侯捷C++STL源码分析
STL六大部件
-
容器(Containers):放东西,需要占用内存。
-
分配器(Allocators):支持容器。
-
算法(Algorithms):操作容器里面的数据。
-
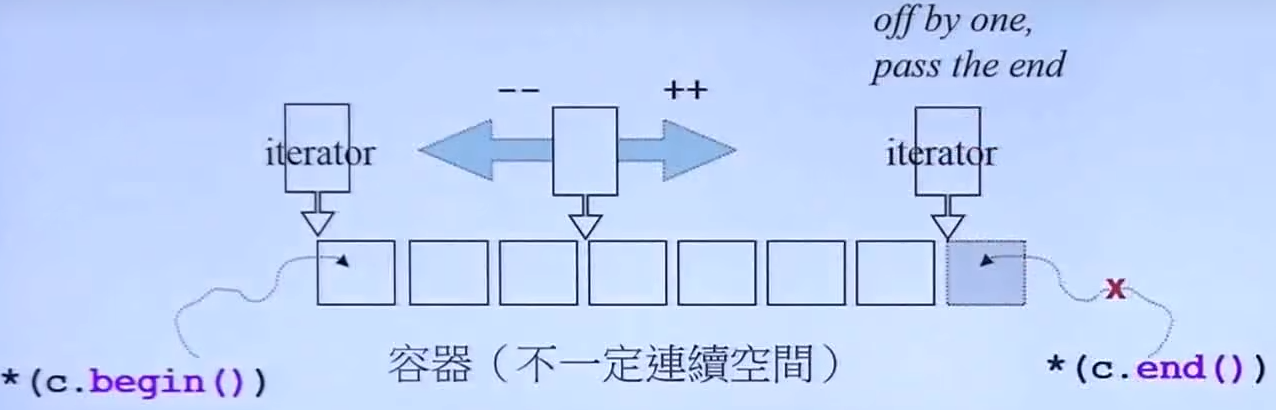
迭代器(Iterators):容器和算法之间的桥梁,泛化的指针。
-
适配器(A dapters)
-
仿函数(Functors)
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ia[6] = {27,210,12,47,109,83};
vector<int,allocator<int>> vi(ia,ia+6)//vector<类型,分配器(/*一般不会写*/)>
cout<<cout_if(vi.begin(),vi.end(),not1(bind2nd(less<int>(),40)));//其中cout_if为algorithm,not1为functionadapter(negator) bind2nd为functionadapter(binder) less<int>为functionobject
return 0;
}
复杂度 Complexity,Big-oh
O(1)或O(c)常数时间(constant time)
O(n):称为线性时间(linear time)
O(log2 n)称为二次线性时间(sub—linlear time)
O(n*n)称为平方时间(quadratic time)
O(nnn)称为立方时间(cubic time)
O(2的n次方)称为指数时间
O(nlog2 n):
前闭后开区间
range-based for statement (since C++11)
for(decl:coll){
statement
}
for(int i :{2,3,57,9,13,17,19}){
std::cout<<i<<std::endl;
}
std::vector<double> vec;
...
for(auto elem:vec){
std::cout<<elem<<std::endl;
}
for(auto& elem:vec){
elem *= 3;
}
auto key
list<string> c;
list<string>::iterator ite;
ite = ::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);

list<string> c;
....
auto ite = ::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);
容器——结构及分类
Sequence Contaioners(序列式容器)
Array:数组(c++11增加的,连续空间)

Vector:动态数组(分配器去处理)

Deque:双向队列(先进先出)

List:双向链表
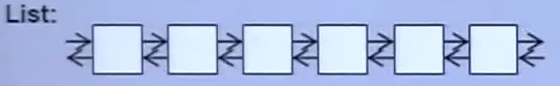
Forward-List:单向链表

Associative Containers(关联式容器)适合快速查找
Set/Multiset(红黑树是高度平衡二叉树,Set放的元素不能重复,Multiset放的元素可以重复)

Map/Multimap(key:value)

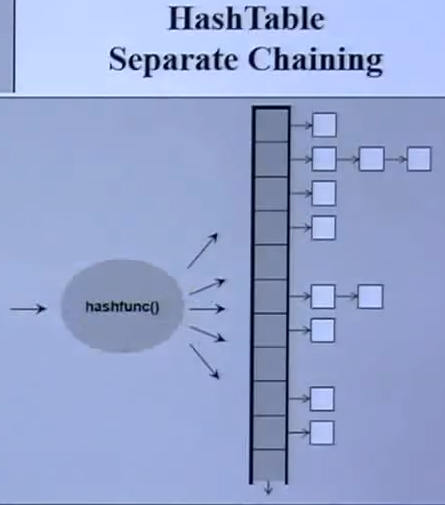
Unordered Containers(HashTable)
一次测试程序之辅助函数
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::string;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target = 0 ;
cout<<"target 0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target = 0 ;
char buf[10];
cout <<"target (0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):"
cin>> target;
snprintf(buf,10,"%d",target);//把后面的字符串赋值给buf,长度为min(10,后面那个字符串长度)-1
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a,const void* b)
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b);
}
使用容器array
#include<array>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>//qsort bsearch NULL
namespace jj01
{
void test_arry()
{
cout<<"\ntest_array()............\n";
array<long,ASIZE> c;
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i = 0 ; i<ASIZE;++i){
c[i] = rand();
}
cout<<"milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart<<endl;
cout<<"array.size()="<<c.size()<<endl;
cout<<"array.front()="<<c.front()<<endl;
cout<<"array.back()="<<c.back()<<endl;
cout<<"array.data()="<<c.data()<<endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
qsort(c.data(),ASIZE,sizeof(long),compareLongs);
long* pItem = (long*)bsearch(&target,(c.data()),ASIZE,siezeof(long), compareLongs);
cout<<"qsort()+bsearch(),milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;//要使用二分查找之前,数据一定要排序
if(pItem != NULL)
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found"<<endl;
}
}
使用容器Vector
#include<vector>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
namespace jj02
{
void test_vector(long& value)
{
cout<"\ntest_vector()..........\n";
vector<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i = 0; i<value;++i)
{
try{
snprintf(buf,10,"%d",rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}catch(exception& p){
cout<<"i="<<i<<""<<p.what()<<endl;
//曾经最高i=58389486 then std::dac_alloc
abort();
}
}
cout <<"milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
cout <<"vector.size():"<<c.size()<<endl;
cout<<"vector.front():"<<c.front<<endl;
cout<<"vector.back():"<<c.back()<<endl;
cout<<"vector.data():"<<c.data()<<endl;
cout<<"vector.capacity()="<<c.capacity()<<endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem=::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);
//find模板函数跟普通函数是一样的。其中双冒号是一个全局的东西
if(pItem != c.end())
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found!" <<endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin,c,end())
string* pItem = (string*) bsearch(&target,(c.data()),c.size(),sizeof(string)),compareLongs);
cout<<"sort()+bsearch(),milli-seconds:"<<(clock-timeStart);
if(pItem != NULL)
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found" <<endl;
}
}
}
//总结:不一定排序+二分查找 查找速度就快。
使用容器list
#include<vector>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
namespace jj03
{
void test_list(long& value)
{
cout<<"\ntest_list()....................\n"
list<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i = 0; i< value;++i)
{
try{
snprintf(buf,10,"%d",rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}catch(exception& p){
cout<<"i="<<i""<<p.what()<<endl;
abort();
}
}
cout<<"milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
cout<<"list.size():"<<c.size()<<endl;
cout<<"list.max_size()"<<c.max_size()<<endl;
cout<<"list.front()"<<c.front<<endl;
cout<<"list.back()"<<c.back()<<endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = ::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);
cout<<"::find(),milli-seconds"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
if(pItem != c.end())
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found"<<endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout<<"c.sort,milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号