weak引用表原理探究
一、weak引用实现原理探究
首先对《Xcode 10 下如何调试objc4-723》建立的objc源码调试工程表示感谢!
地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/9e0fc8295c4b
大多数文章阐述了基本过程:
1 2 3 4 5 | 1.初始化一个weak对象时,runtime会调用一个objc_initWeak函数,初始化一个新的weak指针指向该对象的地址2.在objc_initWeak函数中会继续调用objc_storeWeak函数,在这个过程是用来更新weak指针的指向,同时创建对应的弱引用表3.在对象释放时,会调用clearDeallocating函数,这个函数会根据对象地址获取所有weak指针数组,然后遍历这个数组置为nil。最后把该条对象的记录从weak表中删除。 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 | id objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj) { // 查看对象实例是否有效 // 无效对象直接导致指针释放 if (!newObj) { *location = nil; return nil; } // 这里传递了三个 bool 数值 // 使用 template 进行常量参数传递是为了优化性能 return storeWeak<false/*old*/, true/*new*/, true/*crash*/> (location, (objc_object*)newObj);}template <bool HaveOld, bool HaveNew, bool CrashIfDeallocating>static idstoreWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj){ assert(HaveOld || HaveNew); if (!HaveNew) assert(newObj == nil); Class previouslyInitializedClass = nil; id oldObj; SideTable *oldTable; SideTable *newTable; // Acquire locks for old and new values. // Order by lock address to prevent lock ordering problems. // Retry if the old value changes underneath us. retry: if (HaveOld) { oldObj = *location; oldTable = &SideTables()[oldObj]; } else { oldTable = nil; } if (HaveNew) { newTable = &SideTables()[newObj]; } else { newTable = nil; } SideTable::lockTwo<HaveOld, HaveNew>(oldTable, newTable); if (HaveOld && *location != oldObj) { SideTable::unlockTwo<HaveOld, HaveNew>(oldTable, newTable); goto retry; } // Prevent a deadlock between the weak reference machinery // and the +initialize machinery by ensuring that no // weakly-referenced object has an un-+initialized isa. if (HaveNew && newObj) { Class cls = newObj->getIsa(); if (cls != previouslyInitializedClass && !((objc_class *)cls)->isInitialized()) { SideTable::unlockTwo<HaveOld, HaveNew>(oldTable, newTable); _class_initialize(_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, (id)newObj)); // If this class is finished with +initialize then we're good. // If this class is still running +initialize on this thread // (i.e. +initialize called storeWeak on an instance of itself) // then we may proceed but it will appear initializing and // not yet initialized to the check above. // Instead set previouslyInitializedClass to recognize it on retry. previouslyInitializedClass = cls; goto retry; } } // Clean up old value, if any. if (HaveOld) { weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location); } // Assign new value, if any. if (HaveNew) { newObj = (objc_object *)weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table, (id)newObj, location, CrashIfDeallocating); // weak_register_no_lock returns nil if weak store should be rejected // Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table. if (newObj && !newObj->isTaggedPointer()) { newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock(); } // Do not set *location anywhere else. That would introduce a race. *location = (id)newObj; } else { // No new value. The storage is not changed. } SideTable::unlockTwo<HaveOld, HaveNew>(oldTable, newTable); return (id)newObj;} |
其中涉及到一个数据结构
1 2 3 4 5 | struct SideTable { spinlock_t slock; // 因为操作对象的引用计数频率很快,因此系统在这里设置了一把自旋锁,保证是原子操作 RefcountMap refcnts; // 引用计数器哈希表,根据对象地址查找对象的引用计数 weak_table_t weak_table; // 维护weak指针的结构体} |
通过下面的代码取得
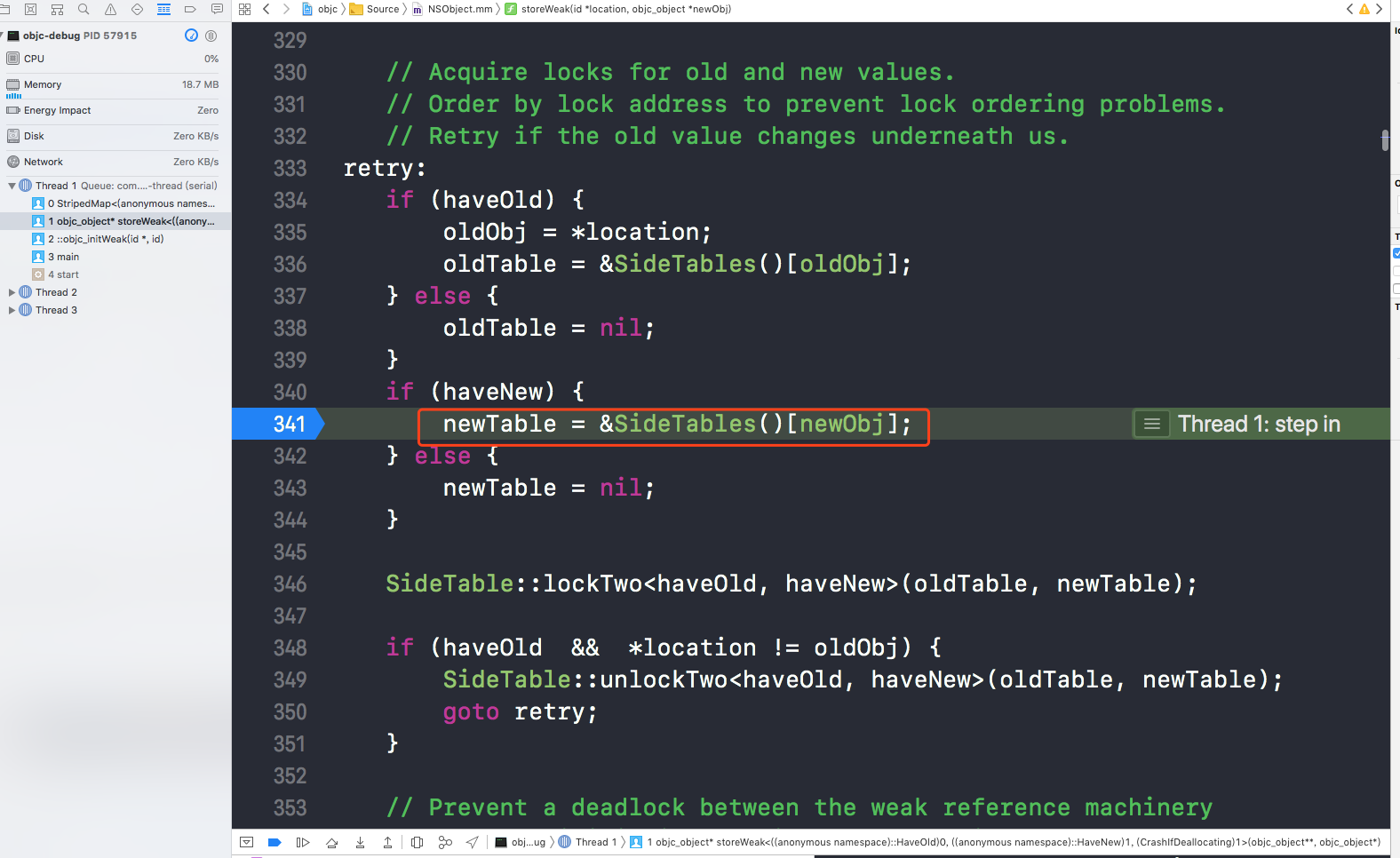
也就是全局的sidetables本身是一个hash表,总共大小为64;每一个value对应的是 sidetable,sidetable中保存引用计数表和weak引用表
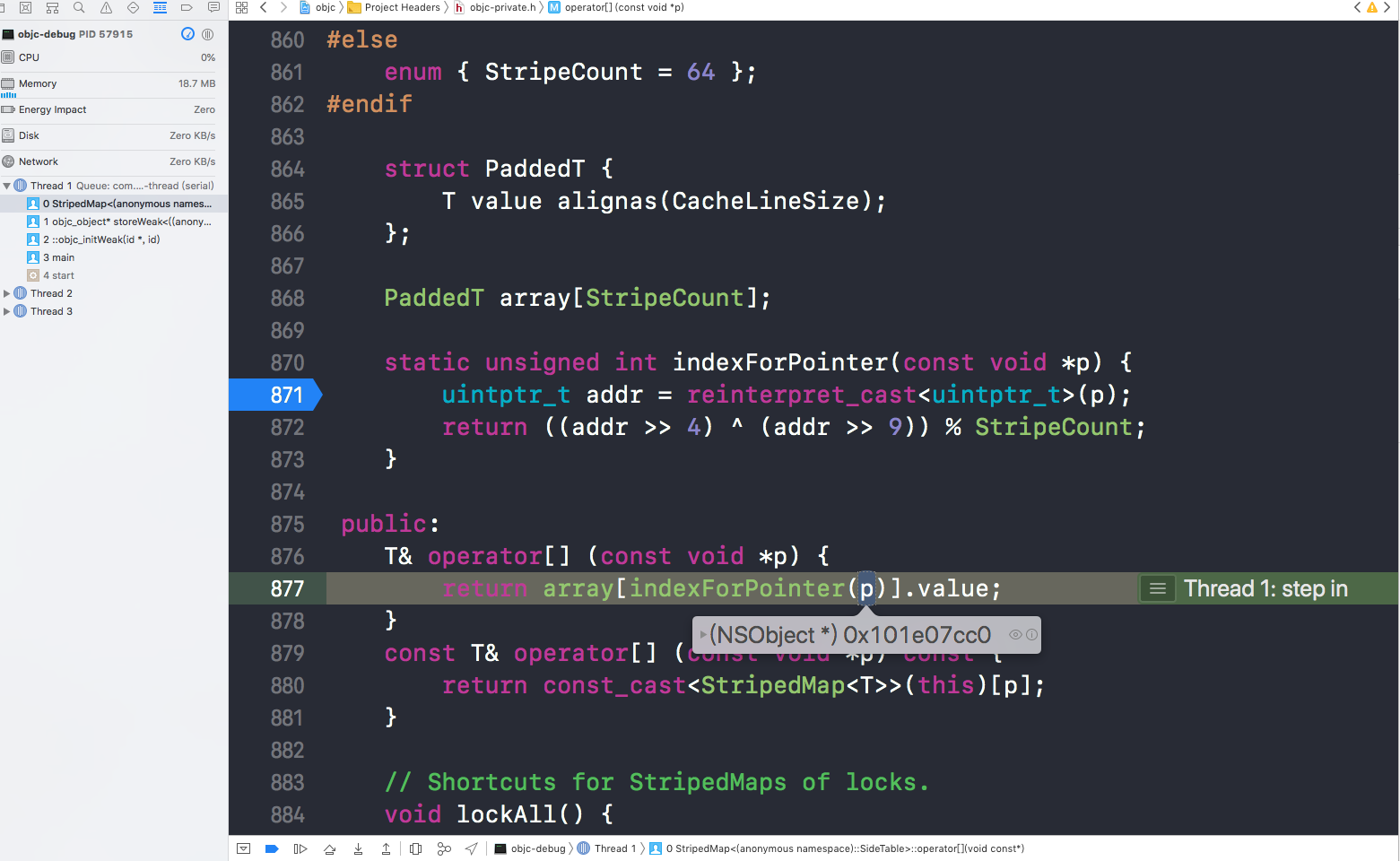
找到一个sidetable表之后,要根据weak所指对象的地址hash值,找到对应存储weak指针的value结构体
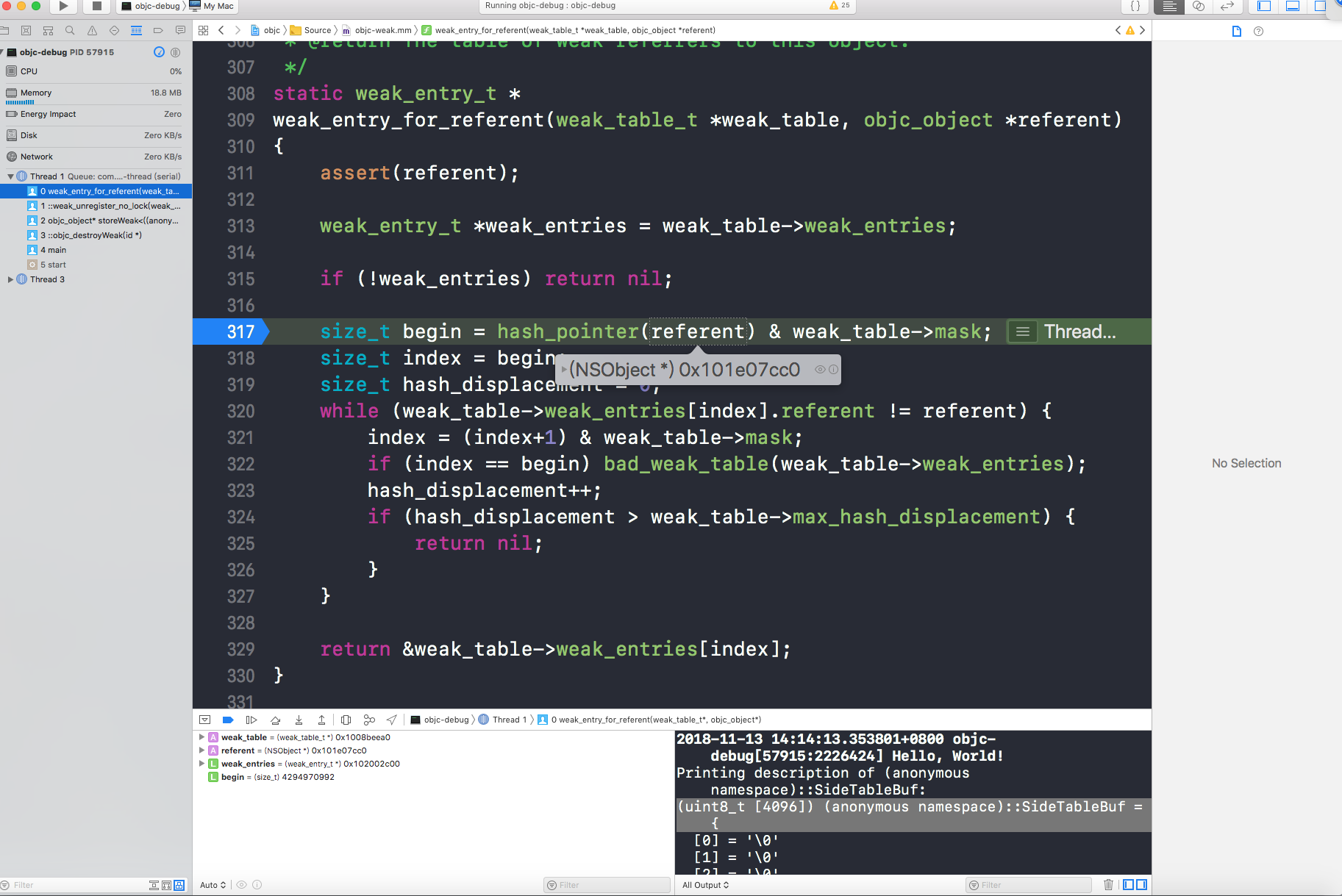
接下来的操作就是修改weak引用表了




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架