封装、反射、描述符以及学生登陆系统
一、封装
-
-
广义上的封装:把方法和属性根据类别装到类中
-
侠义上的封装:私有化的方法和属性
-
-
方法、静态变量、实例化变量(对象属性)都可以私有化
-
所谓的私有化:就是只能在类的内部可见,类的外部是不能访问或查看的
 讲解
讲解#私有属性 class Goods: def __init__(self,name,price): self.name = name self.__price = price # 私有属性 def get_price(self): print(self.__price) apple= Goods('苹果',5) print(apple.name) # 苹果 apple.get_price() # 5 print(apple.__price) # AttributeError: 'Goods' object has no attribute '__price' # 私有的静态变量 class Role: __Country='China' # 静态变量的私有化 def func(self): print(self.__Country) print(Role.__Country) # 报错 : 因为不能再类的外部引用变量 Role().func() # China #私有方法 import hashlib class Auth: def __init__(self,user,pwd): self.username = user self.password = pwd def __md5_code(self): md5 = hashlib.md5(self.username.encode('utf-8')) md5.update(self.password.encode('utf-8')) return md5.hexdigest() def login(self): if self.username == 'alex' and 'ee838c58e5bb3c9e687065edd0ec454f' == self.__md5_code(): return True # print(Auth.__dict__) #{'__module__': '__main__', '__init__': <function Auth.__init__ at 0x02FF2390>,'_Auth__md5_code': <function Auth.__md5_code at 0x02FF2ED0>,'login': <function Auth.login at 0x02FF2FA8>, '__dict__': <attribute'__dict__' of 'Auth' objects>, '__doc__': None} print(Auth.__module__) #'__main__' user = input('user>>>') pwd = input('password>>>') obj = Auth(user,pwd) # obj.__md5_code() # 报错的,私有的方法不能在类的外部被使用 obj._Auth__md5_code() # 不报错的 ret = obj.login() if ret: print('登陆成功') #私有化是怎么完成的?在类部定义的时候完成的,加载类时。 class Goods: def __init__(self,name,price): self.name = name self.__price = price # 私有属性 def get_price(self): print(self.__price) def set_num(self): self.__num = 20 # 只要在类中有__的赋值,就会进行私有化 def __private(self): print(_Goods__private) # 私有的形成 5, 也就是说我们是可以查看私有属性的的 _类名__属性 apple = Goods('苹果',5) print(apple.__dict__) print(Goods.__dict__) #{'_Goods__private': <function Goods.__private at 0x03312ED0>,……} print(apple._Goods__price) # 私有的形成 print(apple._Goods__private) # 类私有<bound method Goods.__private of <__main__.Goods object at 0x03746E30>> # print(apple.__private()) # 报错,没有这个函数 # 所有的私有的变化都是在类的[内部]定义的时候完成的 apple.__num = 10 print(apple.__dict__) #{'name': '苹果', '_Goods__price': 5, '__num': 10} apple.set_num() print(apple.__dict__) #{'name': '苹果', '_Goods__price': 5, '__num': 10, '_Goods__num': 20} print(apple.__num) #10 class Foo: def __init__(self): self.__func() #这里的__func是_Foo__func(),各自的私有化在加载的就已经私有了 def __func(self): print('in foo') # 私有的属性可以被继承么? 不能,在加载类时,就已经把名字私有化了 class Son(Foo): def __func(self): # 此方法不会加载, print('in son') #def _Foo__func(self): # 此方法会加载,哈哈哈,如果自己把名字改成父类名字,就会执行自己的 #print('in son') # 下面的结果就会改为:in son a=Son() #in foo print(Son.__dict__) #{……'_Son__func': <function Son.__func at 0x03022C90>,} print(Foo.__dict__) #{……'_Foo__func': <function Foo.__func at 0x03022F60>, } print(a.__dict__) #{} #例2 class User: def __wahaha(self): print('in user') class VipUser(User): def func(self): self.__wahaha() #所以不继承父类,因为名字都不一样,私有化后 VipUser().func() # 报错,因为在命名空间中根本不存在一个_VipUser__wahaha
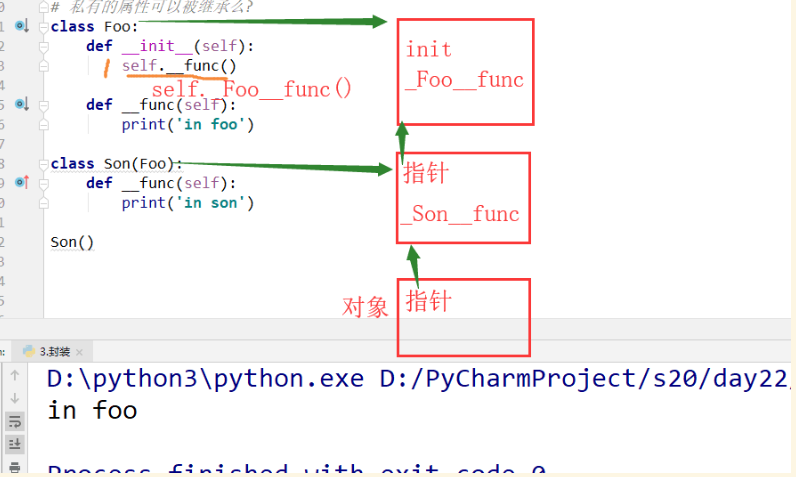
总结:
私有的这个概念 :但凡在类的外面 都不能用,因为实际名字变了,但也可以改名字来继承
私有的所有内容 : 实例变量(对象属性),静态变量(类变量),方法都不能被子类继承
公有的 在类的内部外部随便用 public
私有的 private 只能在类的内部使用 既不能被继承 也不能在类的外部使用
二、类的描述符
1、

#装饰器返回年纪 import time class Person: def __init__(self,name,birth): self.name = name self.birth = birth @property def age(self): # 返回年纪 struct_t = time.localtime() age = struct_t.tm_year - int(self.birth.split('-')[0]) return age alex = Person('alex','1965-5-12') print(alex.age) #54 #装饰器返回 class Goods: discount = 0.8 def __init__(self, name, price): self.name = name self.__price = price @property def price(self): #私有变量虽然不可以按原本的方式访问,但是可以使用property,改变 p = self.__price * self.discount return p apple = Goods('苹果', 5) # {'name': '苹果', '_Goods__price': 5} 返回私有变量, banana = Goods('香蕉', 10) #{'name': '香蕉', '_Goods__price': 10} print(apple.__dict__) print(banana.__dict__) print(apple.name) # 苹果 print(apple.price) # 4.0 print(banana.price) #8.0 Goods.discount = 1 print(apple.price) #5 print(banana.price) #10 #属性.setter修改属性 class Goods: discount = 0.8 def __init__(self, name, price): self.name = name self.__price = price @property # 只支持obj.price的方式查看这个结果,不支持修改,也不支持删除 def price(self): p = self.__price * self.discount return p @price.setter # 其实这里是类似于纵向装饰器,先设置,在进入上面的peoperty,最后返回属性 def price(self,value): self.__price = value apple = Goods('苹果', 5) banana = Goods('香蕉', 10) print(apple.price) # 4 apple.price = 8 # 对应的调用的是被setter装饰的price方法 print(apple.price) # 6.4 对应调用的是被property装饰的price方法 class Goods: discount = 0.8 def __init__(self, name, price): self.name = name self.__price = price @property # 只支持obj.price的方式查看这个结果,不支持修改,也不支持删除 def price(self): p = self.__price * self.discount return p @price.setter # 设置属性 def price(self,value): if type(value) is int or type(value) is float: self.__price = value # @price.deleter # 删除属性 会自动删除属性 # def price(self): # del self.__price # 想删除一个属性 apple = Goods('苹果', 5) print(Goods.__dict__) # del apple.price #执行后 就没有price属性了,后面都报错 print(apple.__dict__) #{'name': '苹果', '_Goods__price': 5} apple.price apple.price = 9 #设置 print(apple.price) #7.2 #总结 # 私有的 :通过过给__名字这样的属性或者方法加上当前所在类的前缀,把属性隐藏起来了 # 只能在本类的内部使用,不能在类的外部使用,不能被继承 # property 把一个方法伪装成属性 # property和私有的两个概念一起用 # 定义一个私有的 # 再定义一个同名共有的方法,被property装饰 # @方法名.setter # @方法名.deleter
2、

class Fruits: __discount = 0.8 def __init__(self, name, price): print('init',self) self.name = name self.__price = price #给对象创建一个以类名为基础的变量,以便下次类调用 @classmethod # 把一个方法从对象方法,变成一个类方法 def change_discount(cls,value): cls.__discount = value # cls到底是谁??? Fruits @classmethod def get_discount(cls): return cls.__discount print(Fruits.get_discount()) # 0.8 Fruits.change_discount(1) print(Fruits.get_discount()) # 1 # 类方法 # 1. 有些时候我们要修改的是类中的静态变量/类变量,此时根本不会和self有任何的操作关联 # 2.这时传一个self参数对我们来说完全没有用, 我们希望接受的是当前我们所在的类 apple = Fruits('apple',8) apple.change_discount(0.5) # 会去找父类 print(Fruits.get_discount()) # 0.5 # 类方法推荐使用类名调用而不是使用对象名调用
3、

class A: @staticmethod # 声明这个方法只是一个普通的不会使用任何和这个类中的变量相关的方法 def func(): # 此时 func是一个静态方法 print('既不操作和self相关的内容') print('也不操作和类名相关的内容') A.func() #打印…… class Student: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name @staticmethod def login(): pass # 先获取这个学生的用户名和密码 # 判断他登录成功之后进行实例化 # Student.login() # stu = Student('alex')
三、反射
1、反射 通过字符串属性名 得到真正的这个字符串的名字对应的对象的属性值

class Student: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name def show_courses(self): print('调用了 show courses') def select_course(self): print('调用了 select course') def show_selected_course(self): print('调用了 show_selected_course') def quit(self): print('调用了 quit') wu = Student('吴彪') # 反射 通过字符串属性名 得到真正的这个字符串的名字对应的对象的属性值 ret = getattr(wu,'name') # 内置函数 可以查看属性 print(ret) # 吴彪 # print(getattr(wu,'show_courses')) # wu.show_courses getattr(wu,'show_courses')() #调用了 show courses getattr(wu,'select_course')() #调用了 select course ***** while True: name = input('user>>>') if hasattr(wu,name): func_attr = getattr(wu,name) # 如果取出对象属性名 if callable(func_attr): #是否可以调用 func_attr() else: print(func_attr)
四、学生登陆课程

import hashlib import pickle import os def md(user,pw): md1=hashlib.md5(user.encode('utf-8')) md1.update(pw.encode('utf-8')) return md1.hexdigest() def write(person,path): with open(path,'ab') as f: pickle.dump(person,f) class Person: def __init__(self,name,pw): self.name = name self.pw = pw class Student(Person): #学生类 def __init__(self,name,pw,course=None): super().__init__(name,pw) self.identity='student' def register(user,pw): pw = md(user,pw) student= Student(user,pw) write(student,f'./user/{user}') return True def choose_course(self,course): self.course =course write(self,f'./student_course/{self.name}_course') return 'register success!' def read_data(self): student_user_course = os.listdir('./student_course/') if f'{self.name}_course' in student_user_course: return pick_read(f'./student_course/{self.name}_course') return False class Admin(Person): def __init__(self,user,pw): super().__init__(user,pw) self.identity = 'admin' def admin_register(user,pw): pw = md(user,pw) person = Admin(user,pw) write(person,f'./user/{user}') return True def see_student(self): student_user = os.listdir('./user/') for i in student_user: if i != self.name:print(f'ID:{pick_read(f"./user/{i}").name}'.center(40)) def see_student_course(self): student_user_course = os.listdir('./student_course/') for i in student_user_course: course_read(pick_read(f'./student_course/{i}')) # Admin.admin_register('admin','123') class Course: def __init__(self,name,price,month,teacher): self.name =name self.price =price self.month = month self.teacher = teacher def create_course(name,price,month,teacher): course = Course(name,price,month,teacher) # print(course.name) with open('./course/course','ab') as f:pickle.dump(course,f) return True def read_course(): li = [] with open('./course/course','rb') as f: while True: try: li.append(pickle.load(f).__dict__) except:break # print(li) return li def course_read(obj): print(f'ID:{obj.name},course:{obj.course.name},course_price{obj.course.price},teacher:{obj.course.teacher}') def see_all_course(): course = Course.read_course() for i,v in enumerate(course,1): print(f'order:{i} course:{course[i-1]["name"]} course price:{course[i-1]["price"]}'.center(30)) return course def login_in(user,pw): listsdir = os.listdir('./user/') if user in listsdir: with open(f'./user/{user}','rb') as f: user_dic = pickle.load(f) # print(user_dic.__dict__) if user == user_dic.name and md(user,pw)==user_dic.pw: return user_dic else:return def login_input(): while True: user= input('Please input your ID: ').strip() pw = input('your Password: ').strip() if user and pw :break return user,pw def courese_input(): name = input('请输入课程名称>>>').replace(' ', '') price = int(input('请输入课程价格>>>').replace(' ', '')) month = input('请输入课程周期>>>').replace(' ', '') teacher = input('请输入授课老师>>>').replace(' ', '') Course.create_course(name, price, month, teacher) return f'create {name}course success'.center(40) def pick_read(path): with open(path,'rb') as f2: a = pickle.load(f2) return a taget = True while taget: user,pw = login_input() ret = login_in(user,pw) if ret: if ret.identity =='admin': print(f'{ret.name} 欢迎登陆!'.center(50)) while taget: li_1 =['创建用户' ,'创造课程' ,' 查看课程' , '查看学生', '查看学生选课 ', ' 退出程序 '] for i,v in enumerate(li_1,1):print(i,v) choose = input('choose your action: ') if choose and choose.isnumeric() and 0<int(choose)<=6 : if choose =='1': user,pw =login_input() if Student.register(user,pw):print('sign up success!'.center(50)) elif choose == '2':print(courese_input()) elif choose =='3': see_all_course() elif choose =='4': ret.see_student() elif choose =='5':ret.see_student_course() elif choose =='6': break elif ret.identity == 'student': while taget: li_2 =['search for course' ,'choose course' ,'my course' , 'exit'] for i,v in enumerate(li_2,1):print(i,v) choose=input('take your action: ').strip() if choose and choose.isnumeric() and int(choose) <= 4 and int(choose) > 0: if choose =='1':see_all_course() elif choose =='2': li_3=see_all_course() num = input('choose course num: ').strip() if num and num.isnumeric() and int(num) <= len(li_3) and int(num) > 0: n=int(num)-1 choose_course = Course(li_3[n]['name'],li_3[n]['price'],li_3[n]['month'],li_3[n]['teacher']) a = ret.choose_course(choose_course) # print(a) elif choose =='3': a = ret.read_data() if a ==False:print('No course'.center(50)) else:course_read(a) elif choose =='4': print('see you later!'.center(50)) break else:print('something of your choose is wrong!'.center(50)) else:print(" wrong! ID doesn't find ".center(50))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号