算法笔试题面试题
算法笔试面试
十大排序算法:冒泡排序,选择排序,插入排序,归并排序,堆排序,快速排序、希尔排序、计数排序,基数排序,桶排序。
ps:重点在理解原理,写代码的时候要由里往外写。
冒泡排序:
思想:两个相邻的元素比较并交换。
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr.length == 0){
return;
}
// 一共进行元素-1次排序
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length -1; i++) {
// 只需要对没有排序的进行排序
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
//将前一个比后一个大的两元素进行交换
if (arr[j+1] < arr[j]) {
// int tmp = arr[j+1];
// arr[j+1] = arr[j];
// arr[j] = tmp;
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {5, 8, 6, 3, 9, 2, 1, 7};
bubbleSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 3, 4, 7, 2, 9};
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++){
if(nums[i] < nums[j]){ //降序排列
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
Arrays.stream(nums).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
选择排序
思想:每次从剩余元素中找最大(最小)元素进行交换。
选择排序可以看做是冒泡排序的一种优化。
public class Solution {
public int[] choiceSort(int[] nums){
if(nums.length == 0){
return nums;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 最小数的下标,每个循环开始总是假设第一个数最小
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) {
if(nums[j] < nums[minIndex]){
minIndex = j;
}
}
// 进行元素的交换
int temp = nums[minIndex];
nums[minIndex] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
return nums;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {5, 8, 6, 3, 9, 2, 1, 7};
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] ret = solution.choiceSort(arr);
Arrays.stream(ret).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
插入排序
思想:就是将要待排序的元素,在已经排好序的序列中找到合适的位置进行插入即可。
对于基本有序的数组来说最好用。
思想:就好像是打麻将或者是玩扑克牌。只不过略微有点区别。
public static void insertSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr.length == 0){
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i ; j >0; j--) {
if(arr[j ] < arr[j - 1]){
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = tmp;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {5, 8, 6, 3, 9, 2, 1, 7};
insertSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
第二种写法:// TODO 待理解
public class Solution {
public int[] insertSort(int[] nums){
// 健壮性校验
if(nums.length == 0){
return nums;
}
// 当前待排序数据,该元素之前的元素均已被排序过
int currentValue;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length -1; i++) {
// 已被排序数据的索引
int preIndex = i;
currentValue = nums[preIndex + 1];
// 在已被排序过数据中倒序寻找合适的位置,如果单管待排序数据比比较的元素要小,将比较的元素后移一位
while (preIndex >= 0 && currentValue < nums[preIndex]){
// 将当前元素后移一位
nums[preIndex + 1] = nums[preIndex];
preIndex--;
}
// while循环结束时,说明已经找到了当前待排序数据的合适位置,插入
nums[preIndex + 1] = currentValue;
}
return nums;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {5, 8, 6, 3, 9, 2, 1, 7};
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] ret = solution.insertSort(arr);
Arrays.stream(ret).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
快速排序
思想:首先选择一个基准数,然后将数组中剩余的数据依次和基准数进行比较,所有比基准数小的放到基准数前面,所有比基准数大的元素放到基准数后面,这样就将整个数组分成了两部分,然后再将这每一部分分别进行快速排序,说白了就是运用了一种分而治之的思想。
视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ey4y1k7s1/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=273847a809b909b44923e3af1a7ef0b1
public class Solution {
/**
* 快速排序
* @param arr 待排序数组
* @param left 左指针
* @param right 右指针
* @return
*/
public int[] quickSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
// 健壮性校验
if (arr.length == 0) {
return arr;
}
int l = left;
int r = right;
// 基准值
int pivot = arr[(left+right)/2];
while (l<r){
// 如果左指针位置的数字小于基准值,就让左指针往后移动
while (arr[l]< pivot){
l++;
}
// 如果右指针位置的数字大于基准值,就让右指针往前移动
while (arr[r] > pivot){
r--;
}
// 特殊情况:如果左指针大于右指针的话,就跳出循环
if(l >= r){
break;
}
// 如果pivot轴左右指针位置对应的数字,左指针对应的数字大于右指针对应的数字,就将这两个位置的数字进行交换
int temp = arr[r];
arr[r] = arr[l];
arr[l] = temp;
// 还会有两种特殊情况,就是左指针对应的数字等于pivot值,右指针对应的数字等于pivot值
if(arr[l] == pivot){
r--;
}
if(arr[r] == pivot){
l++;
}
}
if(l == r){
l++;
r--;
}
if(left<r){
quickSort(arr,left,r);
}
if(l<right){
quickSort(arr,l,right);
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {5, 8, 6, 3, 9, 2, 1, 7};
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] ret = solution.quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
Arrays.stream(ret).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
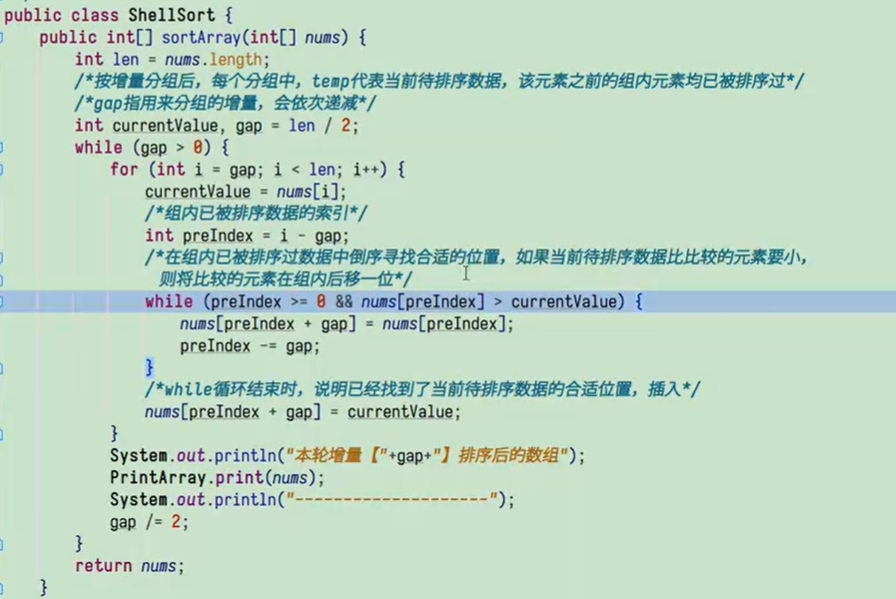
希尔排序
希尔排序是一种基于插入排序的算法,通过将整个数组分成多个子序列进行插入排序来提高排序的效率。说白了就是分成gap组。
一开始将整个待排序列分成gap= nums.length/2组,接着会分成gap= gap/2组,直到最后分成一组,将整个待排序数组进行一次插入排序就好了。
归并排序
思想:采用的是先分再治的思想,就是将待排序数组分成两块,然后每一块再进行划分,直到划分的每一块都只有一个元素的时候,这个时候再进行合并,当然合并的过程中要进行排序。
堆排序
适用场景:比方说我们有一个待排序数组,但是我们可能只是想要其中的最大值或者最小值,也就是说没有必要将整个数组都排好序,这个时候我们就可以使用堆排序了。
底层使用到了二叉树。
计数排序
计数排序是一种不比较元素大小的排序算法。
计数排序对一定范围内的整数排序时候的速度非常快,一般快于其他排序算法。但是计数排序局限性比较大,只限于对整数进行排序,而且待排序元素值分布较连续、跨度小的情况。
如果一个数组里面所有元素都是整数,而且都在0-k以内,那对于数组里每个元素来说,如果能知道数组里有多少项小于或等于该元素,就能够准确地给出该元素在排序后的数组中的位置。
除了待排序数组之外,还需要引入一个计数数组。
桶排序
桶排序是计数排序的升级版。
工作原理:假设输入数据服从均匀分布,将数据分到有限数量的桶里,每个桶再分别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序)。
基数排序
原理:利用个位、十位、百位的方式进行排序,说白了就是个位安排0-9个桶,十位也是,百位也是,等等。
leecode 二分查找
二分查找要求数组必须是有序的。
方式一:使用循环的方式
public class Solution {
/**
* 二分查找
*
* @return
*/
public int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
// 循环查找
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (target > arr[mid]) {
start = mid + 1;
} else if (target < arr[mid]) {
end = mid - 1;
} else { // 表示找到了
return mid;
}
}
// -1 表示没有查找到
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int target = 7;
Solution solution = new Solution();
int ret = solution.binarySearch(arr, target);
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
// TODO 方式二,采用递归方式。
爬楼梯
方法一:递归解法
public static int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n == 0){return 0;}
if(n == 1){return 1;}
if(n == 2){return 2;}
return climbStairs(n-1) + climbStairs(n-2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(climbStairs(3));
}
以上的解法存在重复计算的问题,我们可以使用hashmap集合来保存我们已经计算过的结果。
private static HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap();
public static int climbStairs2(int n) {
if(n == 0){return 0;}
if(n == 1){return 1;}
if(n == 2){return 2;}
if(null != map.get(new Integer(n))){
return map.get(new Integer(n));
}
int reslut = climbStairs(n-1) + climbStairs(n-2);
map.put(new Integer(n),reslut);
return reslut;
}
## 合并两个排序的链表
输入两个递增排序的链表,合并后的这两个链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
public class Test {
private static class ListNode<E>{
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val){
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val,ListNode<E> next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head){
while (null != head){
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private ListNode<Integer> mergeTwoLists(ListNode<Integer> head1, ListNode<Integer> head2){
ListNode<Integer> dummy = new ListNode<>(-1);
ListNode<Integer> pre = dummy;
while(head1 != null && head2 != null){
if(head1.val <= head2.val){
pre.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
}else {
pre.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
if(null == head1){
pre.next = head2;
}
if(null == head2){
pre.next = head1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode<Integer> list1 = new ListNode<>(1);
ListNode<Integer> list2 = new ListNode<>(3);
ListNode<Integer> list3 = new ListNode<>(5);
ListNode<Integer> list4 = new ListNode<>(7);
ListNode<Integer> list5 = new ListNode<>(9);
list1.next = list2;
list2.next = list3;
list3.next = list4;
list4.next = list5;
ListNode<Integer> l1 = new ListNode<>(2);
ListNode<Integer> l2 = new ListNode<>(4);
ListNode<Integer> l3 = new ListNode<>(6);
ListNode<Integer> l4 = new ListNode<>(8);
ListNode<Integer> l5 = new ListNode<>(10);
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = l3;
l3.next = l4;
l4.next = l5;
Test test = new Test();
ListNode<Integer> reslut = test.mergeTwoLists(list1, l1);
print(reslut);
}
}
请写出Java代码实现如下功能:读取一篇文章,输出其中出现次数最多的单词。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
words.add("hello");
words.add("world");
words.add("goods");
words.add("world");
words.add("world");
words.add("world");
words.add("world");
Map<String, Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {
if(countMap.get(words.get(i)) == null){
countMap.put(words.get(i), 1);
}else {
countMap.put(words.get(i), countMap.get(words.get(i)) + 1);
}
}
int maxCount = 0;
String maxCountWord = null;
// 遍历map
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : countMap.entrySet()){
if(maxCount < entry.getValue()){
maxCount = entry.getValue();
maxCountWord = entry.getKey();
}
}
System.out.println("出现次数最多的单词是:"+ maxCountWord + "出现次数:" + maxCount);
}
}
请写代码实现s=1+2-3+4-5+6-7...n请编写一个函数int calc(int n),传入参数n,返回s的值.
public class Test {
public static int calc(int n){
int sum = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if(i % 2 == 0){
sum += i;
}else {
sum -= i;
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Test.calc(5));
}
}
请写出Java代码,实现从一个无序数组中找到最大的5个元素
// 总体思路是先进行冒泡排序,之后再找出前五个元素。
public class Test {
public static int[] calc(int[] arr) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j ++) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1 - j; i++) {
int temp = 0;
if (arr[i] < arr[i + 1]) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5, 8, 2, 3, 9, 7, 4, 6, 10};
Test.calc(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print("\t" + arr[i]);
}
}
}
找出两数之和的下标
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出何为目标值的那两个整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中的同一个元素不能使用两遍。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
方法一:使用暴力枚举
public class Test {
// 方法一:使用暴力枚举
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length ; j++) {
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target){
System.out.println(nums[i] + " + " + nums[j] + " = " + (nums[i] + nums[j]));
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
// 如果没有找到就返回0
return new int[]{0};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {2,7,11,15};
int target = 9;
// 输出结果:[0,1]
Arrays.stream(twoSum(nums, target)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public class Test {
// 方法二:使用map进行映射
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// map.get(target - nums[i]) != i 也就是说找到的另外一个元素一定不能是第一个元素
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i]) && map.get(target - nums[i]) != i){
result[0] = i;
result[1] = map.get(target - nums[i]);
}
return result;
}
// 如果没有找到就返回0
return new int[]{0};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
// 输出结果:[0,1]
Arrays.stream(twoSum(nums, target)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public class Test {
// 方法三:还是使用map进行映射,只不过在第二种的基础上进行了简化。
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
result[0] = i;
result[1] = map.get(target - nums[i]);
return result;
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
// 如果没有找到就返回0
return new int[]{0};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
// 输出结果:[0,1]
Arrays.stream(twoSum(nums, target)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
链表翻转
第一种方式:通过改动指针的方式
public class Test {
// 定义链表节点和指针
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public static void print(ListNode head){
while(head != null){
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
public static ListNode iterate(ListNode head){
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode next = null;
while(head != null){
next = head.next; // 先将当前节点的下一个节点保存到next变量中
head.next = prev; // 将当前节点的下一个节点指向前一个节点
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(5);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
ListNode head = iterate(listNode1);
print(head);
}
}
public class Test {
// 定义链表节点和指针
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public static void print(ListNode head){
while(head != null){
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
// 使用递归的方式
public static ListNode recursion(ListNode head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode newhead = recursion(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newhead;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(5);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
ListNode head = recursion(listNode1);
print(head);
}
}
数组中三个数的最大乘积
思路,先对数组进行排序,排完序之后,在进行计算前三个或者是后三个数的乘积值。
public class Test {
public static int multiMost(int[] nums) {
// 先对数组进行排序,先手写一遍冒泡排序吧
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0 + i; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
// 如果想偷懒直接使用 Arrays.sort(nums);
return Math.max(nums[0] * nums[1] * nums[2], nums[nums.length - 1] * nums[nums.length - 2] * nums[nums.length - 3]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int result = multiMost(arr);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
TODO:还有另外一种算法,待看。
求斐波那契数列的第N为的值是多少
方法一:使用暴力递归算法
public class Test {
public static int calculate(int num) {
if(0 == num){
return 0;
}
if(1 == num){
return 1;
}
return calculate(num-1) + calculate(num -2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(calculate(10));
}
}
// TODO 还有两种算法待看
排列硬币
public class Test {
/**
*
* @param n 一共有的硬币数
* @return
*/
public static int arrangeCoins(int n) {
// i 表示第几层
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
n = n -i;
if(n <= i){
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(arrangeCoins(10));
}
}
// TODO 还有另外两种算法,待看
判断链表中是否有环
方式一:使用set集合
public class Test {
private static class ListNode<E>{
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val){
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val,ListNode<E> next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head){
while (null != head){
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private static boolean hasCycle(ListNode<Integer> head){
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while(head != null){
if(!set.add(head)){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode<Integer> list1 = new ListNode<>(1);
ListNode<Integer> list2 = new ListNode<>(3);
ListNode<Integer> list3 = new ListNode<>(5);
ListNode<Integer> list4 = new ListNode<>(7);
ListNode<Integer> list5 = new ListNode<>(9);
list1.next = list2;
list2.next = list3;
list3.next = list4;
list4.next = list5;
// 模拟存在环
list5.next = list3;
System.out.println(hasCycle(list1));
}
}
方式二:使用快慢指针的方式
private static boolean hasCycle(ListNode head){
if(null == head){
return false;
}
// 使用快慢指针进行判断
ListNode slowPtr = head, fastPtr = head;
while (slowPtr.next != null && fastPtr.next.next != null){
if(slowPtr.next == fastPtr.next.next){
return true;
}
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
}
return false;
}
质数的最大距离
public class Test {
public static boolean isPremium(int x) {
if (x == 1) {
return false;
}
if (x == 2) {
return true;
}
boolean flag = true; // true:是质数 false:不是质数
for (int i = 2; i < x; i++) {
if (x % i == 0) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
public static int maxDistance(int[] nums) {
// TODO 待完善边界条件
// 一个从前遍历,一个从后遍历
// 查找第一个质数
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
if (isPremium(nums[i])) {
// 查找第二个质数
for (int j = nums.length - 1; ; j--) {
if (isPremium(nums[j])) {
return j - i;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] nums = new int[]{4, 2, 9, 5, 3};
int[] nums = new int[]{10};
int distance = maxDistance(nums);
System.out.println(distance);
}
}
方式二:写一种给人看的
public static int maxDistance(int[] nums){
if(null == nums){
return -1;
}
int i,j;
for (i = 0; i < nums.length -1; i++) {
if(isPreim(nums[i])){
break;
}
}
for (j = nums.length - 1; j > 0; j--) {
if (isPreim(nums[j])){
break;
}
}
return j - i;
}
环形链表 II
public class Solution {
private static class ListNode<E> {
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val, ListNode<E> next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head) {
while (null != head) {
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private static ListNode hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (null == head) {
return null;
}
// 使用快慢指针进行判断
// 慢指针每次只移动一个单位,快指针每次移动两个单位
ListNode slowPtr = head, fastPtr = head;
boolean isCycle = false;
while (slowPtr.next != null && fastPtr.next.next != null) {
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
if (slowPtr == fastPtr) {
isCycle = true;
break;
}
}
if (isCycle) {
// 如果存在环的话,就让慢指针指指回到头结点,并且快慢指针往后移动相同的单位
slowPtr = head;
while (slowPtr != fastPtr) {
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next;
}
return slowPtr;
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode<Integer> list1 = new ListNode<>(1);
ListNode<Integer> list2 = new ListNode<>(2);
ListNode<Integer> list3 = new ListNode<>(3);
ListNode<Integer> list4 = new ListNode<>(4);
ListNode<Integer> list5 = new ListNode<>(5);
list1.next = list2;
list2.next = list3;
list3.next = list4;
list4.next = list2;
ListNode node = hasCycle(list1);
System.out.println(node.val);
}
}
合并两个有序数组
方式一:使用jdk自带的工具类进行排序
public class Test {
public static int[] merge(int[] arr1, int num1, int[] arr2, int num2){
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
arr1[num1 + i] = arr2[i];
}
// 利用jdk自带的工具类进行排序
Arrays.sort(arr1);
return arr1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0};
int m = 3;
int[] nums2 = {2, 5, 6};
int n = 3;
int[] result = merge(nums1, m, nums2, n);
Arrays.stream(result).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
方式二:使用双指针的方式
public class Test {
// 方式二:使用双指针进行排序
public static int[] merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int k = m + n;
int[] temp = new int[k];
int num1index = 0;
int num2index = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < k; index++) {
if (num1index >= m) { // nums1数组已经取完,完全取nums2数组的值即可
temp[index] = nums2[num2index++];
}else if(num2index >= n){ // nums2数组已经取完,完全取nums1数组的值即可
temp[index] = nums1[num1index++];
}else if(nums1[num1index] < nums2[num2index]){ // nums1数组元素中的值小于nums2数组中元素的值,就取nums1数组元素中的值
temp[index] = nums1[num1index++];
}else { // nums2数组元素中的值小于nums1数组中元素的值,就取nums2数组元素中的值
temp[index] = nums2[num2index++];
}
}
// 将temp数组中的元素
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
nums1[i] = temp[i];
}
return nums1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0};
int m = 3;
int[] nums2 = {2, 5, 6};
int n = 3;
int[] result = merge(nums1, m, nums2, n);
Arrays.stream(result).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
// TODO 还有另外一种方法,待看
判断两个链表有无相交
public class Test {
// 定义链表节点和指针
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
ListNode pl = headA, ps = headB;
while (pl != null) {
lenA++;
pl = pl.next;
}
while (ps != null) {
lenB++;
ps = ps.next;
}
// 因为你上面遍历了一下,所以需要重新指向
pl = headA;
ps = headB;
int len = lenA - lenB;
if (len < 0) {
pl = headB;
ps = headA;
len = lenA - lenB;
}
// 一定是pl指向的是最长的单链表
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
pl = pl.next;
}
// ps 和 pl一定是在同一个起跑线上了
while (ps != pl && null != pl && null != ps) {
ps = ps.next;
pl = pl.next;
}
if(ps == pl && null != pl && null != ps){
return pl;
}
return null; // 如果没有相交就返回null
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(5);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = listNode4;
// 注意两个链表相交一定是Y型的,不可能是X型的
ListNode intersectionNode = getIntersectionNode(listNode1, node1);
System.out.println(intersectionNode);
}
}
方式二:使用双指针的方式
private static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
// 使用双指针的方式
ListNode ptr1 = head1;
ListNode ptr2 = head2;
while (ptr1 != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1 == null ? head2 : ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2 == null ? head1 : ptr2.next;
}
return ptr1;
}
链表中的节点每K个一组进行翻转
public class Solution {
public static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {
}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public static void print(ListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 先设置一个虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
// 虚拟节点的next指针要指向head节点
dummy.next = head;
// pre表示每次要翻转的链表的头结点【上一个节点】
ListNode pre = dummy;
// end表示每次要翻转的链表的尾节点
ListNode end = dummy;
while(end.next != null){
// 通过for循环,找到每一组翻转链表的尾部
for (int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++) {
end = end.next;
}
// 如果发现end == null,说明此时反转的额链表的节点数小于K,保持原有的顺序就可以了
if(end == null){
break;
}
ListNode next = end.next;
end.next = null;
ListNode start = pre.next;
pre.next = null;
pre.next = reverseList(start);
start.next = next;
pre = start;
end = start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
/**
* 翻转链表
* @param head
*/
// 使用递归的方式
public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode newhead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newhead;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 这个题目目前自己还不是很懂,下来再好好看看吧!!!
}
}
移动0
使用双指针 i 用来遍历数组中的每一个元素; j用来记录数组中0元素的个数
public class Solution {
public static void moveZero(int[] nums){
if(null == nums){
return;
}
// 使用双指针
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(0 != nums[i]){
nums[j++] = nums[i];
}
}
for (int i = j; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {0,1,0,3,12};
moveZero(arr);
Arrays.stream(arr).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
找到数组中所有消失的元素
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (i != nums[i] - 1 && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1]) {
swap(nums, i, nums[i] - 1);
}
}
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(i + 1 != nums[i]){
res.add(i + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
// 两数交换
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {4,3,2,1,8,2,3,7};
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<Integer> result = solution.findDisappearedNumbers(nums);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
// TODO 还有另外一种算法,待看
删除排序列表中的重复元素
public class Solution {
private static class ListNode<E>{
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val){
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val,ListNode<E> next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head){
while (null != head){
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private static ListNode delDuplicateNode(ListNode head){
if(null == head){
return head;
}
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr.next != null){
if(curr.val == curr.next.val){
curr.next = curr.next.next;
}else{
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode<Integer> list1 = new ListNode<>(1);
ListNode<Integer> list2 = new ListNode<>(3);
ListNode<Integer> list3 = new ListNode<>(3);
ListNode<Integer> list4 = new ListNode<>(5);
ListNode<Integer> list5 = new ListNode<>(5);
list1.next = list2;
list2.next = list3;
list3.next = list4;
list4.next = list5;
ListNode listNode = delDuplicateNode(list1);
print(listNode);
}
}
回文链表
public class Solution {
private static class ListNode<E> {
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val, ListNode<E> next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head) {
while (null != head) {
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
// 判断是否是回文链表 true:表示是回文链表 false:表示不是回文链表
private static boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 使用快慢指针进行判断
ListNode slowPtr = head;
ListNode fastPtr = head;
while (slowPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null){
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
}
// 如果是奇数个节点
if(fastPtr != null){
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
}
fastPtr = head; // 将快指针重新移动到链表的头部
slowPtr = reverse(slowPtr); // 将慢指针进行翻转
while (slowPtr != null){
if(slowPtr.val != fastPtr.val){
return false;
}
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next;
}
return true;
}
// 链表翻转
private static ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode newNode = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newNode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(2);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
boolean flag = isPalindrome(listNode1);
System.out.println(flag);
}
}
找到链表的中间节点
public class Solution {
private static class ListNode<E> {
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val, ListNode<E> next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head) {
while (null != head) {
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private static ListNode findMidNode(ListNode head) {
// 使用快慢指针
ListNode slowPtr = head;
ListNode fastPtr = head;
while (slowPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null){
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
}
return slowPtr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(2);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
ListNode node = findMidNode(listNode1);
System.out.println(node.val);
}
}
找到链表的倒数第K个节点
public class Solution {
private static class ListNode<E> {
E val;
ListNode<E> next;
public ListNode(E val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(E val, ListNode<E> next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static void print(ListNode head) {
while (null != head) {
System.out.print("\t" + head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private static ListNode findNodeFromEnd(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head == null || k < 0){
return head;
}
// 使用快慢指针
ListNode slowPtr = head;
ListNode fastPtr = head;
// 先让快指针提前走K步
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if(fastPtr == null){
return null;
}
fastPtr = fastPtr.next;
}
// 然后快慢指针一起走
while (slowPtr != null && fastPtr != null){
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next;
}
return slowPtr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(5);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
int k = 2;
ListNode node = findNodeFromEnd(listNode1, k);
System.out.println(node.val);
}
}




