声明式事务源码剖析
声明式事务源码剖析
声明式事务是通过注解来实现的,还有一种是编程式事务,是通过try catch来实现的。
原理:
1.解析切面 执行时机:bean的创建前第一个bean的后置处理器进行解析,List
2.创建动态代理 执行时机:bean的初始化后调用bean的后置处理器进行创建动态代理(有接口使用jdk动态代理,没有接口使用cglib动态代理),创建动态代理之前会先根据advisor中的pointcut匹配@Transactional(方法里面是不是有、类上面是不是有、接口或父类上面是不是有),匹配到就创建动态代理。
3.调用 以下是伪代码
try{
创建一个数据库连接connection,并修改数据库连接的autocommit属性为false,禁止此连接的自动提交,这是实现spring事务非常重要的一步。
然后执行目标方法,方法中会执行数据库操作SQL。
}catch(RuntimeException || Error){
如果出现了异常,并且这个异常是需要回滚的,就会进行事务的回滚,否则仍然提交事务
}
执行完当前方法后,如果没有出现异常就直接提交事务。
架构图:

声明式事务小案例:
/**
* 声明式事务配置类,其中@EnableTransactionManagement
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.coding.spring.tx") // 扫描该包下符合条件的类,并添加到spring容器中
@EnableTransactionManagement // -- 开启基于注解的事务管理
public class MyTxConfig {
// 配置数据源
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() throws Exception {
ComboPooledDataSource pool = new ComboPooledDataSource();
pool.setUser("root");
pool.setPassword("123456");
pool.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
pool.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mytest?useSSL=false");
return pool;
}
// 加入模板
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() throws Exception {
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
return template;
}
// 配置事务管理器
// 归根结底是横切逻辑代码,声明式事务要做的就是使⽤Aop(动态代理)来将事务控制逻辑织⼊到业务代码.
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager txManager() throws Exception {
DataSourceTransactionManager tx = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
return tx;
}
}
加上@Transactional注解之后,出现异常,这条数据就不会插入成功了。
@Transactional适用于不是分布式事务的情况。
底层也是基于动态代理来实现的
@Repository
public class MyUserTXDAO {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// 如果你不加rollbackFor = Exception.class,
// @Transactional注解只会回滚RunTimeException和Error的异常
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void insert() throws Exception{
String sql = "INSERT into my_user (name) VALUES(?);";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "tom");
System.out.println("------>插入成功");
// int i = 1 / 0;
// throw new Exception("my exception");
}
}
package com.coding.spring.tx;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyUserTXService {
@Autowired
private MyUserTXDAO myUserTXDAO;
public void insertMyTXUser() throws Exception {
myUserTXDAO.insert();
}
}
@Test
public void testTX() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyTxConfig.class);
MyUserTXService myUserTXService = applicationContext.getBean(MyUserTXService.class);
myUserTXService.insertMyTXUser();
}
源码剖析:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
// 使用@Import注解导入配置类
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
/**
默认为false,表示使用jdk动态代理
true,表示使用cglib动态代理
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
/**
* Indicate the ordering of the execution of the transaction advisor
* when multiple advices are applied at a specific joinpoint.
* <p>The default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE}.
表示最后执行
*/
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> {
/**
从上面的EnableTransactionManagement注解中AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
可以看到默认走PROXY
向spring容器中注入了两个bean,一个是AutoProxyRegistrar,一个是ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
*/
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}
private String determineTransactionAspectClass() {
return (ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", getClass().getClassLoader()) ?
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.JTA_TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME :
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
}
}
下面我们看看ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
// 处理事务的通知器,有@Transactional注解的方法会被切入
// 就把它-BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor理解为是spring aop中的Advisor
// 相当于spring中的声明式事务自己实现了一套类似于aop的逻辑。
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
// 事务增强器
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
// 向事务增强器中注⼊ 属性解析器 transactionAttributeSource
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
// 向事务增强器中注⼊ 事务拦截器 transactionInterceptor
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
// 解析事务属性,见下图
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
// 事务拦截器,调用目标方法时,执行invoke方法
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
看看我们的事务通知器BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
public class BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
@Nullable
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource;
// 看到了熟悉的pointcut
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
/**
* Set the transaction attribute source which is used to find transaction
* attributes. This should usually be identical to the source reference
* set on the transaction interceptor itself.
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionAttributeSource
*/
public void setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
this.transactionAttributeSource = transactionAttributeSource;
}
/**
* Set the {@link ClassFilter} to use for this pointcut.
* Default is {@link ClassFilter#TRUE}.
*/
public void setClassFilter(ClassFilter classFilter) {
this.pointcut.setClassFilter(classFilter);
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}
}
我们再看看AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类,解析@Transactional中的属性
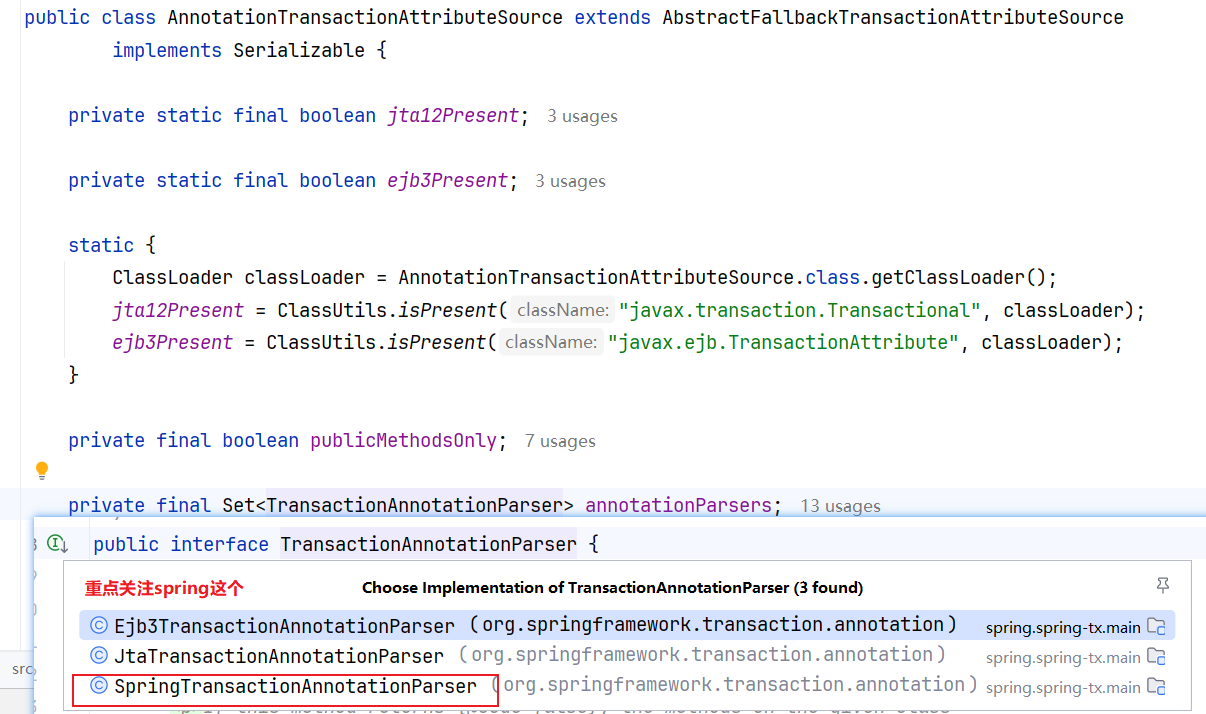
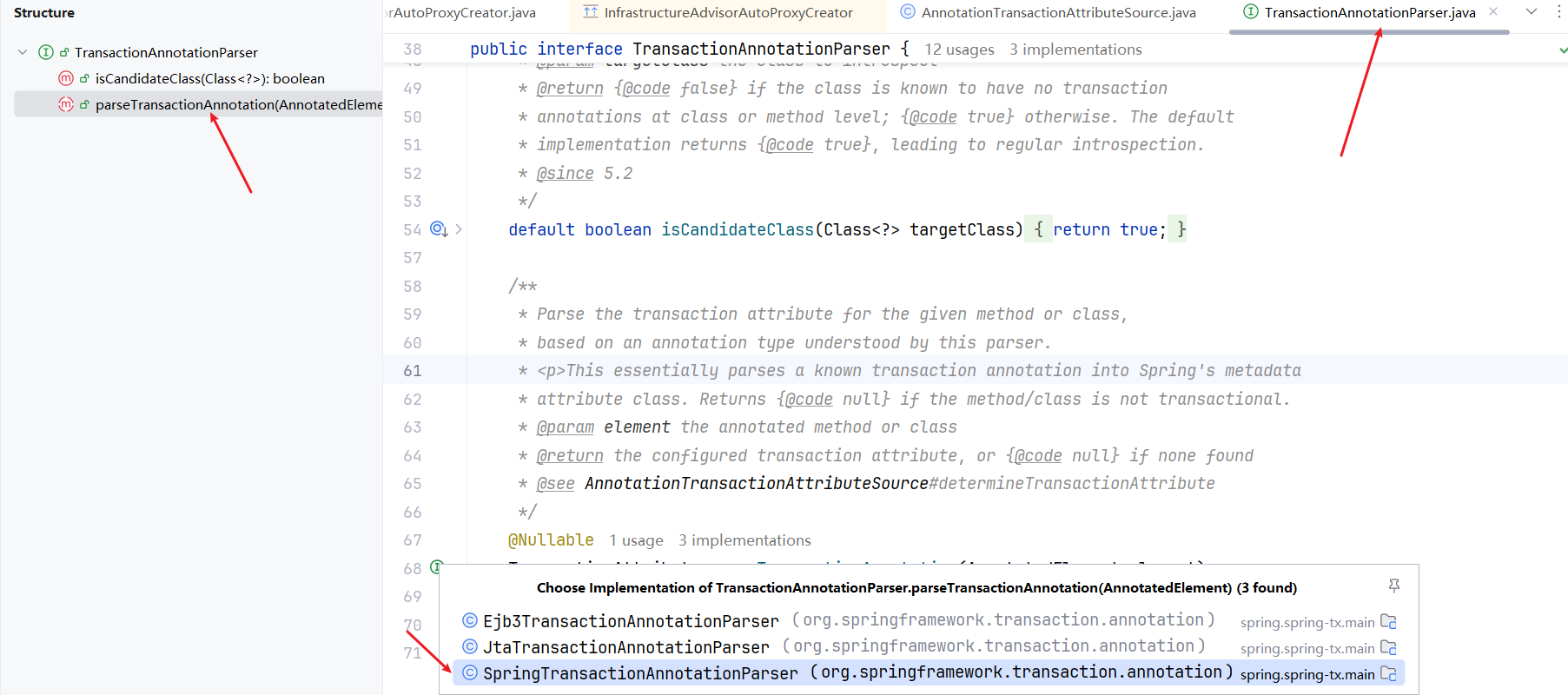

看看AutoProxyRegistrar类
public class AutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/**
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean candidateFound = false;
Set<String> annTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes();
for (String annType : annTypes) {
AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annType);
if (candidate == null) {
continue;
}
Object mode = candidate.get("mode");
Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass");
if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() &&
Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) {
candidateFound = true;
if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) {
// 点进去
/*
我们会看到 AopConfigUtils#registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry, java.lang.Object)
*/
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
// true:表示使用cglib动态代理
if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
return;
}
}
}
}
if (!candidateFound && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
String name = getClass().getSimpleName();
logger.info(String.format("%s was imported but no annotations were found " +
"having both 'mode' and 'proxyTargetClass' attributes of type " +
"AdviceMode and boolean respectively. This means that auto proxy " +
"creator registration and configuration may not have occurred as " +
"intended, and components may not be proxied as expected. Check to " +
"ensure that %s has been @Import'ed on the same class where these " +
"annotations are declared; otherwise remove the import of %s " +
"altogether.", name, name, name));
}
}
}
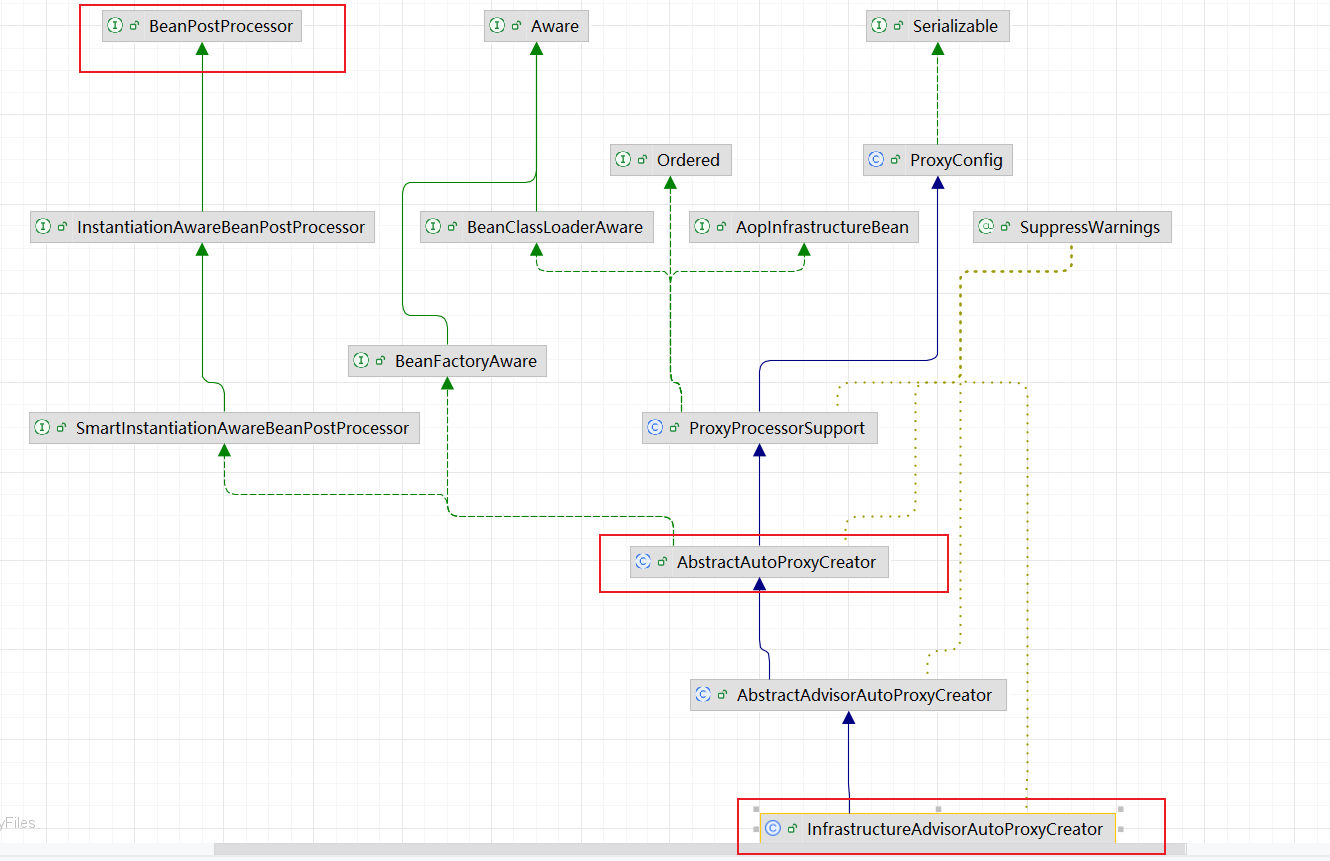
看一下这个类的结构图:
下面我们结合debug看一下整体的执行流程:
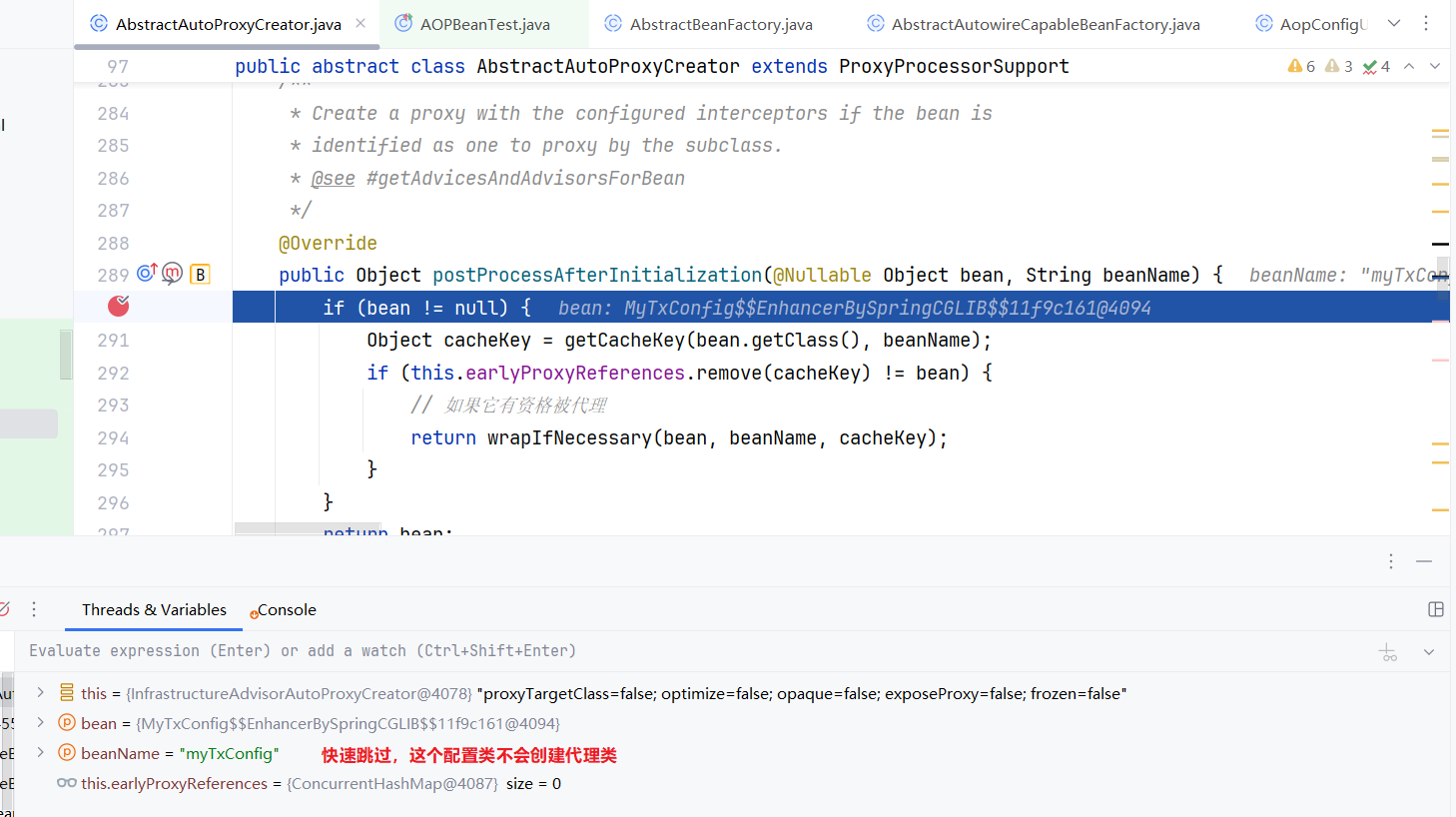
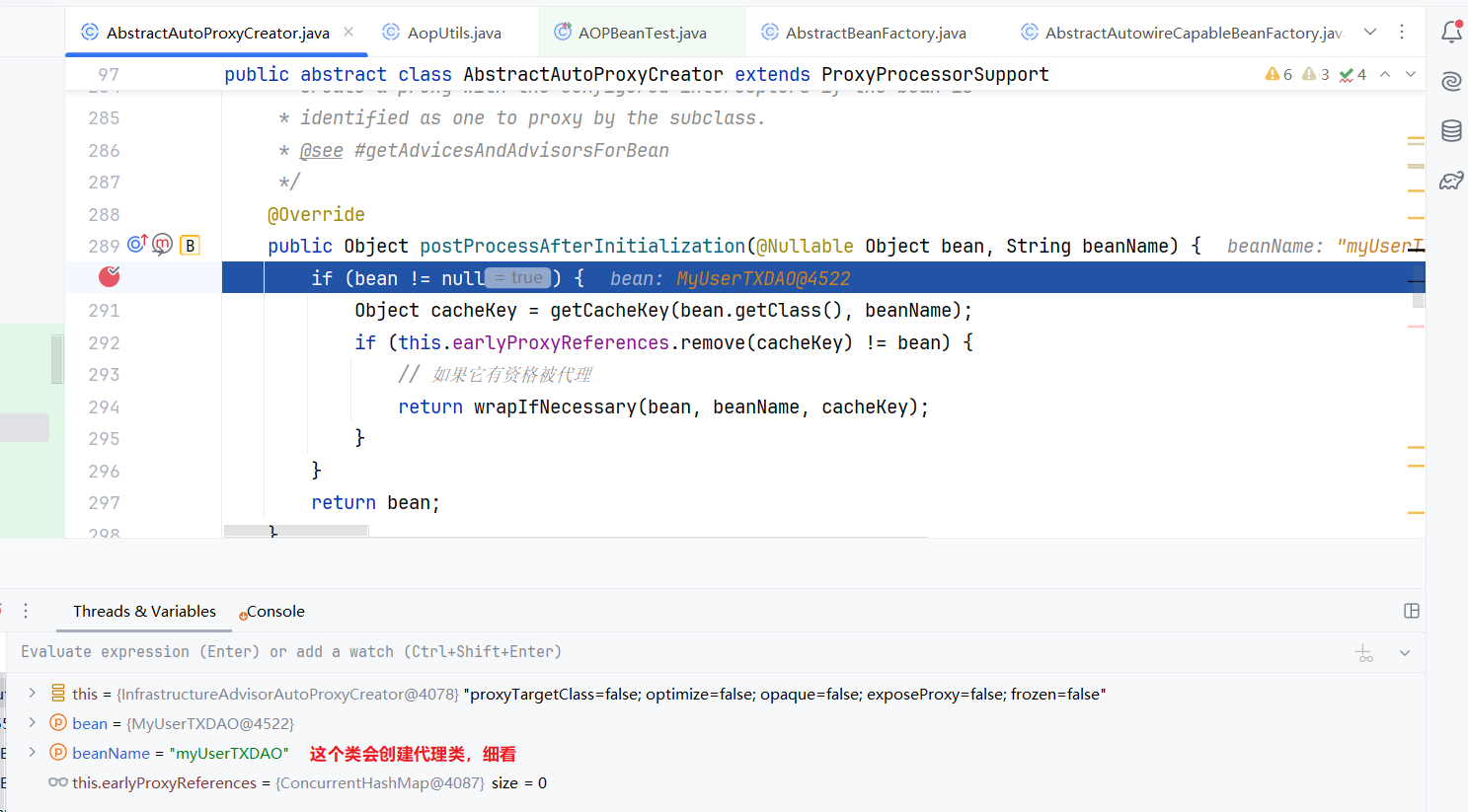
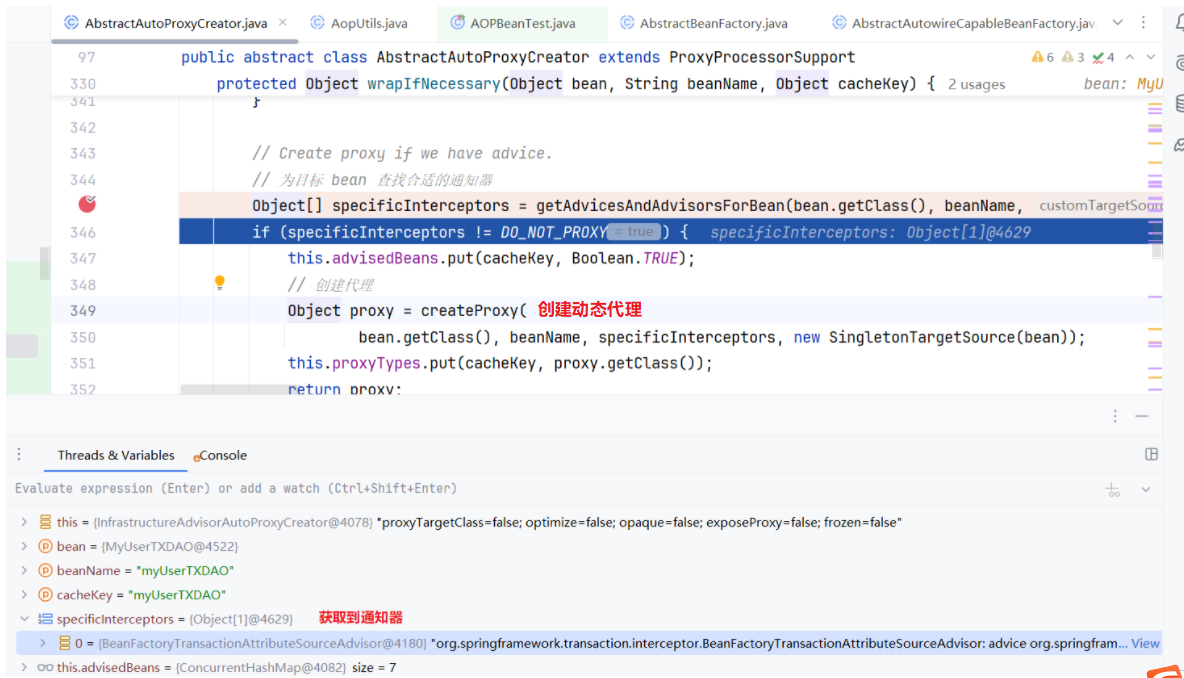
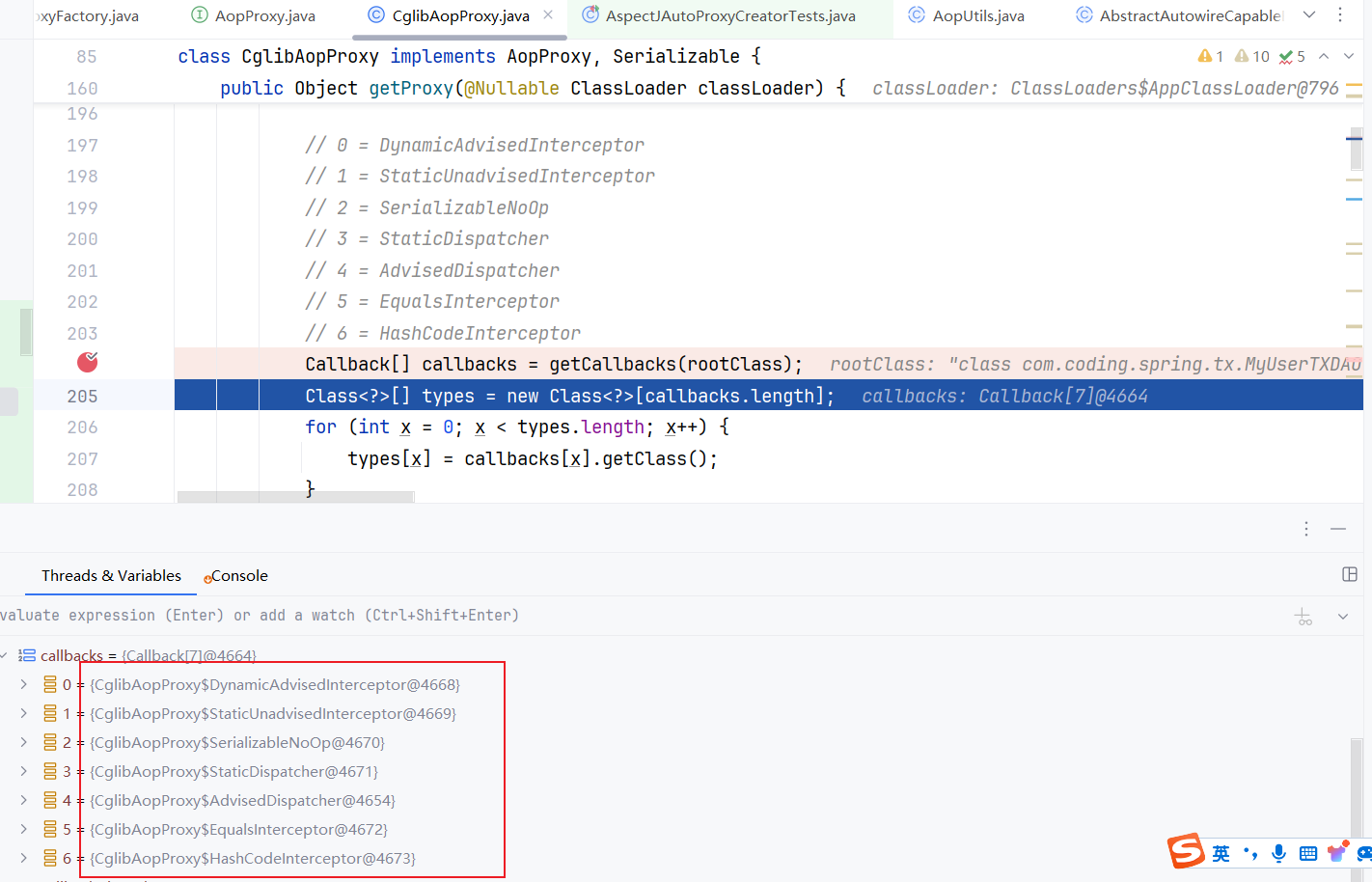
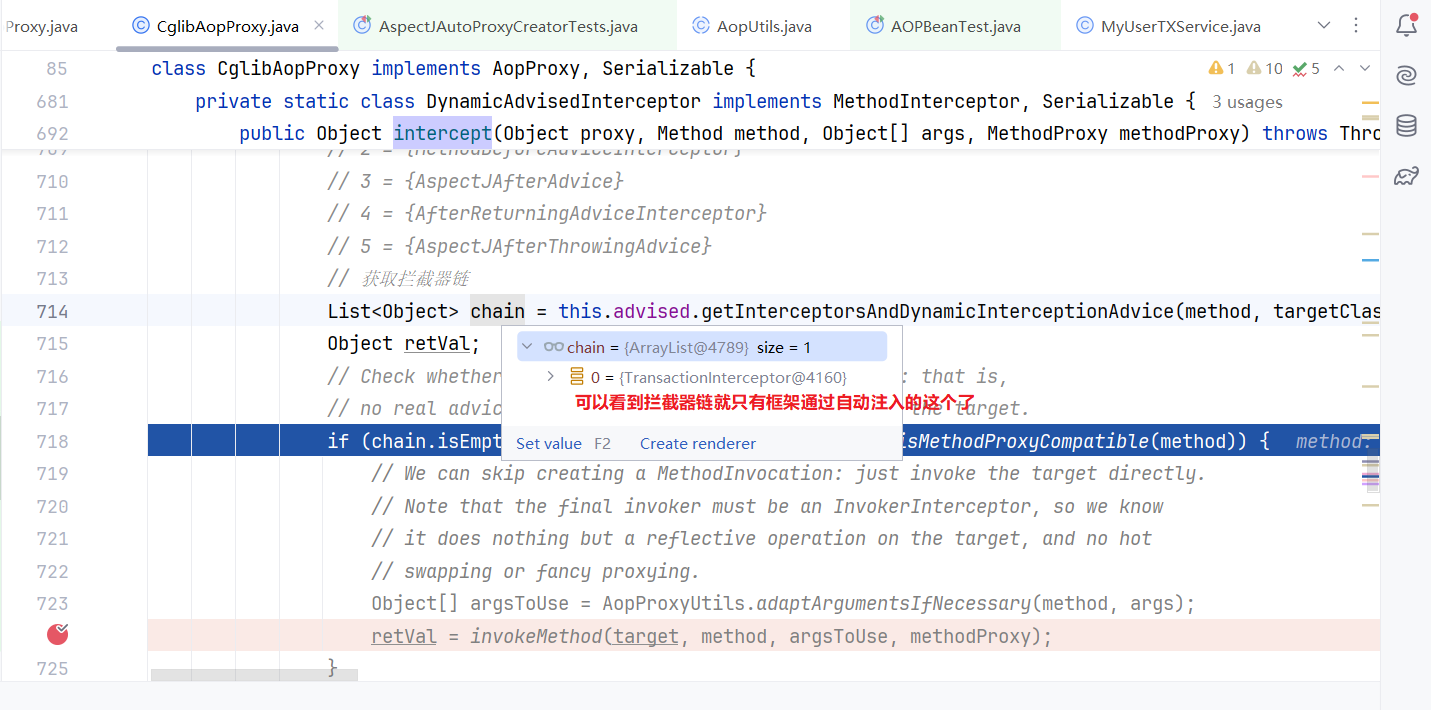
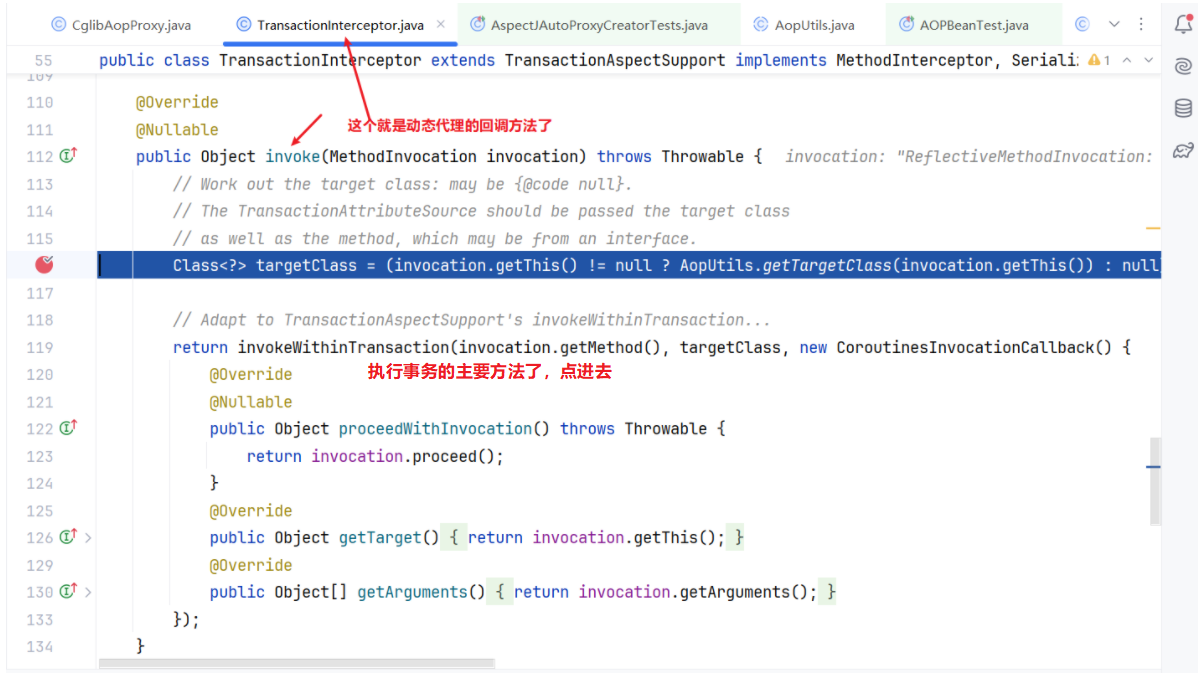
org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
其实里面主要就是try catch finally了
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
boolean isSuspendingFunction = KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method);
boolean hasSuspendingFlowReturnType = isSuspendingFunction &&
COROUTINES_FLOW_CLASS_NAME.equals(new MethodParameter(method, -1).getParameterType().getName());
if (isSuspendingFunction && !(invocation instanceof CoroutinesInvocationCallback)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Coroutines invocation not supported: " + method);
}
CoroutinesInvocationCallback corInv = (isSuspendingFunction ? (CoroutinesInvocationCallback) invocation : null);
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
Class<?> reactiveType =
(isSuspendingFunction ? (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? Flux.class : Mono.class) : method.getReturnType());
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(reactiveType);
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
InvocationCallback callback = invocation;
if (corInv != null) {
callback = () -> CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, corInv.getTarget(), corInv.getArguments());
}
Object result = txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(method, targetClass, callback, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
if (corInv != null) {
Publisher<?> pr = (Publisher<?>) result;
return (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? KotlinDelegate.asFlow(pr) :
KotlinDelegate.awaitSingleOrNull(pr, corInv.getContinuation()));
}
return result;
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 执行目标方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 出现异常进行回滚操作
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 清除事务信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
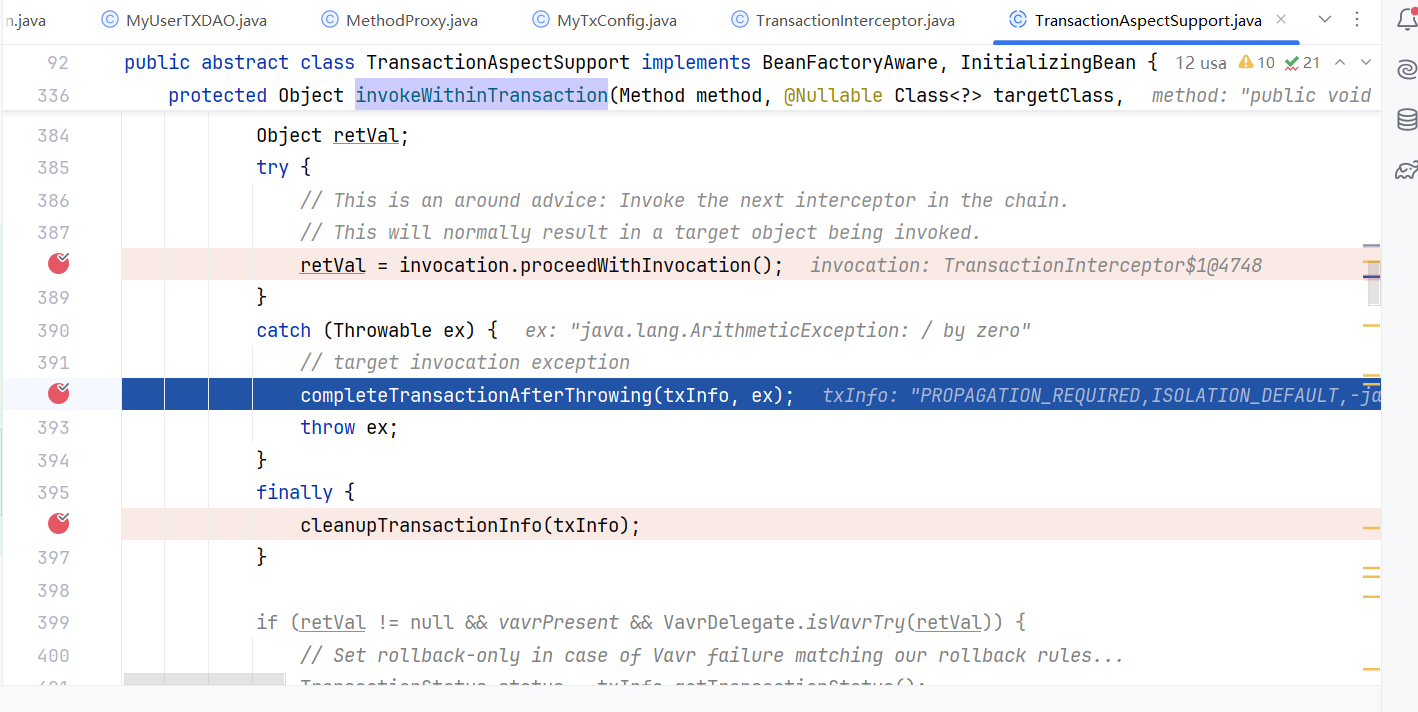
总的来说:spring声明式事务和spring aop的逻辑类似,@Transactionnal就好比是@pointCut,spring通过@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)自动注入了Advisor-通知器和Interceptor拦截器。最后借助动态代理技术实现声明式事务。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY