大佬总结的leetcode回溯算法题目
39.组合总和 √
78. 子集√
90. 子集 II
78题 子集
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
作者:powcai
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai-5/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
回溯法:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); backtrack(0, nums, res, new ArrayList<Integer>()); return res; } private void backtrack(int i, int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> res, ArrayList<Integer> tmp) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));!!!!! for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) { tmp.add(nums[j]); backtrack(j + 1, nums, res, tmp); tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); } } }
此题可以用位掩码方法:
作者:liweiwei1419
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/solution/hui-su-python-dai-ma-by-liweiwei1419/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
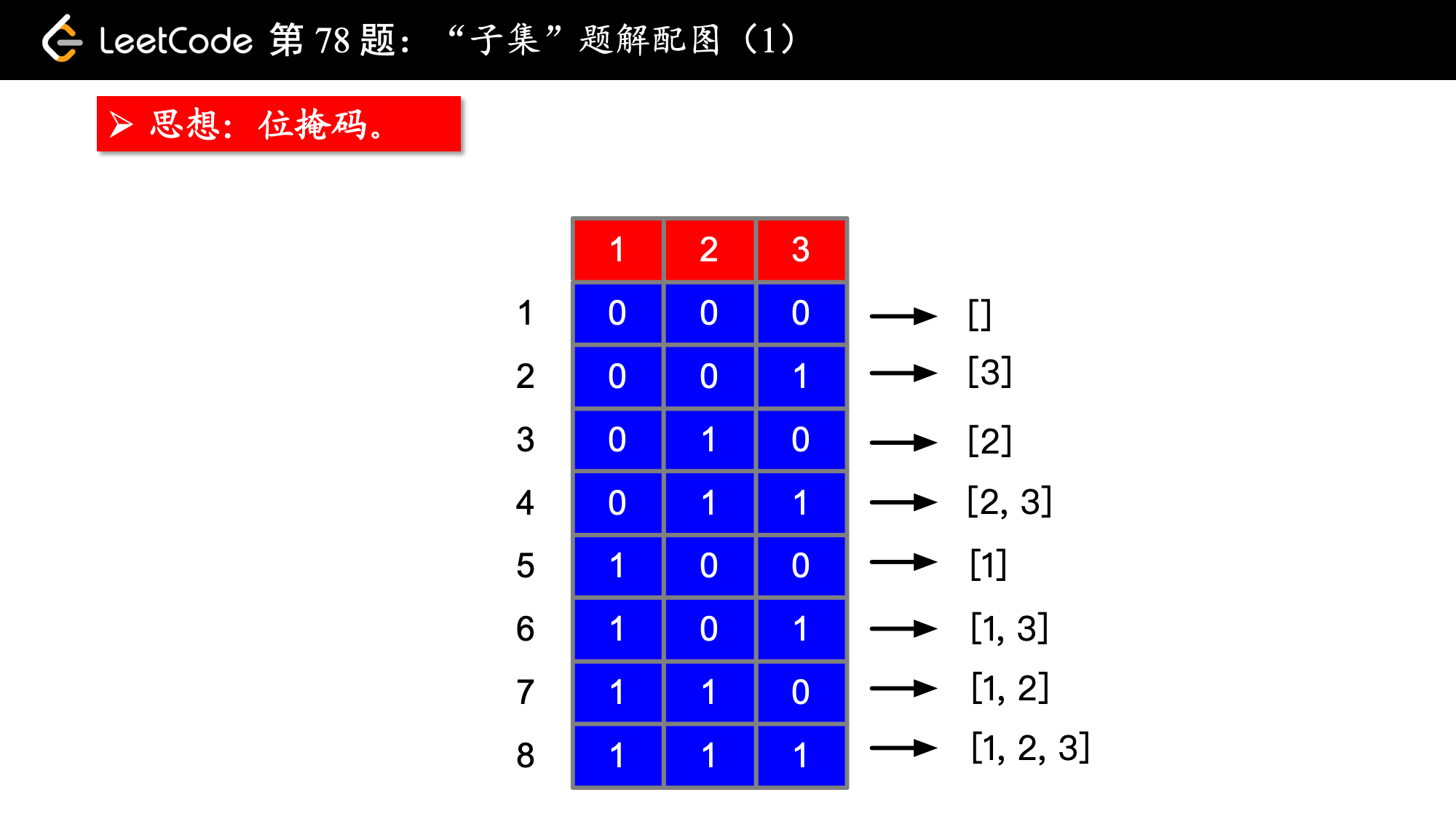
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Solution5 { public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { int size = nums.length; int n = 1 << size; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>(); for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (((i >> j) & 1) == 1) { cur.add(nums[j]); } } res.add(cur); } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 3}; Solution5 solution5 = new Solution5(); List<List<Integer>> subsets = solution5.subsets(nums); System.out.println(subsets); } }
39题 数组总和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
回溯法:
作者:liweiwei1419
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-2/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
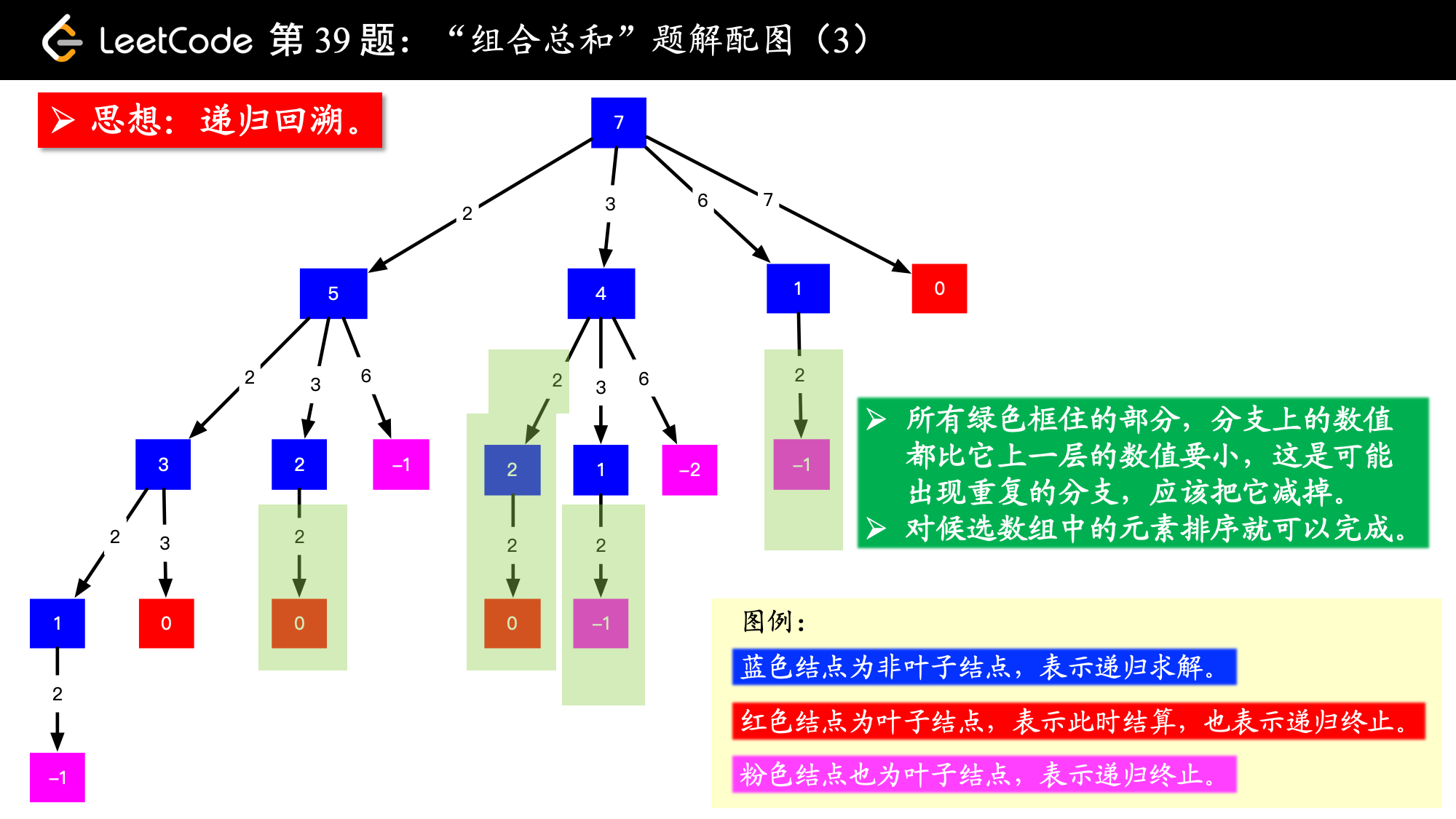
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); private int[] candidates; private int len; private void findCombinationSum(int residue, int start, Stack<Integer> pre) { if (residue == 0) { // Java 中可变对象是引用传递,因此需要将当前 path 里的值拷贝出来 res.add(new ArrayList<>(pre)); return; } // 优化添加的代码2:在循环的时候做判断,尽量避免系统栈的深度 // residue - candidates[i] 表示下一轮的剩余,如果下一轮的剩余都小于 0 ,就没有必要进行后面的循环了 // 这一点基于原始数组是排序数组的前提,因为如果计算后面的剩余,只会越来越小 for (int i = start; i < len && residue - candidates[i] >= 0; i++) { pre.add(candidates[i]); // 【关键】因为元素可以重复使用,这里递归传递下去的是 i 而不是 i + 1 findCombinationSum(residue - candidates[i], i, pre); pre.pop(); } } public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; if (len == 0) { return res; } // 优化添加的代码1:先对数组排序,可以提前终止判断 Arrays.sort(candidates); this.len = len; this.candidates = candidates; findCombinationSum(target, 0, new Stack<>()); return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] candidates = {2, 3, 6, 7}; int target = 7; Solution solution = new Solution(); List<List<Integer>> combinationSum = solution.combinationSum(candidates, target); System.out.println(combinationSum); } }
这里有一个更快的:
作者:powcai
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/xue-yi-tao-zou-tian-xia-hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(candidates); //System.out.println(candidates); backtrack(candidates, target, res, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>()); return res; } private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, List<List<Integer>> res, int i, ArrayList<Integer> tmp_list) { if (target < 0) return; if (target == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp_list)); return; } for (int start = i; start < candidates.length; start++) { if (target < candidates[start]) break; //System.out.println(start); tmp_list.add(candidates[start]); //System.out.println(tmp_list); backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[start], res, start, tmp_list); tmp_list.remove(tmp_list.size() - 1); } } }
40题 组合总数||
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
作者:powcai
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/solution/hui-su-xi-lie-by-powcai/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) { Arrays.sort(candidates); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); backtrack(res, candidates, target, 0, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>()); return res; } private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> res, int[] candidates, int target, int i, int tmp_sum, ArrayList<Integer> tmp_list) { if (tmp_sum == target) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp_list)); return; } for (int start = i; start < candidates.length; start++) { if (tmp_sum + candidates[start] > target) break; if (start > i && candidates[start] == candidates[start - 1]) continue; tmp_list.add(candidates[start]); backtrack(res, candidates, target, start + 1, tmp_sum + candidates[start], tmp_list); tmp_list.remove(tmp_list.size() - 1); } } }
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
作者:powcai
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai-2/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); int[] visited = new int[nums.length]; backtrack(res, nums, new ArrayList<Integer>(), visited); return res; } private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> res, int[] nums, ArrayList<Integer> tmp, int[] visited) { if (tmp.size() == nums.length) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp)); return; } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (visited[i] == 1) continue; visited[i] = 1; tmp.add(nums[i]); backtrack(res, nums, tmp, visited); visited[i] = 0; tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); } } }
更快方法:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return res; List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int num : nums) { list.add(num); } dfs(list, res, 0); return res; } private void dfs(List<Integer> nums, List<List<Integer>> res, int start) { if( start == nums.size()) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(nums)); } else { for (int i = start; i < nums.size(); i++) { Collections.swap(nums, i, start); dfs(nums, res, start+1); //交换当前位置后,从下一个位置开始重新排列填充 Collections.swap(nums, i, start); //重新排列后再恢复 } } } }




