runloop
何时使用 Run Loop?
仅当在为你的程序创建辅助线程的时候,你才需要显式运行一个 run loop。Run loop 是程序主线程基础设施的关键部分。所以,Cocoa 和 Carbon 程序提供了代码运 行主程序的循环并自动启动 run loop。IOS 程序中 UIApplication 的 run 方法(或 Mac OS X 中的 NSApplication)作为程序启动步骤的一部分,它在程序正常启动的时 候就会启动程序的主循环。类似的,RunApplicationEventLoop 函数为 Carbon 程序 启动主循环。如果你使用 xcode 提供的模板创建你的程序,那你永远不需要自己去显 式的调用这些例程。
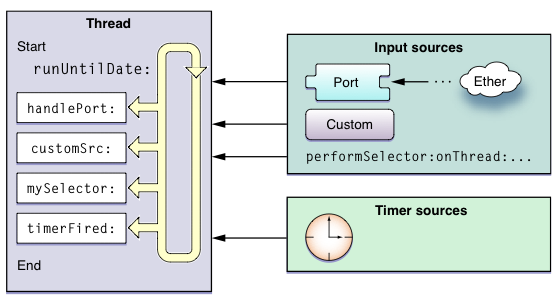
对于辅助线程,你需要判断一个 run loop 是否是必须的。如果是必须的,那么 你要自己配置并启动它。你不需要在任何情况下都去启动一个线程的 run loop。比 如,你使用线程来处理一个预先定义的长时间运行的任务时,你应该避免启动 run loop。Run loop 在你要和线程有更多的交互时才需要,比如以下情况:
使用端口或自定义输入源来和其他线程通信 使用线程的定时器 Cocoa 中使用任何 performSelector...的方法 使线程周期性工作
如果你决定在程序中使用 run loop,那么它的配置和启动都很简单。和所有线程 编程一样,你需要计划好在辅助线程退出线程的情形。让线程自然退出往往比强制关 闭它更好。关于更多介绍如何配置和退出一个 run loop,参阅”使用 Run Loop 对象” 的介绍。
作用
- 使程序一直运行并接收用户的输入
- 决定程序在何时处理哪些事件
- 调用解耦(Message Queue)
- 节省CPU时间(当程序启动后,什么都没有执行的话,就不用让CPU来消耗资源来执行,直接进入睡眠状态)
模式
RunLoop在同一段时间只能且必须在一种特定的模式下运行- 如果要更换 Mode,必须先停止当前的 Loop,然后再重新启动 Loop
-
Mode 是保证滚动流畅的关键
-
NSDefaultRunLoopMode:默认状态、空闲状态 UITrackingRunLoopMode:滚动模式UIInitializationRunLoopMode:私有的,App启动时NSRunLoopCommonModes:默认包含1,2两种模式
模拟 RunLoop 实现
void runEvent(int num){
if (num == 1){
NSLog(@"按钮点击事件");
}
if (num == 2) {
NSLog(@"scrollView拖动事件");
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// insert code here...
//NSLog(@"Hello, World!");
while (YES) {
NSLog(@"请输入选择项,0表示退出");
int num =0;
scanf("%d",&num);
if (num==0) {
break;
}else{
runEvent(num);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
运行循环与时钟
@interface ViewController ()
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSTimer *timer;
@property(nonatomic,assign)int count;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(demo) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//需要将其加入到运行循环里面才能执行
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
}
- (void)demo{
self.count++;
NSLog(@"hello===%d",self.count);
}
- 将时钟添加到其他线程工作
@interface ViewController ()
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSTimer *timer;
@property(nonatomic,assign)int count;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
//1.创建一个子线程
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(threadRun) object:nil];
[thread start];
}
/**
1.在子线程中,如下事件是不会开启的
1.定时源事件
2.输入源事件
3.网络下载
*/
- (void)threadRun{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(demo) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//需要将其加入到运行循环里面才能执行
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
//1.需要我们自己手工开启我们子线程的NSRunLoop
CFRunLoopRun();
}
- (void)demo{
self.count++;
if (self.count==5) {
NSLog(@"---停止子线程运行循环---");
//停止运行循环,这样子线程才能销毁
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent());
}
NSLog(@"hello===%d",self.count);
}
注意:主线程的运行循环是默认启动的,但是子线程的运行循环是默认不工作的,子线程的运行循环需要我们自己手工开启和关闭,只有自己手工关闭,这样才能够保证线程执行完毕后,子线程自动被销毁

