ReentrantReadWriteLock源码剖析
ReentrantReadWriteLock源码剖析
synchronized和ReentrantLock都是互斥锁。
为什么要出现读写锁:如果说有一个操作是读多写少的,还要保证线程安全的话。如果采用上述的两种互斥锁,效率方面很
定是很低的。在这种情况下,咱们就可以使用ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁去实现。读读之间是不互斥的,可以读和读操作并发执行。但是如果涉及到了写操作,那么还得是互斥的操作。
读锁可以并行,写锁只能串行。
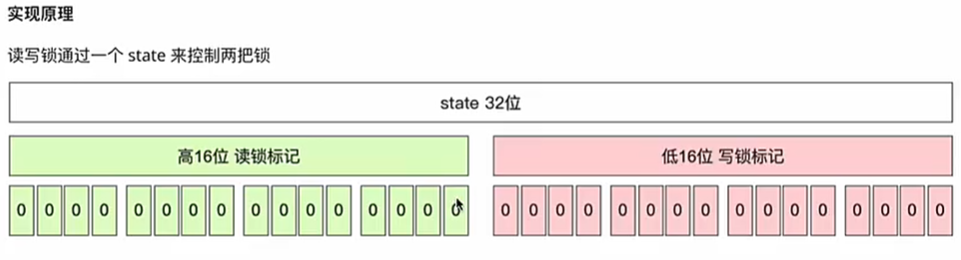
读锁操作:基于state的高16位进行操作。写锁操作:基于state的低16位进行操作。
高16位记录持有读锁线程的数量,低16位记录持有写锁线程的数量。
通过state这一个字段来控制这两把锁。
测试案例:
public class ReentrantReadWriteLockDemo {
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private static Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); // 定义读锁
private static Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); // 定义写锁
private int value = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ReadWriteLockDemo().test();
}
private void test() {
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
if (j % 5 == 0) {
new Thread(this::doWrite).start();
} else {
new Thread(this::doRead).start();
}
}
}
// 读取value的值
private void doRead() {
try {
readLock.lock(); // 上读锁
long timeFlag = System.currentTimeMillis() % 100000;
System.out.println(timeFlag + " -- " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -->> 读取数据 value=" + value);
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readLock.unlock(); // 释放读锁
}
}
// 修改value的值
private void doWrite() {
try {
writeLock.lock(); // 添加写锁
value++;
long timeFlag = System.currentTimeMillis() % 100000;
System.out.println(timeFlag + " -- " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -->> <<写入>>数据 value=" + value);
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
writeLock.unlock(); // 释放写锁
}
}
}
运行结果:
30731 -- Thread-0 -->> <<写入>>数据 value=11
31732 -- Thread-5 -->> <<写入>>数据 value=12
32733 -- Thread-1 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32733 -- Thread-2 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32733 -- Thread-4 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32733 -- Thread-7 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32734 -- Thread-3 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32734 -- Thread-8 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32734 -- Thread-6 -->> 读取数据 value=12
32734 -- Thread-9 -->> 读取数据 value=12
33735 -- Thread-10 -->> <<写入>>数据 value=13
34735 -- Thread-11 -->> 读取数据 value=13
34735 -- Thread-12 -->> 读取数据 value=13
34735 -- Thread-13 -->> 读取数据 value=13
34735 -- Thread-14 -->> 读取数据 value=13
35736 -- Thread-15 -->> <<写入>>数据 value=14
36736 -- Thread-16 -->> 读取数据 value=14
36736 -- Thread-17 -->> 读取数据 value=14
36736 -- Thread-18 -->> 读取数据 value=14
36736 -- Thread-19 -->> 读取数据 value=14
37737 -- Thread-20 -->> <<写入>>数据 value=15
38738 -- Thread-21 -->> 读取数据 value=15
38738 -- Thread-23 -->> 读取数据 value=15
38738 -- Thread-22 -->> 读取数据 value=15
38738 -- Thread-24 -->> 读取数据 value=15
39738 -- Thread-25 -->> <<写入>>数据 value=16
40738 -- Thread-26 -->> 读取数据 value=16
40738 -- Thread-27 -->> 读取数据 value=16
40738 -- Thread-29 -->> 读取数据 value=16
40738 -- Thread-28 -->> 读取数据 value=16
架构图:
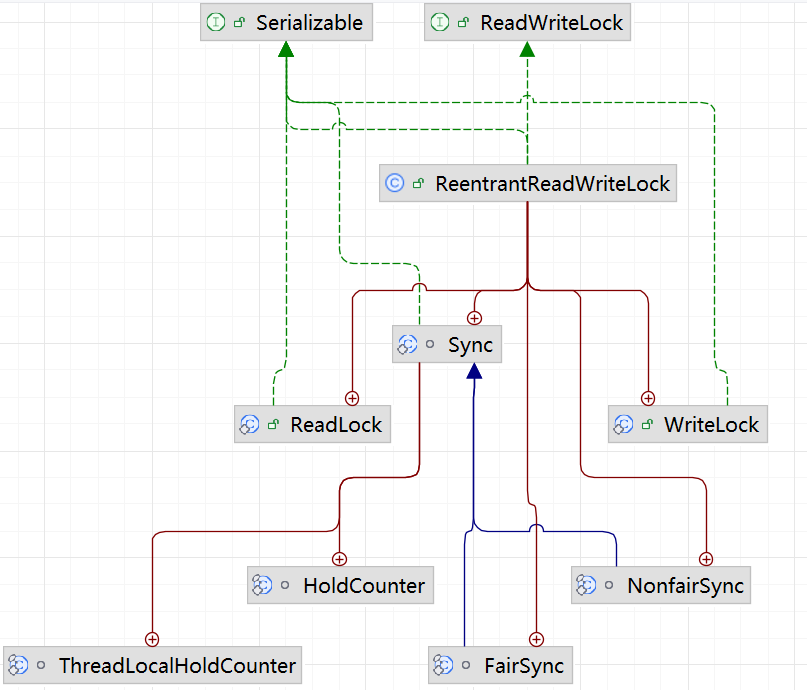
源码剖析:
public class ReentrantReadWriteLock
implements ReadWriteLock, java.io.Serializable {
/** Inner class providing readlock 读锁,内部类提供*/
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readerLock;
/** Inner class providing writelock 写锁,内部类提供*/
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writerLock;
final Sync sync;// 继承AQS
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
// 位数
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
// 共享⾼16位(读锁标记)
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
// 读取最⼤数量
static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
// 写锁最⼤数量
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
/** Returns the number of shared holds represented in count 读锁计数 */
static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }
/** Returns the number of exclusive holds represented in count 写锁计数 */
static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
}
// 非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ......
}
// 公平锁
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
// ......
}
// 读锁
public static class ReadLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
// ......
}
// 写锁
public static class WriteLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
// ......
}
public ReentrantReadWriteLock() {
this(false);
}
public ReentrantReadWriteLock(boolean fair) {
// true:公平锁 false:非公平锁
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
readerLock = new ReadLock(this);
writerLock = new WriteLock(this);
}
}
读锁加锁逻辑:
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock#lock
可以看到底层走的还是AQS的逻辑
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
// 小于0表示尝试加锁失败
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
// 进行排队
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 获取低16位的值(说白了就是写锁位置的值)
// 如果不等于0表示有写锁,
// 紧接着再看看getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current持有写锁的线程是都是当前线程,如果不是,直接返回-1
// 如果getExclusiveOwnerThread() == current,表示当前写锁的线程将要降级为读锁线程。锁降级
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
int r = sharedCount(c); // 获取读锁的数量
/*
readerShouldBlock的实现分为公平锁和非公平锁。
公平锁实现,看看队列里面有没有前驱节点,返回true:有,false:没有
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
}
非公平锁实现,判断头结点是不是独占节点,返回true:是独占节点, false:不是独占节点
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();
}
r < MAX_COUNT:不能超过最大值
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT):通过cas更新读锁的数量
总结:说白了就是判断一下,获取读锁数量,然后更新高16位的值。
*/
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
// 下面的逻辑是,当线程重入的时候,会使用threadlocal变量,来保存重入的次数。
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
// 如果获取读锁失败
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
/*
* This code is in part redundant with that in
* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not
* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between
* retries and lazily reading hold counts.
*/
HoldCounter rh = null;
// 自旋
// 总的来说就是没有获取到读锁,通过自旋的方式一直获取,直到cas更新成功为止。
// 下面写的和上面的代码结构基本上一样。
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here
// would cause deadlock.
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
} else {
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
}
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}
// 逻辑其实和AQS入队是一样的。
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
// 创建一个SHARED类型的节点
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
// 自旋
for (;;) {
// 获取前驱节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果前驱节点是头结点,则说明你就是紧接着要执行的节点,先获取一下锁看看能不能获取成功。
if (p == head) {
// 获取共享锁
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
// 大于0表示获取共享锁成功
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// 没有成功获取共享锁,就老老实实的排队等着
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
读锁释放锁逻辑:
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock#unlock
可以看到底层走的还是AQS的逻辑
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// 尝试释放锁成功
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
// ==1 表示没有重入
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
// 表示有重入
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
// 总结:如果没有重入,就将所有的读锁线程释放掉
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count;
}
// 最后通过CAS更新state高16位的值
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 总结:摘除掉头结点,唤醒后继节点
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
写锁加锁逻辑:
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock#lock
可以看到底层走的还是AQS的逻辑
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 尝试加锁成功,直接返回
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 如果加锁失败,则创建一个EXCLUSIVE类型的Node节点添加到队列中
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
// 上面的翻译:如果读锁的是数量是不为0,或写锁的数量不为0,并且当前线程不一样,就都是失败。
// 如果是读锁,直接失败,如果是写锁再判断一下是否可重入,如果可重入,就往下走,如果不可重入就直接失败。
// 如果线程数量已经饱和了,直接失败
// 否则,如果该线程是可重入或者队列策略允许,则该线程有资格拿锁。如果是这样,更新状态并设置独占。
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c); // 获取独占锁的数量,说白了就是写锁的数量,也就是state变量后16位的数量
// 如果同步状态!=0,说明有写锁或者读锁
if (c != 0) {
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
// 写锁==0 或者 当前线程!=独占线程,
// 说明有读锁,因为读写锁互斥,你加不了写锁了,直接返回false。
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
// 如果之前写锁的数量+本次要加的写锁的数量超过最大值,直接爆Error
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
// 否则,说明可重入。添加写锁成功
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
// 该方法分为公平锁的实现和非公平锁的实现
// 总结,公平锁查看是否有前驱节点,有的话就失败,没有的话就加锁成功,非公平锁一上来就加锁
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
公平锁实现
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
// 查看是否有前驱节点
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
}
非公平锁实现
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return false; // writers can always barge
}
写锁释放锁逻辑:
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock#unlock
可以看到底层走的还是AQS的逻辑
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 总结:尝试释放锁,释放锁成功,唤醒后继节点
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 具体方法实现
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 如果就不是独占线程,直接抛异常,因为写锁肯定是要独占的
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
// 修改state变量的值 减1
int nextc = getState() - releases;
// 看看独占线程的数量是否为0,如果为0,就将独占线程置为null,
// 如果没有独占线程就返回true,如果还有独占线程就返回false。
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
总的来说:ReentrantReadWriteLock底层实现了读锁和写锁、公平锁、非公平锁、。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY