线程池
为什么使用线程池
线程缺乏统一管理,占用过多的系统资源。
缺乏更多功能,如定时执行、定期执行
使用线程池的好处
重用存在的线程,减少对象创建、消亡的开销
有效控制最大并发数,提高系统资源使用率
定时执行、定期执行
线程池所在包:java.util.concurrent
顶级接口是Executor,真正的线程池接口是ExecutorService
java.util.concurrent.Executors类提供创建线程池的方法
常用的方法:
newCachedThreadPool()
newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
newSingleThreadExecutor()
下面分别适用使用Executors类中这些静态方法创建线程:
创建带有缓存的线程池:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.*;public class NewCachedThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = newCachedThreadPool(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executorService.execute(new MyRunnable(i));// try {// Thread.sleep(200);// } catch (InterruptedException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// } } }}class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ int nums; public MyRunnable(int nums) { this.nums = nums; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("当前线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+";正在执行的任务编号:"+nums); }} |
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:0
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:1
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:2
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:3
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:4
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:5
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:6
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:7
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:8
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:9
如果我们将休眠时间注销掉,会看到有更多的线程参与到任务执行的过程中
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-3;正在执行的任务编号:2
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-7;正在执行的任务编号:6
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-6;正在执行的任务编号:5
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-5;正在执行的任务编号:4
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-4;正在执行的任务编号:3
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:0
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2;正在执行的任务编号:1
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-10;正在执行的任务编号:9
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-9;正在执行的任务编号:8
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-8;正在执行的任务编号:7
使用线程池创建单线程:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newCachedThreadPool;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor;public class NewSingleThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = newSingleThreadExecutor(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executorService.execute(new MyRunnable2(i)); } }}class MyRunnable2 implements Runnable{ int nums; public MyRunnable2(int nums) { this.nums = nums; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("当前线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+";正在执行的任务编号:"+nums); }} |
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:0
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:1
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:2
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:3
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:4
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:5
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:6
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:7
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:8
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:9
创建固定线程数的线程池:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newFixedThreadPool;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor;public class NewFixedThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = newFixedThreadPool(3); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { executorService.execute(new MyRunnable2(i)); } }}class MyRunnable3 implements Runnable{ int nums; public MyRunnable3(int nums) { this.nums = nums; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("当前线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+";正在执行的任务编号:"+nums); }} |
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:0
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2;正在执行的任务编号:1
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-3;正在执行的任务编号:2
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2;正在执行的任务编号:4
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2;正在执行的任务编号:6
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:3
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2;正在执行的任务编号:7
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-3;正在执行的任务编号:5
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2;正在执行的任务编号:9
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1;正在执行的任务编号:8
创建带有定时任务的线程池:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newFixedThreadPool;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newScheduledThreadPool;public class NewScheduledThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService executorService = newScheduledThreadPool(3); System.out.println("=====================任务开始执行======================="); executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new MyRunnable4(),1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }}class MyRunnable4 implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("当前线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次"); }} |
=====================任务开始执行=======================
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-1-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-2-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
当前线程名:pool-1-thread-3-延时1秒钟执行,每两秒钟执行一次
........
ThreadPoolExecutor构造器中常用的参数:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
1、corePoolSize:核心线程数
* 核心线程会一直存活,即使没有任务需要执行
* 当线程数小于核心线程数时,即使有线程空闲,线程池也会优先创建新线程处理
* 设置allowCoreThreadTimeout=true(默认false)时,核心线程会超时关闭
2、workQueue:任务队列容量(阻塞队列)
* 当核心线程数达到最大时,新任务会放在队列中排队等待执行
3、maximumPoolSize:最大线程数
* 当线程数>=corePoolSize,且任务队列已满时。线程池会创建新线程来处理任务
* 当线程数=maxPoolSize,且任务队列已满时,线程池会拒绝处理任务而抛出异常
4、 keepAliveTime:线程空闲时间
* 当线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime时,线程会退出,直到线程数量=corePoolSize
* 如果allowCoreThreadTimeout=true,则会直到线程数量=0
5、 unit:参数keepAliveTime的时间单位
6、 Handler:表示当拒绝处理任务时的策略。当任务很多的时候,阻塞队列中的任务也满了的时候,如果还有任务来,这个时候,就需要使用拒绝策略来进行拒绝。
7、 threadFactory:线程工厂,主要用来创建线程。
线程池的执行原理:
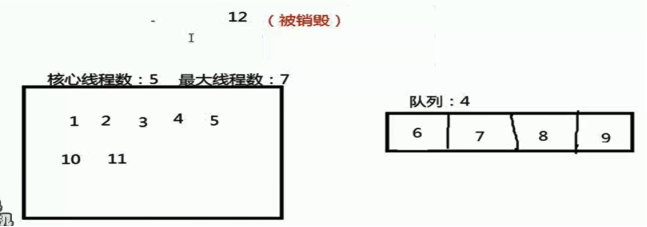
当有12个任务需要被执行的时候,现在线程池中有5个核心线程,分别被安排了 1 2 3 4 5这几个任务执行,后面的6 7 8 9任务会被放到队列中进行排队等待,后面还有任务10 11 12还没有处理,这个时候会在线程池中再创建两个线程来执行任务10 11,这个时候线程池中的线程数已经达到了最大线程数,任务12就会被拒绝策略拒绝掉(因为线程池满了,队列也满了,没有地方存放或者执行任务12了),就只能拒绝掉了。当任务没有那么多的时候,核心线程能处理的时候,经过keepAliveTime的时间,会将多创建出来的2个线程销毁掉,保留核心线程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import static java.util.concurrent.Executors.newCachedThreadPool;public class ThreadPoolExecutorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5, 7, 300, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4)); for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++) { executor.execute(new MyRunnable5(i)); System.out.println("线程池中的线程数:"+executor.getPoolSize() +",队列中等待执行任务的任务数:"+executor.getQueue().size() +",已经执行完的任务数:"+executor.getCompletedTaskCount()); } executor.shutdown();//所有任务都执行完毕之后,销毁线程池 }}class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable { int nums;//当前正在执行的任务编号 public MyRunnable5(int nums) { this.nums = nums; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("任务" + nums + "开始执行"); try { Thread.sleep(200);//假设执行一个任务需要耗费的时间 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("任务" + nums + "执行完毕"); }} |
任务1开始执行
线程池中的线程数:1,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:0,已经执行完的任务数:0
线程池中的线程数:2,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:0,已经执行完的任务数:0
线程池中的线程数:3,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:0,已经执行完的任务数:0
任务2开始执行
任务3开始执行
线程池中的线程数:4,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:0,已经执行完的任务数:0
任务4开始执行
线程池中的线程数:5,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:0,已经执行完的任务数:0
任务5开始执行
线程池中的线程数:5,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:1,已经执行完的任务数:0
线程池中的线程数:5,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:2,已经执行完的任务数:0
线程池中的线程数:5,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:3,已经执行完的任务数:0
线程池中的线程数:5,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:4,已经执行完的任务数:0
线程池中的线程数:6,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:4,已经执行完的任务数:0
任务10开始执行
线程池中的线程数:7,队列中等待执行任务的任务数:4,已经执行完的任务数:0
任务11开始执行
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task com.zyq.mythreadpool.MyRunnable5@2f0e140b rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@7440e464[Running, pool size = 7, active threads = 7, queued tasks = 4, completed tasks = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2063)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:830)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1379)
at com.zyq.mythreadpool.ThreadPoolExecutorTest.main(ThreadPoolExecutorTest.java:21)
任务1执行完毕
任务6开始执行
任务4执行完毕
任务3执行完毕
任务2执行完毕
任务5执行完毕
任务9开始执行
任务8开始执行
任务7开始执行
任务10执行完毕
任务11执行完毕
任务6执行完毕
任务9执行完毕
任务8执行完毕
任务7执行完毕
中间报错的原因是,将第12个任务数使用拒绝策略拒绝掉了。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
2020-04-10 postgresql数据库-number类型模糊查询
2020-04-10 在线朗读软件