]; int j; long long now = mstime(); char byte; size_t processed = 0; /* Note that we have to use a different temp name here compared to the * one used by rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground() function. */ snprintf(tmpfile,256,"temp-rewriteaof-%d.aof", (int) getpid()); fp = fopen(tmpfile,"w"); if (!fp) { redisLog(REDIS_WARNING, "Opening the temp file for AOF rewrite in rewriteAppendOnlyFile(): %s", strerror(errno)); return REDIS_ERR; } server.aof_child_diff = sdsempty(); rioInitWithFile(&aof,fp); if (server.aof_rewrite_incremental_fsync) rioSetAutoSync(&aof,REDIS_AOF_AUTOSYNC_BYTES); for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) { char selectcmd[] = "*2\r\n$6\r\nSELECT\r\n"; redisDb *db = server.db+j; dict *d = db->dict; if (dictSize(d) == 0) continue; di = dictGetSafeIterator(d); if (!di) { fclose(fp); return REDIS_ERR; } /* SELECT the new DB */ if (rioWrite(&aof,selectcmd,sizeof(selectcmd)-1) == 0) goto werr; if (rioWriteBulkLongLong(&aof,j) == 0) goto werr; /* Iterate this DB writing every entry */ while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) { sds keystr; robj key, *o; long long expiretime; keystr = dictGetKey(de); o = dictGetVal(de); initStaticStringObject(key,keystr); expiretime = getExpire(db,&key); /* If this key is already expired skip it */ if (expiretime != -1 && expiretime < now) continue; /* Save the key and associated value */ if (o->type == REDIS_STRING) { /* Emit a SET command */ char cmd[]="*3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n"; if (rioWrite(&aof,cmd,sizeof(cmd)-1) == 0) goto werr; /* Key and value */ if (rioWriteBulkObject(&aof,&key) == 0) goto werr; if (rioWriteBulkObject(&aof,o) == 0) goto werr; } else if (o->type == REDIS_LIST) { if (rewriteListObject(&aof,&key,o) == 0) goto werr; } else if (o->type == REDIS_SET) { if (rewriteSetObject(&aof,&key,o) == 0) goto werr; } else if (o->type == REDIS_ZSET) { if (rewriteSortedSetObject(&aof,&key,o) == 0) goto werr; } else if (o->type == REDIS_HASH) { if (rewriteHashObject(&aof,&key,o) == 0) goto werr; } else { redisPanic("Unknown object type"); } /* Save the expire time */ if (expiretime != -1) { char cmd[]="*3\r\n$9\r\nPEXPIREAT\r\n"; if (rioWrite(&aof,cmd,sizeof(cmd)-1) == 0) goto werr; if (rioWriteBulkObject(&aof,&key) == 0) goto werr; if (rioWriteBulkLongLong(&aof,expiretime) == 0) goto werr; } /* Read some diff from the parent process from time to time. */ if (aof.processed_bytes > processed+1024*10) { processed = aof.processed_bytes; aofReadDiffFromParent(); } } dictReleaseIterator(di); di = NULL; } /* Do an initial slow fsync here while the parent is still sending * data, in order to make the next final fsync faster. */ if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr; if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr; /* Read again a few times to get more data from the parent. * We can't read forever (the server may receive data from clients * faster than it is able to send data to the child), so we try to read * some more data in a loop as soon as there is a good chance more data * will come. If it looks like we are wasting time, we abort (this * happens after 20 ms without new data). */ int nodata = 0; mstime_t start = mstime(); while(mstime()-start < 1000 && nodata < 20) { if (aeWait(server.aof_pipe_read_data_from_parent, AE_READABLE, 1) <= 0) { nodata++; continue; } nodata = 0; /* Start counting from zero, we stop on N *contiguous* timeouts. */ aofReadDiffFromParent(); } /* Ask the master to stop sending diffs. */ if (write(server.aof_pipe_write_ack_to_parent,"!",1) != 1) goto werr; if (anetNonBlock(NULL,server.aof_pipe_read_ack_from_parent) != ANET_OK) goto werr; /* We read the ACK from the server using a 10 seconds timeout. Normally * it should reply ASAP, but just in case we lose its reply, we are sure * the child will eventually get terminated. */ if (syncRead(server.aof_pipe_read_ack_from_parent,&byte,1,5000) != 1 || byte != '!') goto werr; redisLog(REDIS_NOTICE,"Parent agreed to stop sending diffs. Finalizing AOF..."); /* Read the final diff if any. */ aofReadDiffFromParent(); /* Write the received diff to the file. */ redisLog(REDIS_NOTICE, "Concatenating %.2f MB of AOF diff received from parent.", (double) sdslen(server.aof_child_diff) / (1024*1024)); if (rioWrite(&aof,server.aof_child_diff,sdslen(server.aof_child_diff)) == 0) goto werr; /* Make sure data will not remain on the OS's output buffers */ if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr; if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr; if (fclose(fp) == EOF) goto werr; /* Use RENAME to make sure the DB file is changed atomically only * if the generate DB file is ok. */ if (rename(tmpfile,filename) == -1) { redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,"Error moving temp append only file on the final destination: %s", strerror(errno)); unlink(tmpfile); return REDIS_ERR; } redisLog(REDIS_NOTICE,"SYNC append only file rewrite performed"); return REDIS_OK; werr: redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,"Write error writing append only file on disk: %s", strerror(errno)); fclose(fp); unlink(tmpfile); if (di) dictReleaseIterator(di); return REDIS_ERR; }
在AOF重写时,为了不影响服务器处理其他请求,会使用子进程来处理AOF的重写。但是这样会有一个问题:在重写AOF期间,可能会有其他客户端请求命令过来,新的命令修改了数据库状态,这样就使得服务器当前状态和AOF文件所保存的状态不一致。举个例子:
在AOF重写时,数据库中只有一个k1值,在子进程重写过程中,有产生了k2,k3,k4几个键值,这样AOF重写后的状态(k1)就与数据库当前状态(k1,k2,k3,k4)不一致。
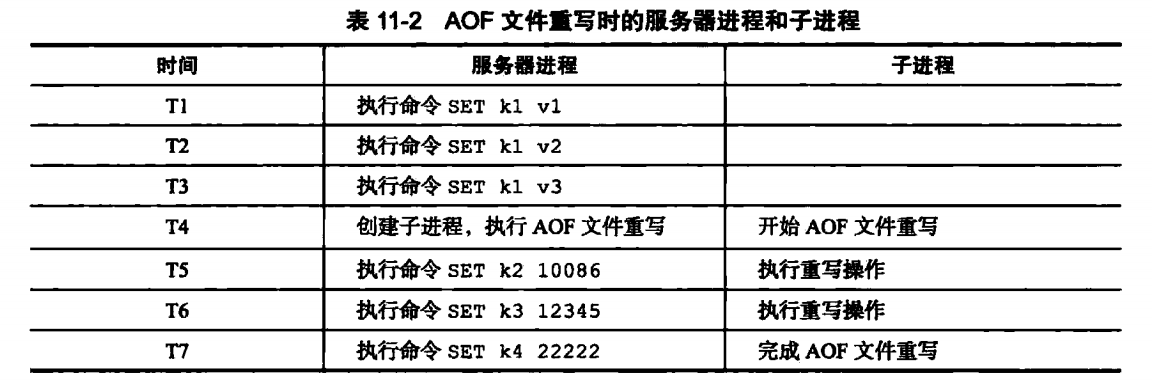
为了解决这个问题,Redis设置了一个重写缓冲区,当Redis服务器执行一个写命令后,会同时将命令写入到AOF缓冲区和AOF重写缓冲区。
在子进程完成AOF重写后,会给父进程发一个信号,父进程会再调用函数,进行以下处理:
1.将AOF重写缓冲区的内容写入到AOF文件,这样AOF保存的数据库状态和当前数据库状态就一致了;
2.将新的AOF文件进行改名,原子的覆盖现有的AOF文件,完成新旧文件的替换。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号