Map接口之HashMap
*Map集合的使用*
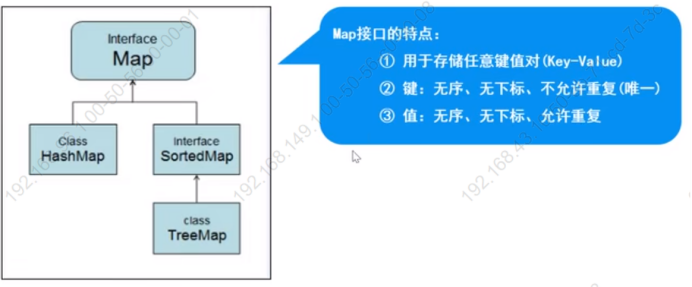
这是Map接口的体系结构
特点:存储一对数据(key-value),无序、无下标,键不可以重复,值可以重复。
常用方法:
put(K key, V value)
将指定的值与该映射中的指定键相关联(可选操作)。
get(Object key)
返回到指定键所映射的值,或 null如果此映射包含该键的映射。
keySet()
返回此集合中包含的键的集合。
values()
返回此集合中包含的值的Collection全集。
entrySet()
返回此集合包含的匹配的Set集合。
*HashMap*
小案例
package com.genericlist;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Map接口的使用
* 特点:1.存储键值对 2.键不能重复,值可以重复 3.当键重复的时候能够,值会被替换掉 4.无序
*/
public class MapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
//1.添加元素
hashMap.put("cn","中国");
hashMap.put("uk","英国");
hashMap.put("us","美国");
hashMap.put("Germany","德国");
hashMap.put("cn","china");
System.out.println("元素的个数:"+hashMap.size());
System.out.println(hashMap);
//2.删除
hashMap.remove("Germany");
System.out.println("删除之后元素的个数:"+hashMap.size());
//3.遍历
//3.1使用keyset方法进行遍历
System.out.println("----------使用keyset方法进行遍历----------");
Set<String> keySet = hashMap.keySet();
for (String s : keySet) {
System.out.println(s+"----------"+hashMap.get(s));
}
//3.2使用entryset方法进行遍历 一个entry包含一个键和一个值
System.out.println("----------使用entryset方法进行遍历----------");
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-------"+entry.getValue());
}
//总结:在实际项目遍历的时候,entrySet的效率要高于keySet,因为keySet先取键再取值,相当于遍历了两次。
//4.判断
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey("uk"));
System.out.println(hashMap.containsValue("英国"));
}
}
运行结果:
运行结果:
元素的个数:4
{uk=英国, cn=china, us=美国, Germany=德国}
删除之后元素的个数:3
----------使用keyset方法进行遍历----------
uk----------英国
cn----------china
us----------美国
----------使用entryset方法进行遍历----------
uk-------英国
cn-------china
us-------美国
true
true、
*使用实体类作为键*
package com.mappractise;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 学生实体类
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int stuNo;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int stuNo) {
this.name = name;
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getStuNo() {
return stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(int stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
//去除重复 重写hashcode方法和equals方法
//重写hashcode方法进行内存地址的判断
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int n1 = this.name.hashCode();
int n2 = this.stuNo;
return n1 + n2;
}
//必须重写equals方法才能判断添加的对象是否重复
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
if (obj instanceof Student) {
Student person = (Student) obj;
if (this.name.equals(person.getName()) && this.stuNo == person.getStuNo()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", stuNo=" + stuNo +
'}';
}
}
package com.mappractise;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* HashMap集合的使用
* 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
* 怎样去重复:使用key的hashcode和equals方法作为判断重复的依据的
*/
public class HashMapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
HashMap<Student, String> hashMap = new HashMap<Student, String>();
//刚创建hashmap的时候table=null size=0
Student stu1 = new Student("孙悟空", 100);
Student stu2 = new Student("猪八戒", 101);
Student stu3 = new Student("沙和尚", 102);
hashMap.put(stu1,"金箍棒");
hashMap.put(stu2,"菜耙子");
hashMap.put(stu3,"降魔杖");
// hashMap.put(stu3,"降魔杖");//不能添加重复的元素
// hashMap.put(stu3,"yyy");//会进行值的替换
//hashMap.put(new Student("孙悟空", 100),"降魔杖");//重写了hashcode方法和equals方法之后就不会重复添加姓名和学号相同的对象了
System.out.println("元素的个数:"+hashMap.size());
System.out.println("集合内容:"+hashMap);
//2.删除
// hashMap.remove(stu1);
// System.out.println("删除之后元素的个数:"+hashMap.size());
// System.out.println("删除之后集合内容:"+hashMap);
//3.集合的遍历
System.out.println("==========keySet==========");
for (Student key : hashMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key+"--"+hashMap.get(key));
}
System.out.println("==========entrySet==========");
for (Map.Entry<Student, String> stringEntry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(stringEntry.getKey()+"--"+stringEntry.getValue());
}
//4.判断
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey(stu1));
System.out.println(hashMap.containsValue("金箍棒"));
}
}
运行结果:
运行结果:
元素的个数:3
集合内容:{Student{name='孙悟空', stuNo=100}=金箍棒, Student{name='猪八戒', stuNo=101}=菜耙子, Student{name='沙和尚', stuNo=102}=降魔杖}
==========keySet==========
Student{name='孙悟空', stuNo=100}--金箍棒
Student{name='猪八戒', stuNo=101}--菜耙子
Student{name='沙和尚', stuNo=102}--降魔杖
==========entrySet==========
Student{name='孙悟空', stuNo=100}--金箍棒
Student{name='猪八戒', stuNo=101}--菜耙子
Student{name='沙和尚', stuNo=102}--降魔杖
true
True





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
2020-01-30 Springmvc框架-json对象的处理
2020-01-30 使用Springmvc框架实现多文件上传(二)
2020-01-30 使用springmvc框架实现多文件上传