VUE
1. vue.js的快速入门使用
1.1 vue.js库的下载
vue.js是目前前端web开发最流行的工具库,由尤雨溪在2014年2月发布的。
另外几个常见的工具库:react.js /angular.js
官方网站:
英文:https://vuejs.org/
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/
vue.js目前有1.x、2.x和3.x 版本,我们学习2.x版本的。
1.2 vue.js库的基本使用
在github下载:
在官网下载地址: https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/installation.html
vue的引入类似于jQuery,开发中可以使用开发版本vue.js,产品上线要换成vue.min.js。
下图是github网站下载的vue.js目录
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
//window.onload 是一个接口函数,功能是必须等到页面所有数据都加载完毕再执行函数里面的代码
window.onload = function(){
// vue.js的代码开始于一个Vue对象。所以每次操作数据都要声明Vue对象开始。
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#app', // 设置当前vue对象要控制的标签范围。
data:{ // data是将要展示到HTML标签元素中的数据。
message: 'hello world!',
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- {{ message }} 表示把vue对象里面data属性中的对应数据输出到页面中 -->
<!-- 在双标签中显示数据要通过{{ }}来完成 -->
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
代码执行效果:
总结:
-
vue的使用要从创建Vue对象开始
var vm = new Vue(); -
创建vue对象的时候,需要传递参数,是json对象,json对象对象必须至少有两个属性成员
var vm = new Vue({ el:"#app", data: { 数据变量:"变量值", 数据变量:"变量值", 数据变量:"变量值", }, }); el:设置vue可以操作的html内容范围,值一般就是css的id选择器。 data: 保存vue.js中要显示到html页面的数据。 -
vue.js要控制器的内容外围,必须先通过id来设置。
<div id="app"> <h1>{{message}}</h1> <p>{{message}}</p> </div>
1.3 vue.js的M-V-VM思想
MVVM 是Model-View-ViewModel 的缩写,它是一种基于前端开发的架构模式。
Model 指代的就是vue对象的data属性里面的数据。这里的数据要显示到页面中。
View 指代的就是vue中数据要显示的HTML页面,在vue中,也称之为“视图模板” 。
ViewModel 指代的是vue.js中我们编写代码时的vm对象了,它是vue.js的核心,负责连接 View 和 Model,保证视图和数据的一致性,所以前面代码中,data里面的数据被显示中p标签中就是vm对象自动完成的。
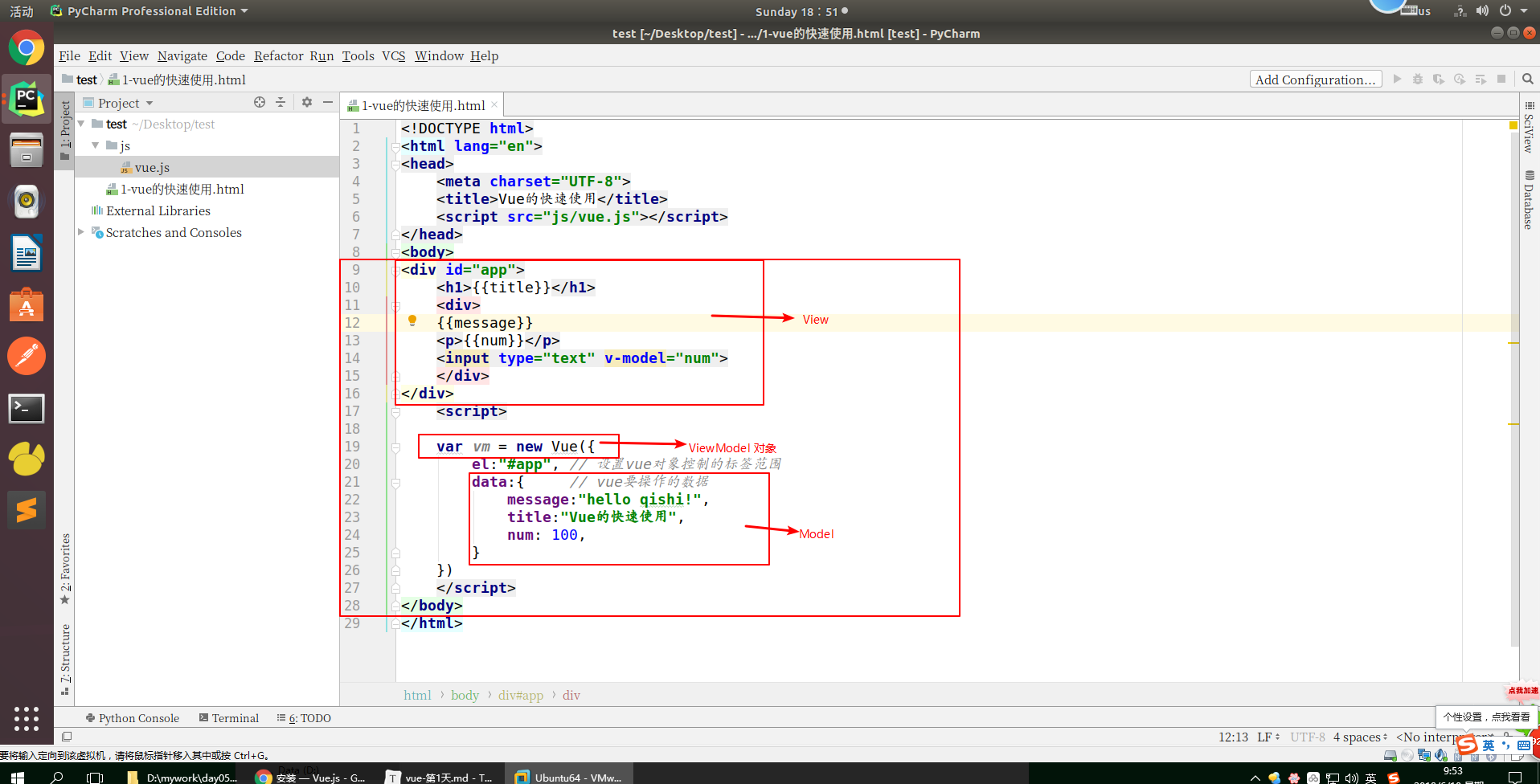
编写代码,让我们更加清晰的了解MVVM:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
// 创建vm对象
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name:"大标题",
age:16,
},
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 在双标签中显示数据要通过{{ }}来完成 -->
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
<p>{{age}}</p>
<!-- 在表单输入框中显示数据要使用v-model来完成,模板语法的时候,我们会详细学习 -->
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</div>
</body>
</html>
在浏览器中可以在 console.log通过 vm对象可以直接访问el和data属性,甚至可以访问data里面的数据
console.log(vm.$el) # #box vm对象可以控制的范围
console.log(vm.$data); # vm对象要显示到页面中的数据
console.log(vm.$data.message); # 访问data里面的数据
console.log(vm.message);# 这个 message就是data里面声明的数据,也可以使用 vm.变量名显示其他数据,message只是举例.
总结:
-
如果要输出data里面的数据作为普通标签的内容,需要使用{{ }}
用法:vue对象的data属性: data:{ name:"小明", } 标签元素: <h1>{{ name }}</h1> -
如果要输出data里面的数据作为表单元素的值,需要使用vue.js提供的元素属性v-model
用法:vue对象的data属性: data:{ name:"小明", } 表单元素: <input v-model="name">注意: 使用v-model把data里面的数据显示到表单元素以后,一旦用户修改表单元素的值,则data里面对应数据的值也会随之发生改变,甚至,页面中凡是使用了这个数据都会发生变化。
1.4 显示数据
- 在双标签中显示数据要通过{{ }}来完成数据显示
- 在表单输入框中显示数据要使用v-model来完成数据显示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
str1: "hello",
num: 20,
url1: "http://www.baidu.com",
url2: "http://www.taobao.com"
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>{{ str1 }}</p>
<p>{{ str1.split("").reverse().join("") }}</p>
<p>num和num2中比较大的数是:{{ num>num2? num:num2 }}</p>
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</body>
</html>
双花括号仅用输出文本内容,如果要输出html代码,则不能使用这个.要使用v-html来输出.
- v-html必须在html标签里面作为属性写出来.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="app">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h3>{{url1}}</h3>
{{img}}<br>
<span v-html="img"></span>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:".app",
data:{
title:"我的vue",
url1:"我的收获地址",
img:'<img src="images/shendan.png">',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
总结:
-
可以在普通标签中使用{{ }} 或者 v-html 来输出data里面的数据
<h1>{{message}}</h1> -
可以在表单标签中使用v-model属性来输出data里面的数据,同时还可以修改data里面的数据
<input type="text" v-model="username">
在输出内容到普通标签的使用{{ }}
v-model或者v-html等vue提供的属性,或者 {{}} 都支持js代码。
<h1>{{str1.split("").reverse().join("")}}</h1>
<!-- 3.2 支持js的运算符-->
<h1>{{num1+3}}</h1>
<!-- 3.3 js还有一种运算符,三元运算符,类似于python里面的三元表达式
三元运算符的语法:
判断条件 ? 条件为true : 条件为false的结果
python 三元表达式[三目运算符]的语法:
a if 条件 else b
-->
<h1>num1和num2之间进行比较,最大值:{{ num2>num1?num2:num1 }}</h1>
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Vue的快速使用</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{url}}</p>
<div>{{text}}</div>
<div v-html="text"></div>
<input v-model="url">
<div>num是{{num%2==0?'偶数':'奇数'}}</div>
<div>num的下一个数字:{{num-0+1}}</div>
<input type="text" v-model="num">
<div>{{message.split("").reverse().join("")}}</div>
<input type="text" v-model="message.split('').reverse().join('')">
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app", // 设置vue对象控制的标签范围
data:{ // vue要操作的数据
url:"http://www.luffycity.com",
text:"<h1>大标题</h1>",
num: 100,
message:"abcdef",
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. 常用指令
指令 (Directives) 是带有“v-”前缀的特殊属性。每一个指令在vue中都有固定的作用。
在vue中,提供了很多指令,常用的有:v-if、v-model、v-for等等。
指令会在vm对象的data属性的数据发生变化时,会同时改变元素中的其控制的内容或属性。
因为vue的历史版本原因,所以有一部分指令都有两种写法:
vue1.x写法 vue2.x的写法
v-html ----> {{ 普通文本 }} # vue2.x 也支持v-html,v-text,输出html代码的内容
v-bind:属性名 ----> :属性
v-on:事件名 ----> @事件名
2.1 操作属性
格式:
<标签名 :标签属性="data属性"></标签名>
<p :title="str1">{{ str1 }}</p> <!-- 也可以使用v-html显示双标签的内容,{{ }} 是简写 -->
<a :href="url2">淘宝</a>
<a v-bind:href="url1">百度</a> <!-- v-bind是vue1.x版本的写法 -->
显示wifi密码效果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="index">
<img :src="url" :alt="title"><br>
<input :type="type" placeholder="请输入wifi密码"> <button @click="type='text'">显示密码</button>
</div>
<script>
let? vm = new Vue({
el:"#index",
data:{
url:"https://www.luffycity.com/static/img/head-logo.a7cedf3.svg",
title:"路飞学成",
type:"password"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.2 事件绑定
有两种事件操作的写法,@事件名 和 v-on:事件名
<button v-on:click="num++">按钮</button> <!-- v-on 是vue1.x版本的写法 -->
<button @click="num+=5">按钮2</button>
总结:
1. 使用@事件名来进行事件的绑定
语法:
<h1 @click="num++">{{num}}</h1>
2. 绑定的事件的事件名,全部都是js的事件名:
@submit ---> onsubmit
@focus ---> onfocus
....
例如:完成商城购物车中的商品增加减少数量
步骤:
- 给vue对象添加操作数据的方法
- 在标签中使用指令调用操作数据的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<button @click="++num">+</button>
<input type="text" v-model="num">
<button @click="sub">-</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
num:0,
},
methods:{
sub(){
if(this.num<=1){
this.num=0;
}else{
this.num--;
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!--#box>(button+input+button) tab键-->
2.3 操作样式
2.3.1 控制标签class类名
格式:
<h1 :class="值">元素</h1> 值可以是字符串、对象、对象名、数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.box1{
color: red;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box2{
background-color: orange;
font-size: 32px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<!--- 添加class类名,值是一个对象
{
class类1:布尔值变量1,
class类2:布尔值变量2,
}
-->
<p :class="{box1:myclass1}">一个段落</p>
<p @click="myclass3=!myclass3" :class="{box1:myclass2,box2:myclass3}">一个段落</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm1=new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
myclass1:false, // 布尔值变量如果是false,则不会添加对象的属性名作为样式
myclass2:true, // 布尔值变量如果是true,则不会添加对象的属性名作为样式
myclass3:false,
},
})
</script>
<!-- 上面的代码可以:class的值保存到data里面的一个变量,然后使用该变量作为:class的值 -->
<style>
.box4{
background-color: red;
}
.box5{
color: green;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<button @click="mycls.box4=!mycls.box4">改变背景</button>
<button @click="mycls.box5=!mycls.box5">改变字体颜色</button>
<p :class="mycls">第二个段落</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm2 = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
mycls:{
box4:false,
box5:true
},
}
})
</script>
<!-- 批量给元素增加多个class样式类 -->
<style>
.box6{
background-color: red;
}
.box7{
color: green;
}
.box8{
border: 1px solid yellow;
}
</style>
<div id="app2">
<p :class="[mycls1,mycls2]">第三个段落</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm3 = new Vue({
el:"#app2",
data:{
mycls1:{
box6:true,
box7:true,
},
mycls2:{
box8:true,
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
代码执行效果:
总结:
1. 给元素绑定class类名,最常用的就是第二种。
vue对象的data数据:
data:{
myObj:{
complete:true,
uncomplete:false,
}
}
html元素:
<div class="box" :class="myObj">2222</div>
最终浏览器效果:
<div class="box complete">2222</div>
2.3.2 控制标签style样式
格式1:值是json对象,对象写在元素的:style属性中
标签元素:
<div :style="{color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }"></div>
data数据如下:
data: {
activeColor: 'red',
fontSize: 30
}
格式2:值是对象变量名,对象在data中进行声明
标签元素:
<div v-bind:style="styleObject"></div>
data数据如下:
data: {
styleObject: {
color: 'red',
fontSize: '13px'
}
}
格式3:值是数组
标签元素:
<div v-bind:style="[style1, style2]"></div>
data数据如下:
data: {
style1:{
color:"red"
},
style2:{
background:"yellow",
fontSize: "21px"
}
}
2.3.2 实例-vue版本选项卡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#card{
width: 500px;
height: 350px;
}
.title{
height:50px;
}
.title span{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color:#ccc;
display: inline-block;
line-height: 50px; /* 设置行和当前元素的高度相等,就可以让文本内容上下居中 */
text-align:center;
}
.content .list{
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
display: none;
}
.content .active{
display: block;
}
.title .current{
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="card">
<div class="title">
<span @click="num=0" :class="num==0?'current':''">国内新闻</span>
<span @click="num=1" :class="num==1?'current':''">国际新闻</span>
<span @click="num=2" :class="num==2?'current':''">银河新闻</span>
<!--<span>{{num}}</span>-->
</div>
<div class="content">
<div class="list" :class="num==0?'active':''">国内新闻列表</div>
<div class="list" :class="num==1?'active':''">国际新闻列表</div>
<div class="list" :class="num==2?'active':''">银河新闻列表</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 思路:
// 当用户点击标题栏的按钮[span]时,显示对应索引下标的内容块[.list]
// 代码实现:
var card = new Vue({
el:"#card",
data:{
num:0,
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
代码运行效果:
2.4 条件渲染指令
vue中提供了两个指令可以用于判断是否要显示元素,分别是v-if和v-show。
2.4.1 v-if
标签元素:
<!-- vue对象最终会把条件的结果变成布尔值 -->
<h1 v-if="ok">Yes</h1>
data数据:
data:{
ok:false // true则是显示,false是隐藏
}
2.4.2 v-else
v-else指令来表示 v-if 的“else 块”,v-else 元素必须紧跟在带 v-if 或者 v-else-if 的元素的后面,否则它将不会被识别。
标签元素:
<h1 v-if="ok">Yes</h1>
<h1 v-else>No</h1>
data数据:
data:{
ok:false // true则是显示,false是隐藏
}
2.4.3 v-else-if
可以出现多个v-else-if语句,但是v-else-if之前必须有一个v-if开头。后面可以跟着v-else,也可以没有。
标签元素:
<h1 v-if="num==1">num的值为1</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="num==2">num的值为2</h1>
<h1 v-else>num的值是{{num}}</h1>
data数据:
data:{
num:2
}
2.4.4 v-show
用法和v-if大致一样,区别在于2点:
- v-show后面不能v-else或者v-else-if
- v-show隐藏元素时,使用的是display:none来隐藏的,而v-if是直接从HTML文档中移除元素[ DOM操作中的remove ]
标签元素:
<h1 v-show="ok">Hello!</h1>
data数据:
data:{
ok:false // true则是显示,false是隐藏
}
2.5 列表渲染指令
在vue中,可以通过v-for指令可以将一组数据渲染到页面中,数据可以是数组或者对象。
数据是数组:
<ul>
<!--book是列表的每一个元素-->
<li v-for="book in book_list">{{book.title}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<!--book是列表的每一个元素,index是每个元素的下标-->
<li v-for="(book, index) in book_list">第{{ index+1}}本图书:{{book.title}}</li>
</ul>
<script>
var vm1 = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
book_list:[
{"id":1,"title":"图书名称1","price":200},
{"id":2,"title":"图书名称2","price":200},
{"id":3,"title":"图书名称3","price":200},
{"id":4,"title":"图书名称4","price":200},
]
}
})
</script>
数据是对象:
<ul>
<!--value是每一个value值-->
<li v-for="value in book">{{value}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<!--i是每一个value值,j是每一个键名-->
<li v-for="attr, value in book">{{attr}}:{{value}}</li>
</ul>
<script>
var vm1 = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
book: {
// "attr":"value"
"id":11,
"title":"图书名称1",
"price":200
},
},
})
</script>
- 练习:
goods:[
{"name":"python入门","price":150},
{"name":"python进阶","price":100},
{"name":"python高级","price":75},
{"name":"python研究","price":60},
{"name":"python放弃","price":110},
]
# 把上面的数据采用table表格输出到页面,价格大于60的数据需要添加背景色橙色[orange]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<style>
.orange{
background: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<table border="1" width="800px">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="good,key in goods" :class="good.price>60?'orange':''">
<td>{{key+1}}</td>
<td>{{good.name}}</td>
<td>{{good.price}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
goods:[
{"name":"python入门","price":150},
{"name":"python进阶","price":100},
{"name":"python高级","price":75},
{"name":"python研究","price":60},
{"name":"python放弃","price":110},
]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
3. Vue对象提供的属性功能
3.1 过滤器
过滤器,就是vue允许开发者自定义的文本格式化函数,可以使用在两个地方:输出内容和操作数据中。
定义过滤器的方式有两种。
3.1.1 使用Vue.filter()进行全局定义
Vue.filter("RMB1", function(v){
//就是来格式化(处理)v这个数据的
if(v==0){
return v;
}
return v+"元";
})
3.1.2 在vue对象中通过filters属性来定义
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{},
filters:{
RMB2:function(value){
if(value==''){
return;
}else{
return '¥ '+value;
}
}
}
});
3.4 计算和侦听属性
3.4.1 计算属性
我们之前学习过字符串反转,如果直接把反转的代码写在元素中,则会使得其他同事在开发时时不易发现数据被调整了,所以vue提供了一个计算属性(computed),可以让我们把调整data数据的代码存在在该属性中。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
str1: "abcdefgh"
},
computed:{ //计算属性:里面的函数都必须有返回值
strRevs: function(){
var ret = this.str1.split("").reverse().join("");
return ret
}
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ str1 }}</p>
<p>{{ strRevs }}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3.4.2 监听属性
侦听属性,可以帮助我们侦听data某个数据的变化,从而做相应的自定义操作。
侦听属性是一个对象,它的键是要监听的对象或者变量,值一般是函数,当侦听的data数据发生变化时,会自定执行的对应函数,这个函数在被调用时,vue会传入两个形参,第一个是变化前的数据值,第二个是变化后的数据值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:20
},
watch:{
num:function(newval,oldval){
//num发生变化的时候,要执行的代码
console.log("num已经发生了变化!");
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ num }}</p>
<button @click="num++">按钮</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3.5 vue对象的生命周期
每个Vue对象在创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程。在这个过程中Vue.js会自动运行一些叫做生命周期的的钩子函数,我们可以使用这些函数,在对象创建的不同阶段加上我们需要的代码,实现特定的功能。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:0
},
beforeCreate:function(){
console.log("beforeCreate,vm对象尚未创建,num="+ this.num); //undefined
this.name=10; // 此时没有this对象呢,所以设置的name无效,被在创建对象的时候被覆盖为0
},
created:function(){
console.log("created,vm对象创建完成,设置好了要控制的元素范围,num="+this.num ); // 0
this.num = 20;
},
beforeMount:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>{{num}}</p>
console.log("beforeMount,vm对象尚未把data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num ); // 20
this.num = 30;
},
mounted:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>30</p>
console.log("mounted,vm对象已经把data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num); // 30
},
beforeUpdate:function(){
// this.$el 就是我们上面的el属性了,$el表示当前vue.js所控制的元素#app
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>30</p>
console.log("beforeUpdate,vm对象尚未把更新后的data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num); // beforeUpdate----31
},
updated:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>31</p>
console.log("updated,vm对象已经把过呢更新后的data数据显示到页面中,num=" + this.num ); // updated----31
},
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{num}}</p>
<button @click="num++">按钮</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
总结:
在vue使用的过程中,如果要初始化操作,把初始化操作的代码放在 mounted 中执行。
mounted阶段就是在vm对象已经把data数据实现到页面以后。一般页面初始化使用。例如,用户访问页面加载成功以后,就要执行的ajax请求。
另一个就是created,这个阶段就是在 vue对象创建以后,把ajax请求后端数据的代码放进 created
3.2 阻止事件冒泡和刷新页面
使用.stop和.prevent
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: #ccc;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: pink;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box1" @click="alert('box1')">
<div class="box2" @click.stop.prevent="alert('box2')"></div> <!-- @click.stop来阻止事件冒泡 -->
</div>
<form action="#">
<input type="text">
<input type="submit">
<input type="submit" value="提交02" @click.prevent=""> <!-- @click.prevent来阻止表单提交 -->
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3.3 综合案例-todolist
我的计划列表
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist</title>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="list_con">
<h2>To do list</h2>
<input type="text" name="" id="txt1" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" name="" value="增加" id="btn1" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<!-- javascript:; # 阻止a标签跳转 -->
<li>
<span>学习html</span>
<a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a>
</li>
<li><span>学习css</span><a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a></li>
<li><span>学习javascript</span><a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
特效实现效果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist</title>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="todolist" class="list_con">
<h2>To do list</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="message" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" @click="addItem" value="增加" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<li v-for="item,key in dolist">
<span>{{item}}</span>
<a @click="upItem(key)" class="up" > ↑ </a>
<a @click="downItem(key)" class="down"> ↓ </a>
<a @click="delItem(key)" class="del">删除</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
// 计划列表代码
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#todolist",
data:{
message:"",
dolist:[
"学习html",
"学习css",
"学习javascript",
]
},
methods:{
addItem(){
if(this.messsage==""){
return false;
}
this.dolist.push(this.message);
this.message = ""
},
delItem(key){
// 删除和替换
// 参数1: 开始下表
// 参数2: 元素长度,如果不填默认删除到最后
// 参数3: 表示使用当前参数替换已经删除内容的位置
this.dolist.splice(key, 1);
},
upItem(key){
if(key==0){
return false;
}
// 向上移动
let result = this.dolist.splice(key,1);
this.dolist.splice(key-1,0,result[0]);
},
downItem(key){
// 向下移动
let result = this.dolist.splice(key, 1);
console.log(result);
this.dolist.splice(key+1,0,result[0]);
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号