ConcurrentHashMap源码剖析
ConcurrentHashMap源码剖析
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Qg41197FG/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=273847a809b909b44923e3af1a7ef0b1
ConcurrentHashMap是Hashmap的并发形式。虽然Hashtable也是线程安全的,但是它的并发能力相比于ConcurrentHashMap要低的多。
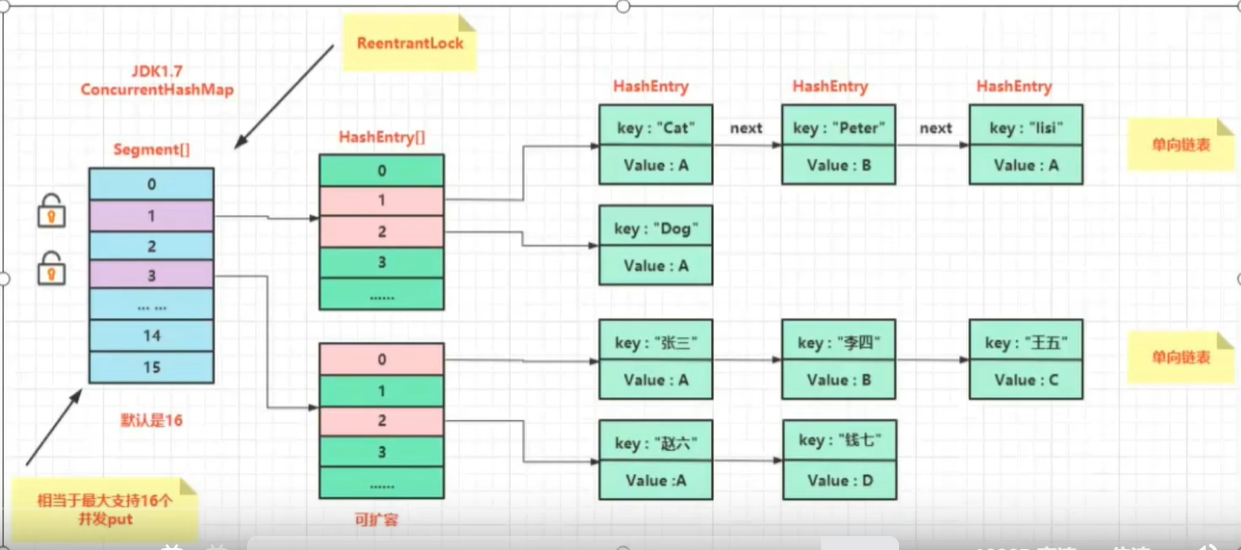
在jdk1.7的时代ConcurrentHashMap使用分段锁的设计来维护线程安全。
在jdk1.8的时代对其进行了改进,只锁一个节点,利用CAS 算法。 同时加入了更多的辅助变量来提高并发度。
jdk1.8源码剖析:
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable {
// 表的最⼤容量 只能是 2 的 n 次幂,最⼤ 1 << 30, 因为第⼀位是符号位
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认表的⼤⼩ 最⼩值 1 << 1, 默认值 1 << 4
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
// 最⼤数组⼤⼩
static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
// 默认并发数
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
// 加载因子
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 转化为红黑树的阈值
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 由红黑树转换为链表的阈值
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 转化为红黑树的表的最小容量
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
// 每次进行转移的最小值
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
// 生成sizeCtl所使用的bit位数
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
// 进行扩容所允许的最大线程数
private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;
// 记录sizeCtl中的⼤⼩所需要进⾏的偏移位数
private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
// ⼀系列的标识
static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash
// 获取可⽤的CPU个数
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// 进⾏序列化的属性
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields = {
new ObjectStreamField("segments", Segment[].class),
new ObjectStreamField("segmentMask", Integer.TYPE),
new ObjectStreamField("segmentShift", Integer.TYPE)
};
/* ---------------- Fields -------------- */
// 表
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
// 下一个表
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
// 基本计数
private transient volatile long baseCount;
// 对表初始化和扩容控制
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
// 扩容下另一个表的索引
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
// 旋转锁
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
// counterCell表
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
// views 视图
private transient KeySetView<K,V> keySet;
private transient ValuesView<K,V> values;
private transient EntrySetView<K,V> entrySet;
// 添加元素
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); // 计算hash值
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // 第一次放的时候,要进行table数组的初始化,也就是懒加载
tab = initTable();
// tabAt方法用于获取 Node 数组 table(桶)指定下标位置上的 Node 节点
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { // 计算槽位,如果槽位为空,则可以插入
// 使用CAS的方式进行插入
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)// 如果该槽位不为空,且正在扩容
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); // 协助扩容
else { // 如果有冲突,则插入链表或红黑树
V oldVal = null;
// 将这个节点锁住,这个f就是数组上的节点,相当于是链表或红黑树的头结点
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { // 检查头结点是否有变化
if (fh >= 0) {// 说明是链表
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 说明是红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 链表转红黑树
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) // 这里是8的原因是因为hash冲突的概率很小
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount); // 计数,超过sizeCtl会进⾏扩容
return null;
}
}
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
// 扩容的时候也用到了CAS
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode()); // 通过key计算hash值,说白了就是计算在数组下标的位置
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;// 如果当前位置存在,则直接拿出来返回就可以了
}
// eh=-1,说明当前的数据正被迁移,调用ConcurrentHashMap.ForwardingNode#find方法在新的数组中查找
// eh=-2,说明该节点是一个TreeBin,此时调用TreeBin的find方法遍历红黑树
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 如果还没有找到,奶遍历链表
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
ConcurrentHashMap之所以不会取到脏数据,是因为它的变量被volitile进行了修饰,结合MESI协议能够保证是最新的值。
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
// .......
}
jdk1.7源码剖析:
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V>
implements ConcurrentMap<K, V>, Serializable {
/* ---------------- Constants -------------- */
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;
static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16; // slightly conservative
static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;
/* ---------------- Fields -------------- */
final int segmentMask;
final int segmentShift;
// 分段锁设计基于Segment<K,V>[]数组
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
transient Set<K> keySet;
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
transient Collection<V> values;
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V value;
volatile HashEntry<K,V> next;
//.......
}
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)
concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;
// Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments
int sshift = 0;
int ssize = 1;
// concurrencyLevel并发等级,默认是16,最终退出循环的时候ssize=16
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;
while (cap < c)
cap <<= 1;
// create segments and segments[0]
// 初始化HashEntry[]数组
Segment<K,V> s0 =
new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]);
// 初始化Segment[]数组
Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize];
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]
this.segments = ss;
}
}
分类:
并发编程





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY