如何实现Python调用C代码--python与C之间如何通信(swig)
转载: https://www.zhihu.com/question/23003213
1. C代码如何调用Python
1.1 test
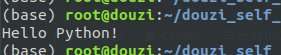
#include <Python.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Py_SetProgramName(argv[0]);
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("print ('Hello Python!')\n");
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
Linux下执行:
gcc -Wall cpython01.c -o cpython01.out -I/usr/include/python2.7 -lpython2.7
注意是Python2.7不是python3...不然好像报错....
1.2 C调用Python函数
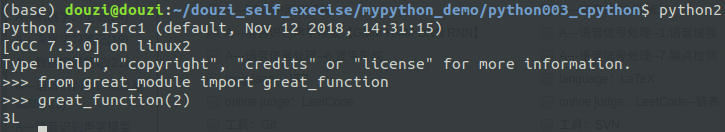
great_module.py
#!/usr/bin/python3 #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- def great_function(a): return a + 1
include_module_from_py.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <Python.h> int include_module_from_py(int a) { int res = 0; PyObject *pModule, *pFunc; PyObject *pArgs, *pValue; //import great_module.py pModule = PyImport_Import(PyString_FromString("great_module")); // //great_module.great_function(args) pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "great_function"); //build args pArgs = PyTuple_New(1); //Pyxxx_new录创建类型为xxx的变量 PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 0, PyInt_FromLong(a)); //若a为tuple, 则a[i]=b对应于 PyTuple_SetItem(a, i, b) //call pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs); res = PyInt_AsLong(pValue); return res; } int main() { Py_Initialize(); printf("res = %d\n", include_module_from_py(3)); Py_Finalize(); return 0; }
运行时,需要先:
export PYTHONPATH=.:$PYTHONPATH
编译:
gcc -Wall include_module_from_py.c -o include_module.out -I/usr/include/python2.7 -lpython2.7
![]()
2. python调用C/C++
great_module.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <Python.h> int great_function(int a) { return a + 1; } static PyObject * _great_function(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) { int _a; int res; //负责将Python的参数转换为C的参数 if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "i", &_a)) { return NULL; } res = great_function(_a); return PyLong_FromLong(res); } //导出表, 负责告诉Python这个模块有哪些函数可以被Python调用 static PyMethodDef GreateModuleMethods[] = { { "great_function", // 函数名 _great_function, // 包裹函数 METH_VARARGS, // 参数变长 "" // 说明性文字 }, { NULL, NULL, 0, NULL } //总是如此 }; //导出函数, 名字: module名称+前缀init PyMODINIT_FUNC initgreat_module() { (void) Py_InitModule("great_module", GreateModuleMethods); }
gcc -fPIC -shared great_module.c -o great_module.so -I/usr/include/python2.7 -lpython2.7
3. ctypes: Python调用C
#include <stdio.h> int add_int(int a, int b) { return a + b; } double add_double(double a, double b) { return a + b; }
gcc -shared -Wl,-soname,adder -o adder.so -fPIC add.c
#!/usr/bin/python3 #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- from ctypes import * adder = CDLL('./adder.so') res_int = adder.add_int(4, 5) print("4 + 5 = %d " % (res_int)) a = c_double(5.5) b = c_double(4.1) add_double = adder.add_double add_double.restype = c_double print("5.5 + 4.1 = ", str(add_double(a, b)))
工作中用了之后, 想想看还是用ctypes方便点....工程生成.so动态链接库, 然后直接在Python里导入.
最好是在C代码中, 将需要的功能接口写的易调用点!! 然后Python也不需要传很多的参数, 直接获取一个结果等等...
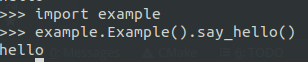
4. 使用SWIG使Python调用C/C++
example.h
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Example { public: void say_hello(); };
example.cpp
#include "example.h" void Example::say_hello() { cout << "hello\n"; }
example.i
%module example %{ #include "example.h" %} %include "example.h"
setup.py
#!/usr/bin/python3 #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ setup.py file for SWIG C\+\+/Python example """ from distutils.core import setup, Extension example_module = Extension('_example', sources=['example.cpp', 'example_wrap.cxx',], ) setup ( name = 'example', version = '0.1', author = "douzi", description = """Simple swig C\+\+/Python example""", ext_modules = [example_module], py_modules = ["example"], )
然后使用:
swig -c\+\+ -python example.i
python3 setup.py build_ext --inplace