Entity Framework应用:使用Code First模式管理数据库创建和填充种子数据
一、管理数据库连接
1、使用配置文件管理连接之约定
在数据库上下文类中,如果我们只继承了无参数的DbContext,并且在配置文件中创建了和数据库上下文类同名的连接字符串,那么EF会使用该连接字符串自动计算出数据库的位置和数据库名。比如,我们的数据库上下文定义如下:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Data.Entity; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace ConventionConfigure.EF 9 { 10 /// <summary> 11 /// 继承无参数的DbContext 12 /// </summary> 13 public class SampleDbEntities :DbContext 14 { 15 public SampleDbEntities() 16 { 17 // 数据库不存在时创建数据库 18 Database.CreateIfNotExists(); 19 } 20 } 21 }
在配置文件中定义的连接字符串如下:
<connectionStrings>
<add name="SampleDbEntities" connectionString="Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=TestDb;Integrated Security=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
定义的连接字符串中name的value值和创建的数据库上下文类的类名相同,这样EF会使用该连接字符串执行数据库操作,究竟会发生什么呢?
运行程序,Program类定义如下:
1 using ConventionConfigure.EF; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace ConventionConfigure 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 using (var context = new SampleDbEntities()) 15 { } 16 17 Console.WriteLine("创建成功"); 18 Console.ReadKey(); 19 } 20 } 21 }
当运行应用程序时,EF会寻找我们的数据库上下文类,即“SampleDbEntities”,并在配置文件中寻找和它同名的连接字符串,然后它会使用该连接字符串计算出应该使用哪个数据库provider,之后检查数据库位置,之后会在指定的位置创建一个名为TestDb.mdf的数据库文件,同时根据连接字符串的Initial Catalog属性创建了一个名为TestDb的数据库。创建的数据库结构如下:
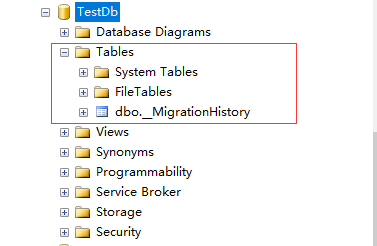
查看创建后的数据库,会发现只有一张迁移记录表。
2、使用已经存在的ConnectionString
如果我们已经有了一个定义数据库位置和名称的ConnectionString,并且我们想在数据库上下文类中使用这个连接字符串,连接字符串如下:
<connectionStrings>
<add name="AppConnection" connectionString="Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=TestDb;Integrated Security=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
以上面创建的数据库TestDb作为已经存在的数据库,新添加实体类Student,使用已经存在的ConnectionString查询数据库的Student表,Student实体类定义如下:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace ExistsConnectionString.Model 9 { 10 [Table("Student")] 11 public class Student 12 { 13 public int Id { get; set; } 14 15 public string Name { get; set; } 16 17 public string Sex { get; set; } 18 19 public int Age { get; set; } 20 } 21 }
我们将该连接字符串的名字传入数据库上下文DbContext的有参构造函数中,数据库上下文类定义如下:
1 using ExistsConnectionString.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Entity; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace ExistsConnectionString.EF 10 { 11 public class SampleDbEntities : DbContext 12 { 13 public SampleDbEntities() 14 : base("name=AppConnection") 15 { 16 17 } 18 19 // 添加到数据上下文中 20 public virtual DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } 21 } 22 }
上面的代码将连接字符串的名字传给了DbContext类的有参构造函数,这样一来,我们的数据库上下文就会开始使用该连接字符串了,在Program类中输出Name和Age字段的值:
1 using ExistsConnectionString.EF; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace ExistsConnectionString 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 using (var context = new SampleDbEntities()) 15 { 16 foreach (var item in context.Students) 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("姓名:"+item.Name+" "+"年龄:"+item.Age); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }
运行程序,发现会报下面的错误:
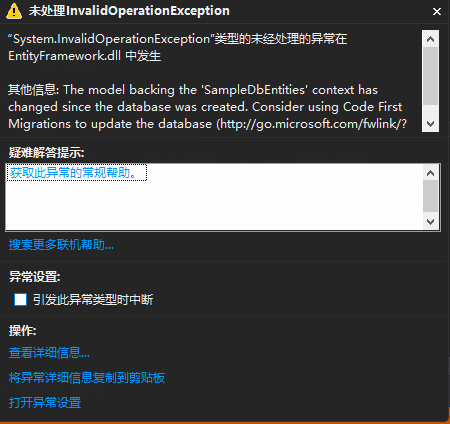
出现上面报错的原因是因为数据库上下文发生了改变,与现有数据库不匹配。解决方案:
1、把数据库里面的迁移记录表删掉或者重命名即可。
重新运行程序,结果如下:
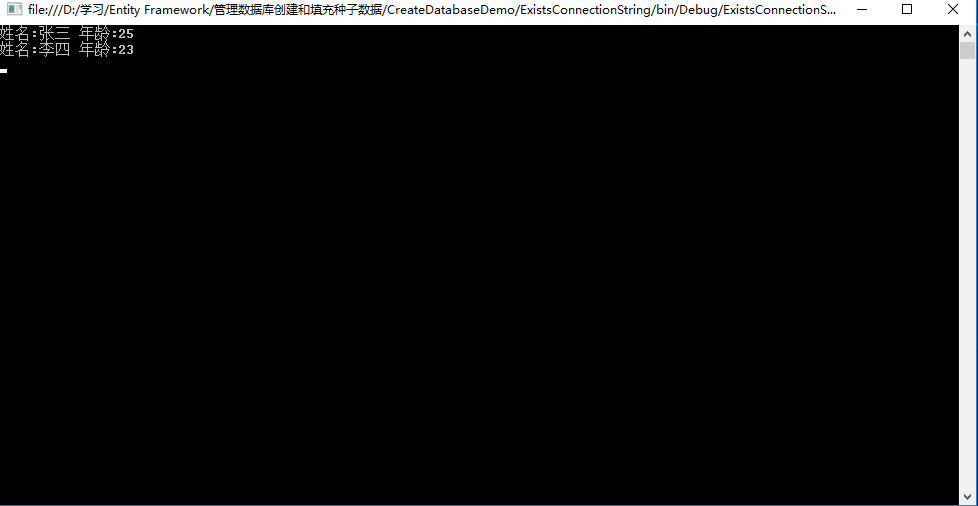
注意:如果在配置文件中还有一个和数据库上下文类名同名的ConnectionString,那么就会使用这个同名的连接字符串。无论我们对传入的连接字符串名称如何改变,都是无济于事的,也就是说和数据库上下文类名同名的连接字符串优先权更大。(即约定大于配置)
3、使用已经存在的连接
通常在一些老项目中,我们只会在项目中的某个部分使用EF Code First,同时,我们想对数据上下文类使用已经存在的数据库连接,如果要实现这个,可将连接对象传给DbContext类的构造函数,数据上下文定义如下:
1 using ExistsDbConnection.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Common; 5 using System.Data.Entity; 6 using System.Linq; 7 using System.Text; 8 using System.Threading.Tasks; 9 10 namespace ExistsDbConnection.EF 11 { 12 public class SampleDbEntities :DbContext 13 { 14 public SampleDbEntities(DbConnection con) 15 : base(con, contextOwnsConnection: false) 16 { 17 18 } 19 20 public virtual DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } 21 } 22 }
这里要注意一下contextOwnsConnection参数,之所以将它作为false传入到上下文,是因为它是从外部传入的,当上下文超出了范围时,可能会有人想要使用该连接。如果传入true的话,那么一旦上下文出了范围,数据库连接就会立即关闭。
Program类定义如下:
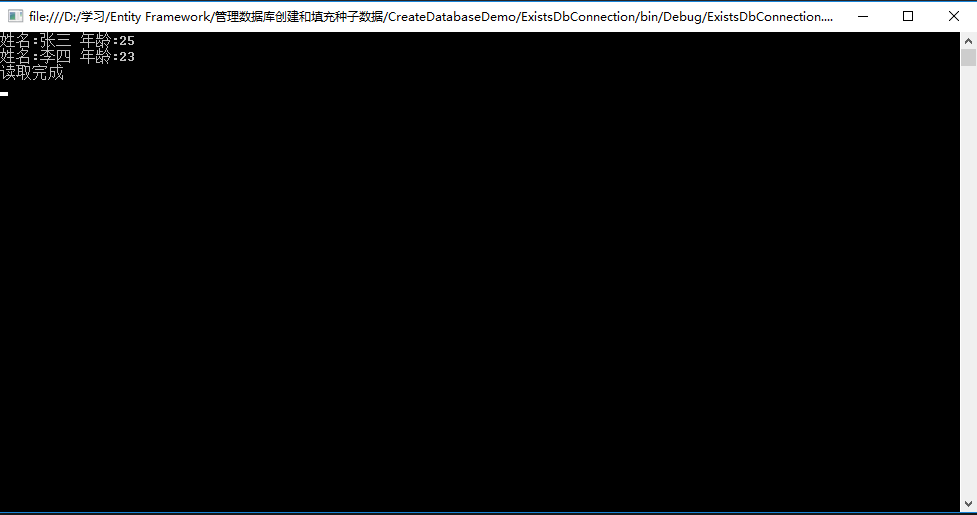
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Data.Common; 4 using System.Data.SqlClient; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 using System.Configuration; 9 using ExistsDbConnection.EF; 10 11 namespace ExistsDbConnection 12 { 13 class Program 14 { 15 static void Main(string[] args) 16 { 17 // 读取连接字符串 18 string conn = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["AppConnection"].ConnectionString; 19 // DbConnection是抽象类,不能直接实例化,声明子类指向父类对象 20 DbConnection con = new SqlConnection(conn); 21 using (var context = new SampleDbEntities(con)) 22 { 23 foreach (var item in context.Students) 24 { 25 Console.WriteLine("姓名:" + item.Name + " " + "年龄:" + item.Age); 26 } 27 } 28 29 Console.WriteLine("读取完成"); 30 Console.ReadKey(); 31 } 32 } 33 }
运行程序,结果如下:
二、管理数据库创建
首次运行EF Code First应用时,EF会做下面的这些事情:
1、检查正在使用的DbContext类。
2、找到该上下文类使用的connectionString。
3、找到领域实体并提取模式相关的信息。
4、创建数据库。
5、将数据插入系统。
一旦模式信息提取出来,EF会使用数据库初始化器将该模式信息推送给数据库。数据库初始化器有很多可能的策略,EF默认的策略是如果数据库不存在,那么就重新创建;如果存在的话就使用当前存在的数据库。当然,我们有时也可能需要覆盖默认的策略,可能用到的数据库初始化策略如下:
CreateDatabaseIfNotExists:CreateDatabaseIfNotExists:顾名思义,如果数据库不存在,那么就重新创建,否则就使用现有的数据库。如果从领域模型中提取到的模式信息和实际的数据库模式不匹配,那么就会抛出异常。
DropCreateDatabaseAlways:如果使用了该策略,那么每次运行程序时,数据库都会被销毁。这在开发周期的早期阶段通常很有用(比如设计领域实体时),从单元测试的角度也很有用。
DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges:这个策略的意思就是说,如果领域模型发生了变化(具体而言,从领域实体提取出来的模式信息和实际的数据库模式信息失配时),就会销毁以前的数据库(如果存在的话),并创建新的数据库。
MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion:如果使用了该初始化器,那么无论什么时候更新实体模型,EF都会自动地更新数据库模式。这里很重要的一点是:这种策略更新数据库模式不会丢失数据,或者是在已有的数据库中更新已存在的数据库对象。MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion初始化器只有从EF4.3才可用。
1、设置初始化策略
EF默认使用CreateDatabaseIfNotExists作为默认初始化器,如果要覆盖这个策略,那么需要在DbContext类中的构造函数中使用Database.SetInitializer方法,下面的例子使用DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges策略覆盖默认的策略。数据库上下文类定义如下:
1 using InitializationStrategy.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Entity; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace InitializationStrategy.EF 10 { 11 public class SampleDbEntities : DbContext 12 { 13 public SampleDbEntities() 14 : base("name=AppConnection") 15 { 16 // 使用DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges策略覆盖默认的策略 17 Database.SetInitializer<SampleDbEntities>(new DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges<SampleDbEntities>()); 18 } 19 20 // 添加到数据上下文中 21 public virtual DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } 22 } 23 }
这样一来,无论什么时候创建上下文类,Database.SetInitializer()方法都会被调用,并且将数据库初始化策略设置为DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges。
Student领域实体类新增加Email和Address两个属性:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace InitializationStrategy.Model 9 { 10 [Table("Student")] 11 public class Student 12 { 13 public int Id { get; set; } 14 15 public string Name { get; set; } 16 17 public string Sex { get; set; } 18 19 public int Age { get; set; } 20 21 public string Email { get; set; } 22 23 public string Address { get; set; } 24 } 25 }
Program类定义如下:
1 using InitializationStrategy.EF; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace InitializationStrategy 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 using (var context = new SampleDbEntities()) 15 { 16 foreach (var item in context.Students) 17 { 18 19 } 20 } 21 22 Console.WriteLine("创建成功"); 23 Console.ReadKey(); 24 } 25 } 26 }
运行程序后,数据库表结构如下:
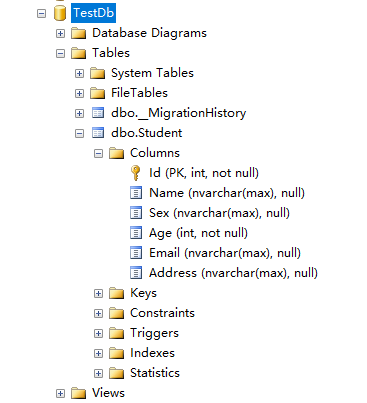
注意:如果处于生产环境,那么我们肯定不想丢失已经存在的数据。这时我们就需要关闭该初始化器,只需要将null传给Database.SetInitlalizer()方法,如下所示:
public SampleDbEntities(): base("name=AppConnection") { Database.SetInitializer<SampleDbEntities>(null); }
2、填充种子数据
到目前为止,无论我们选择哪种策略初始化数据库,生成的数据库都是一个空的数据库。但是许多情况下我们总想在数据库创建之后、首次使用之前就插入一些数据。此外,开发阶段可能想以admin的资格为其填充一些数据,或者为了测试应用在特定的场景中表现如何,想要伪造一些数据。
当我们使用DropCreateDatabaseAlways和DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges初始化策略时,插入种子数据非常重要,因为每次运行应用时,数据库都要重新创建,每次数据库创建之后在手动插入数据非常乏味。接下来我们看一下当数据库创建之后如何使用EF来插入种子数据。
为了向数据库插入一些初始化数据,我们需要创建满足下列条件的数据库初始化器类:
1、从已存在的数据库初始化器类中派生数据。
2、在数据库创建期间种子化。
下面演示如何初始化种子数据
1、定义领域实体类
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace InitializationSeed.Model 9 { 10 [Table("Employee")] 11 public class Employee 12 { 13 public int EmployeeId { get; set; } 14 public string FirstName { get; set; } 15 public string LastName { get; set; } 16 17 } 18 }
2、创建数据库上下文
使用EF的Code First方式对上面的模型创建数据库上下文:
public class SampleDbEntities : DbContext { public virtual DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; } }
3、创建数据库初始化器类
假设我们使用的是DropCreateDatabaseAlways数据库初始化策略,那么初始化器类就要从该泛型类继承,并传入数据库上下文作为类型参数。接下来,要种子化数据库就要重写DropCreateDatabaseAlways类的Seed()方法,而Seed()方法拿到了数据库上下文,因此我们可以使用它来将数据插入数据库:
1 using InitializationSeed.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Entity; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace InitializationSeed.EF 10 { 11 12 /// <summary> 13 /// 数据库初始化器类 14 /// </summary> 15 public class SeedingDataInitializer : DropCreateDatabaseAlways<SampleDbEntities> 16 { 17 /// <summary> 18 /// 重写DropCreateDatabaseAlways的Seed方法 19 /// </summary> 20 /// <param name="context"></param> 21 protected override void Seed(SampleDbEntities context) 22 { 23 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) 24 { 25 var employee = new Employee 26 { 27 FirstName="测试"+(i+1), 28 LastName="工程师" 29 }; 30 31 context.Employees.Add(employee); 32 33 } 34 base.Seed(context); 35 } 36 } 37 }
上面的代码通过for循环创建了6个Employee对象,并将它们添加给数据库上下文类的Employees集合属性。这里值得注意的是我们并没有调用DbContext.SaveChanges()方法,因为它会在基类中自动调用。
4、将数据库初始化器类用于数据库上下问类
1 using InitializationSeed.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Entity; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace InitializationSeed.EF 10 { 11 public class SampleDbEntities :DbContext 12 { 13 public SampleDbEntities() 14 : base("name=AppConnection") 15 { 16 // 类型传SeedingDataInitializer 17 Database.SetInitializer<SampleDbEntities>(new SeedingDataInitializer()); 18 } 19 20 // 领域实体添加到数据上下文中 21 public virtual DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; } 22 } 23 }
5、Main方法中访问数据库
1 using InitializationSeed.EF; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace InitializationSeed 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 using (var context = new SampleDbEntities()) 15 { 16 foreach (var item in context.Employees) 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("FirstName:"+item.FirstName+" "+"LastName:"+item.LastName); 19 } 20 } 21 22 Console.WriteLine("读取完成"); 23 Console.ReadKey(); 24 } 25 } 26 }
6、运行程序,查看结果
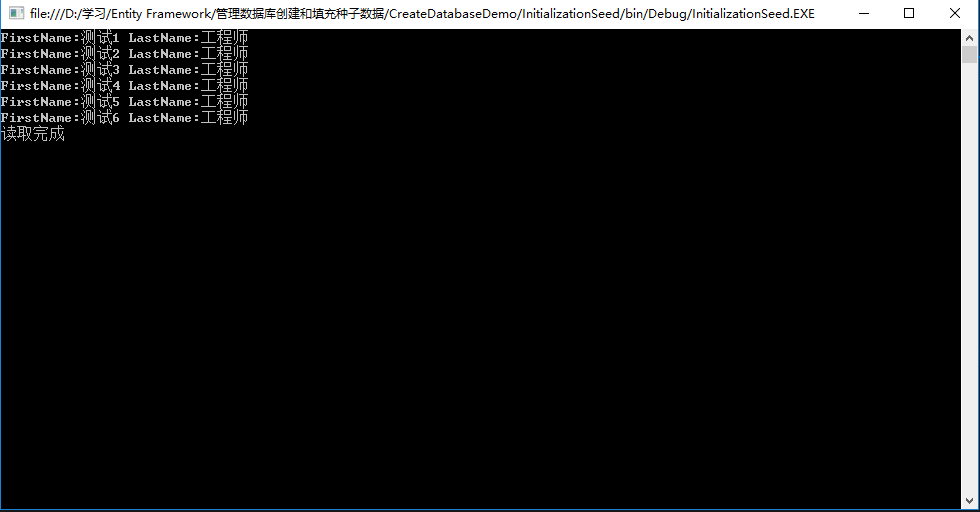
查看数据库
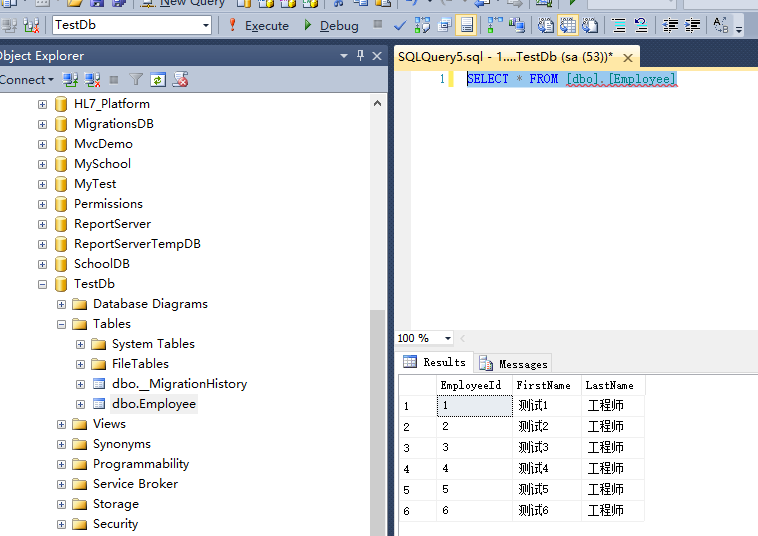
种子数据填充完成。
5、使用数据迁移的方式填充种子数据
使用数据迁移的方式会生成Configuration类,Configuration类定义如下:
1 namespace DataMigration.Migrations 2 { 3 using System; 4 using System.Data.Entity; 5 using System.Data.Entity.Migrations; 6 using System.Linq; 7 8 internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<DataMigration.SampleDbEntities> 9 { 10 public Configuration() 11 { 12 AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false; 13 } 14 15 protected override void Seed(DataMigration.SampleDbEntities context) 16 { 17 // This method will be called after migrating to the latest version. 18 19 // You can use the DbSet<T>.AddOrUpdate() helper extension method 20 // to avoid creating duplicate seed data. 21 } 22 } 23 }
重写Configuration类的Seed()方法也可以实现插入种子数据,重写Seed()方法:
1 namespace DataMigration.Migrations 2 { 3 using DataMigration.Model; 4 using System; 5 using System.Data.Entity; 6 using System.Data.Entity.Migrations; 7 using System.Linq; 8 9 internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<DataMigration.SampleDbEntities> 10 { 11 public Configuration() 12 { 13 AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false; 14 } 15 16 protected override void Seed(DataMigration.SampleDbEntities context) 17 { 18 // This method will be called after migrating to the latest version. 19 20 // You can use the DbSet<T>.AddOrUpdate() helper extension method 21 // to avoid creating duplicate seed data. 22 23 context.Employees.AddOrUpdate( 24 new Employee { FirstName = "测试1", LastName = "工程师" }, 25 new Employee { FirstName = "测试2", LastName = "工程师" } 26 27 ); 28 } 29 } 30 }
使用数据迁移,然后查看数据库结果:
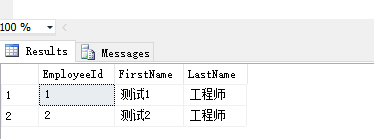
发现使用数据迁移的方式也将种子数据插入到了数据库中。
代码下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i5By8EL




· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
2016-12-14 Windows服务二:测试新建的服务、调试Windows服务
2016-12-14 Windows服务一:新建Windows服务、安装、卸载服务