BlueZ
一、BlueZ在ubuntu PC上的基础应用
1、bluez的安装及基本功能
dong@ubuntu:~/bluez$ ls
bluez-5.47.tar.xz SPP-loopback.py
dong@ubuntu:~/bluez$ tar xvf bluez-5.47.tar.xz
dong@ubuntu:~/bluez/bluez-5.47$ ./configure --prefix=/usr --mandir=/usr/share/man --sysconfdir=/etc --localstatedir=/var
make
make install
装完bluez,然后插上蓝牙适配器就可以测试了,如果不能启动就注销或者重启一下电脑。
2、bluez配对
dong@ubuntu:~/bluez/bluez-5.47$ cd test/
dong@ubuntu:~/bluez/bluez-5.47/test$ python simple-agent
Agent registered
然后可以用手机蓝牙助手(Bluetooth spp pro/蓝牙串口助手 Pro)来扫描配对蓝牙适配器,ubuntu上的simple-agent会弹出配对确认信息,输入yes回车完成配对
simple-agent是通过主从机之间的交互来实现的,可以实现加密配对。
3、bluez spp蓝牙透传demo
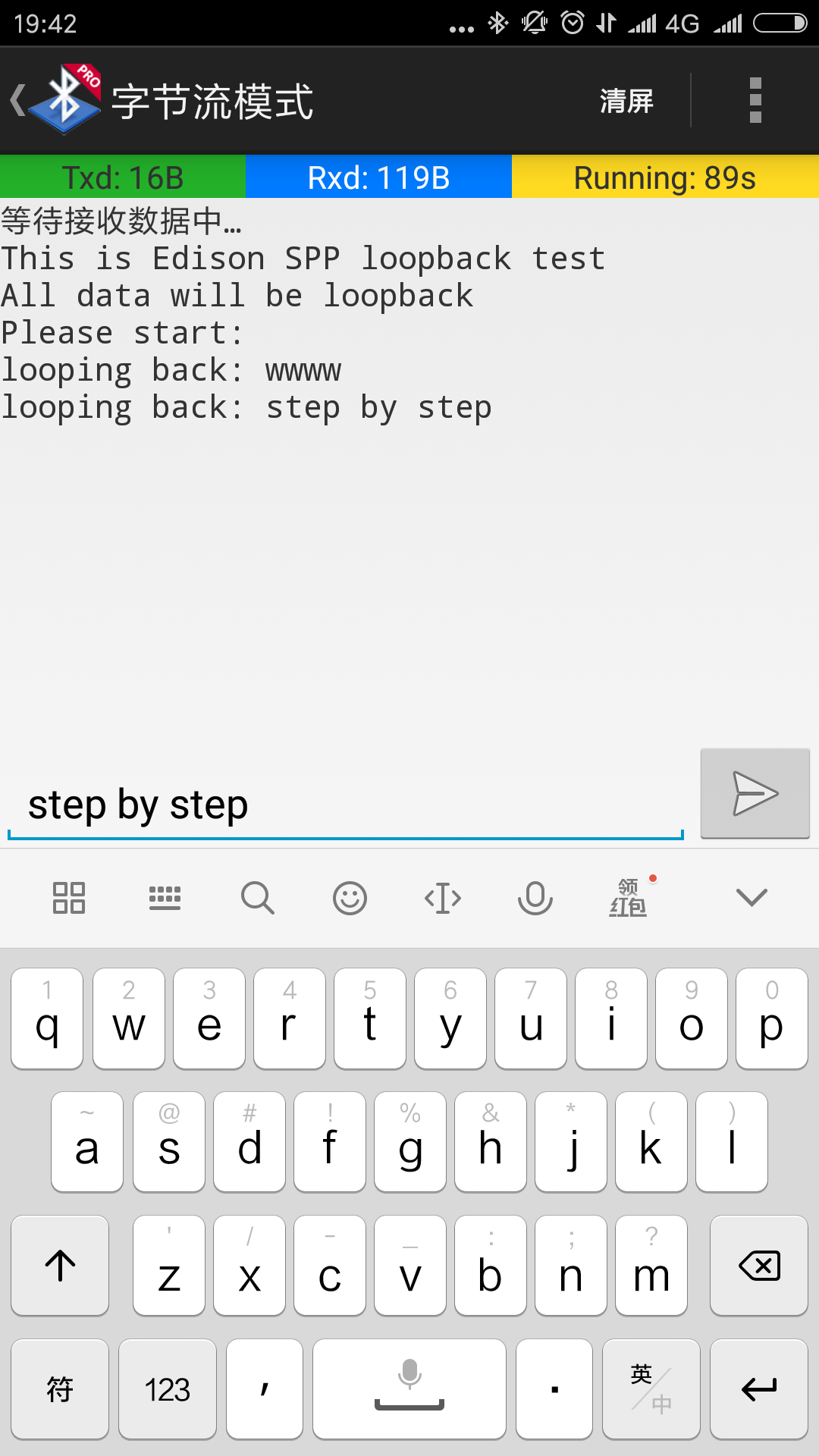
SPP-loopback.py和bluez5-spp-example分别是用python和c语言实现的SPP Demo,SPP-loopback.py更简单一些,运行即可透传与手机交互。
如果是ubuntu版本太低,安装bluez可能会缺一些库文件,装上库文件即可,可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/twy76/article/details/23851587
过了几年了,还有人看,刚好整理手机,补两张图上来。
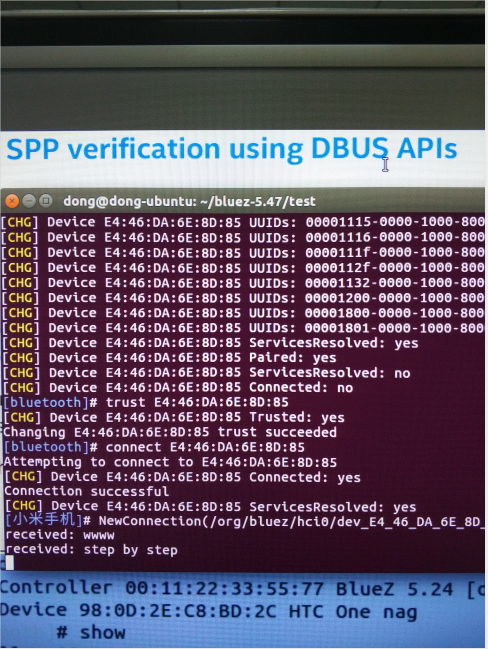
PC上也可以用图形工具来配置蓝牙,blueman-applet比较方便。
4、BlueZ文件共享
示例:BlueZ设备(这里是ubuntu PC)与手机之间的文件收发
dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ lsusb Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub Bus 001 Device 004: ID 0a12:0001 Cambridge Silicon Radio, Ltd Bluetooth Dongle (HCI mode) Bus 001 Device 002: ID 17ef:6019 Lenovo Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ hciconfig -a hci0: Type: BR/EDR Bus: USB BD Address: 00:1A:7D:DA:71:13 ACL MTU: 310:10 SCO MTU: 64:8 UP RUNNING PSCAN ISCAN RX bytes:1932 acl:0 sco:0 events:125 errors:0 TX bytes:4107 acl:0 sco:0 commands:125 errors:0 Features: 0xff 0xff 0x8f 0xfe 0xdb 0xff 0x5b 0x87 Packet type: DM1 DM3 DM5 DH1 DH3 DH5 HV1 HV2 HV3 Link policy: RSWITCH HOLD SNIFF PARK Link mode: SLAVE ACCEPT Name: 'BlueZ 5.47' Class: 0x0c0104 Service Classes: Rendering, Capturing Device Class: Computer, Desktop workstation HCI Version: 4.0 (0x6) Revision: 0x22bb LMP Version: 4.0 (0x6) Subversion: 0x22bb Manufacturer: Cambridge Silicon Radio (10) dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ hcitool scan Scanning ... 00:19:86:00:12:12 ZHDZXD 00:90:A2:CC:57:D8 ZHDGIS 50:68:0A:42:C5:67 wifitest E4:46:DA:6E:8D:85 小米手机 44:C3:46:56:2E:50 Honor 8 Lite dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ sdptool browse E4:46:DA:6E:8D:85 Browsing E4:46:DA:6E:8D:85 ... Service RecHandle: 0x10000 Service Class ID List: "Generic Attribute" (0x1801) Protocol Descriptor List: "L2CAP" (0x0100) PSM: 31 "ATT" (0x0007) uint16: 0x0001 uint16: 0x0005 ... ...
Browsing E4:46:DA:6E:8D:85 ... Service Search failed: Invalid argument Service Name: OBEX Object Push Service RecHandle: 0x1000b Service Class ID List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Protocol Descriptor List: "L2CAP" (0x0100) "RFCOMM" (0x0003) Channel: 6 "OBEX" (0x0008) Profile Descriptor List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Version: 0x0102 Browsing E4:46:DA:6E:8D:85 ... Service Search failed: Invalid argument //send file to moble dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ obex_test -b E4:46:DA:6E:8D:85 6 Using Bluetooth RFCOMM transport OBEX Interactive test client/server. > c Made some progress... Connect OK! Version: 0x10. Flags: 0x00 > x PUSH file> test.txt name=test.txt, size=5 Going to send test.txt(test.txt), 5 bytes Filling stream! Filling stream! Made some progress... Made some progress... PUT successful! > q dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ sudo sdptool add OPUSH OBEX Object Push service registered dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ sudo sdptool browse local Browsing FF:FF:FF:00:00:00 ... Service RecHandle: 0x10000 Service Class ID List: "PnP Information" (0x1200) Profile Descriptor List: "PnP Information" (0x1200) Version: 0x0103 ... ... Service Name: OBEX Object Push Service RecHandle: 0x10008 Service Class ID List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Protocol Descriptor List: "L2CAP" (0x0100) "RFCOMM" (0x0003) Channel: 9 "OBEX" (0x0008) Profile Descriptor List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Version: 0x0100 //receive file from moble dong@dong-ubuntu:~$ obex_test -b local 9 Using Bluetooth RFCOMM transport OBEX Interactive test client/server. > s OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 Unknown event 0b! connect_server() connect_server() Skipped header c0 Made some progress... Server request finished! server_done() Command (00) has now finished OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 Made some progress... OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 Made some progress... OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 Made some progress... OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 ... ... Made some progress... OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 put_server() put_server() Found name put_server() Skipped header 42 put_server() Skipped header c3 put_server() Found body Filename = Screenshot_2017-12-19-15-44-49-059_com.baidu.searchbox.png Wrote Screenshot_2017-12-19-15-44-49-059_com.baidu.searchbox.png (257776 bytes) Made some progress... Server request finished! server_done() Command (02) has now finished OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 Unknown event 0b! We got a disconnect-request Made some progress... Server request finished! Disconnect done! OBEX_HandleInput() returned 1 >
二、BlueZ在ARM上的基础应用
1、BlueZ移植
BlueZ依赖的第三方库比较多,编译起来很繁琐,给每个库都创建一个config.sh文件,并设置777权限,
创建安装目录/usr/local/bluez,也设置777权限,
如下依次运行每个库的配置文件./config.sh可完整的编译出ARM的可执行文件。
编译环境
ubuntu + linaro gcc
gcc编译器https://www.linaro.org/downloads/
硬件环境
CPU: Cortex A5
Bluetooth: wg7813(bluetooth和wifi的复合模块,芯片是TI的wl18xx)
移植主要参考这个wiki,依赖库的版本最好也按wiki里的版本,一堆开源库,不同版本会有冲突,wiki里的版本是一次编译通过,配合如下脚本。
http://wiki.beyondlogic.org/index.php?title=Cross_Compiling_BlueZ_Bluetooth_tools_for_ARM
1) zlib-1.2.8
#!/bin/bash cd /home/dong/bluez/zlib-1.2.8 CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc \ AR=arm-linux-gnueabihf-ar \ RANLIB=arm-linux-gnueabihf-ranlib \ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/bluez make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
zlib第一次还不能运行脚本,一步一步来,其他库都能通过脚本自动化编译,安装。
Download, cross compile and install the zlib compression libraries. Configure doesn't accept the --host parameter (reports unknown option), so you need to hack the makefile.
wget http://zlib.net/zlib-1.2.8.tar.gz
tar -xzf zlib-1.2.8.tar.gz
cd zlib-1.2.8/
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/bluez
Edit the makefile and prefix the build tools with arm-linux-gnueabi-.
CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc LDSHARED=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -shared -Wl,-soname,libz.so.1,--version-script,zlib.map CPP=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -E AR=arm-linux-gnueabihf-ar RANLIB=arm-linux-gnueabihf-ranlib
Make and install:
make make install
2) libffi-3.0.13
#!/bin/bash ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/usr/local/bluez make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
3) glib-2.40.0
#!/bin/bash ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf \ LIBFFI_CFLAGS="-I/usr/local/bluez/lib/libffi-3.0.13/include" \ LIBFFI_LIBS="-lffi -L/usr/local/bluez/lib" \ ZLIB_CFLAGS="-I/usr/local/bluez/include" \ ZLIB_LIBS="-lz -L/usr/local/bluez/lib" \ --prefix=/usr/local/bluez PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/usr/local/bluez/lib/pkgconfig glib_cv_stack_grows=no glib_cv_uscore=yes ac_cv_func_posix_getpwuid_r=yes ac_cv_func_posix_getgrgid_r=yes make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
报错configure: error: Could not find a glib-genmarshal in your PATH,缺了libglib2.0-dev
sudo apt-get install libglib2.0-dev
4) expat-2.1.0
#!/bin/bash ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/usr/local/bluez make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
5) dbus-1.8.0
#!/bin/bash ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/usr/local/bluez PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/usr/local/bluez/lib/pkgconfig \ --disable-tests \ --sysconfdir=/usr/local/bluez/etc \ --localstatedir=/usr/local/bluez/var \ --enable-user-session \ --disable-doxygen-docs \ --disable-xml-docs \ --disable-static \ --docdir=/usr/local/bluez/share/doc/dbus-1.8.0 \ --with-console-auth-dir=/usr/local/bluez/var/run/console \ --with-system-pid-file=/usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus/pid \ --with-system-socket=/usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket \ CPPFLAGS='-I/usr/local/bluez/include/' \ CFLAGS='-I/usr/local/bluez/include/' \ LDFLAGS='-L/usr/local/bluez/lib' make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
6) libical-1.0
#!/bin/bash export CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc export CXX=arm-linux-gnueabihf-g++ cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/bluez make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
7) ncurses-5.9
#!/bin/bash cd /home/dong/bluez/ncurses-5.9 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/bluez --with-shared \ CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc \ CXX=arm-linux-gnueabihf-g++ \ --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
8) readline-6.3
#!/bin/bash ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/usr/local/bluez bash_cv_wcwidth_broken=yes \ PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/usr/local/bluez/lib/pkgconfig \ CPPFLAGS='-I/usr/local/bluez/include/' \ CFLAGS='-I/usr/local/bluez/include/' \ LDFLAGS='-lncurses -L/usr/local/bluez/lib' #make SHLIB_LIBS=-lncurses make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
9) bluez-5.18
#!/bin/bash ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf \ --prefix=/usr/local/bluez \ CC="arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc \ -L/usr/local/bluez/lib \ -I/usr/local/bluez/include \ -I/usr/local/bluez/include/glib-2.0 \ -I/usr/local/bluez/include/dbus-1.0 \ -I/usr/local/bluez/lib/glib-2.0/include \ -I/usr/local/bluez/lib/dbus-1.0/include \ -I/usr/local/bluez/lib/libffi-3.0.13/include " \ PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/usr/local/bluez/lib/pkgconfig \ CPPFLAGS='-I/usr/local/bluez/include/' \ CFLAGS='-I/usr/local/bluez/include/' \ LDFLAGS='-lrt -lreadline -lncurses -L/usr/local/bluez/lib' \ --disable-systemd --disable-udev --disable-cups --enable-library make if [ $? == 0 ]; then make install else echo -e "\n\tmake fail\n" fi
再次说明版本务必要匹配,否则会冲突,怎么检查版本匹配,暂时不清楚,新版本库匹配在下面这网站去找,下面两个版本都有匹配好的BlueZ Dependencies
BlueZ-5.46
http://www.linuxfromscratch.org/blfs/view/stable/general/bluez.html
BlueZ-5.48
http://www.linuxfromscratch.org/blfs/view/svn/general/bluez.html
2、板载bluez调试
1)linux内核配置bluetooth驱动参考 http://blog.csdn.net/new_abc/article/details/7639326 (bluetooth和wifi)
[*]Networking support --->
<*> Bluetooth subsystem support ---> //蓝牙子系统必须选择
<*> L2CAP protocol suppor //逻辑链路控制和适配协议。
<*> SCO links support //蓝牙语音和耳机支持
<*> RFCOMM protocol suppor //面向流的传输协议,支持拨号网络等
[*] RFCOMM TTY support
<*> BNEP protocol support //蓝牙网络封装协议,自组网支持
[*] Multicast filter support //蓝牙多播,支持支持BNEP
[*] Protocol filter support //蓝牙多播,支持支持支持BNEP
<*> HIDP protocol support //基本支持协议
Bluetoothdevice drivers --->
<*>HCI USB driver //USB蓝牙模块支持
<*>HCIUART driver //基于串口,CF卡或PCMCIA的蓝牙
<*>HCI BlueFRITZ! USB driver
<*>HCI VHCI (Virtual HCI device) driver
其余的选项,根据自己的蓝牙设备进行调整。
2)移植完的bluez,把安装文件拷贝到板子上,只需要dbus和bluez的安装文件,总共应该不超过5M,我的在/usr/local/bluez,然后添加环境变量。
拷贝几个库文件,添加messagebus用户,还是参考刚才的wiki
addgroup -S messagebus adduser -S messagebus -G messagebus
http://wiki.beyondlogic.org/index.php?title=Cross_Compiling_BlueZ_Bluetooth_tools_for_ARM
可以试试hciconfig, hcitool, dbus-deamon等工具是否正常,正常了就移植成功了。
板子内存紧张可以用nfs挂载的方式来调试,挂载好了,环境变量设置到挂载的路径就可以了。
先安装好nfs服务器
https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/e5c39bf5abc8f739d76033be.html
开发板挂载ubuntu,在ubuntu用户目录下的nfs目录中准备好文件
在开发板上挂载ubuntu
mkdir /mnt/bluez
#在开发板端挂载板子网卡,这里用的USB模拟的网卡,挂载到usb0,真实的网卡就不需要模拟这一步了。
modprobe g_multi.ko file=/dev/mmcblk0p5,/dev/mmcblk0p6 ro=0,0 luns=2 stall=0 removable=1,1 iSerialNumber=3000111
ifconfig usb0 192.168.10.2
在ubuntu端打开网卡
ifconfig enp0s20f0u2 192.168.10.6 netmask 255.255.255.0
ifconfig enp0s20f0u2 up 192.168.10.6
#在开发板端挂载ubuntu上的nfs服务器
mount -t nfs -o nolock 192.168.10.6:/home/dong/nfs /mnt
#umount -t nfs -a nolock 192.168.10.6:/home/dong/nfs /mnt
开发板添加环境变量
#add path
export PATH=/mnt/bluez/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/bluez/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
或者在/etc/profile里添加环境变量永久生效
export PATH=\
/bin:\
/sbin:\
/usr/bin:\
/usr/sbin:\
/usr/bin/X11:\
/usr/local/bin:\
/mnt/bluez/bin:\
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/bluez/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
source /etc/profile
创建并运行脚本文件bluez.init.sh,运行成功就可以用手机搜到BlueZ-5.18的蓝牙设备
#power on echo 49 > /sys/class/gpio/export echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/direction echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value sleep 0.2 echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value sleep 0.2 #load firmware hciattach -s 115200 /dev/ttyS2 texas 115200 flow hciconfig hci0 up sleep 0.1 hciconfig hci0 iscan sleep 0.1 rm -rf /usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus/pid dbus-daemon --system sleep 0.2 bluetoothd & sleep 1 hciconfig hci0 iscan
有时候环境变量写到配置文件会失效,程序运行会从系统库目录/lib /usr/lib查找库文件,不从我们配置的/mnt/bluez/lib目录里找
运行临时环境变量配置指令即可生效
export PATH=/mnt/bluez/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/bluez/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
3、python移植
新版本bluez的demo都是python写的,所以还需要把python也移植到板子上。
1)下载好Python-2.7.2.tgz和补丁文件Python-2.7.2-xcompile.patch
2)编译PC上运行的pgen
./configure
make python Parser/pgen
mv python hostpython
mv Parser/pgen Parser/hostpgen
make distclean
3)给Python-2.7.2打补丁
patch -p1 < Python-2.7.2-xcompile.patch
4)交叉编译,编译器arm-linux-gnueabihf-
CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
CXX=arm-linux-gnueabihf-g++ AR=arm-linux-gnueabihf-ar
RANLIB=arm-linux-gnueabihf-ranlib ./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf
--build=x86_64-linux-gnu --prefix=/home/dong/_install
chmod 777 ./setup.py
如果空间紧张,可以更改Makefile,不需要debug,去掉-g,优化等级调成-o2
#OPT= -DNDEBUG -g -fwrapv -O3 -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes
OPT= -DNDEBUG -fwrapv -O2 -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes
make
HOSTPYTHON=./hostpython HOSTPGEN=./Parser/hostpgen
BLDSHARED="arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -shared"
CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET=yes
HOSTARCH=arm-linux-gnueabihf BUILDARCH=x86_64-linux-gnu
make
install HOSTPYTHON=./hostpython BLDSHARED="arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
-shared" CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET=yes
prefix=/home/dong/_install
如果安装报错
python: Syntax error: word unexpected (expecting ")")
将install-sh文件第一行#!/bin/sh改成#!/bin/bash
5)把安装目录下的文件复制到arm设备上,并吧Python路径添加到PATH中,然后执行测试
python /usr/local/python/lib/python2.7/test/test___all__.py
我的板内存空间紧张,先用nfs挂载来调试
转自
http://blog.csdn.net/xiwenfuor/article/details/38384687
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_609b4c0d01012j5q.html
我移植完了,发现这个blog写得很简洁。
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28351465/article/details/54406180
4、板载python调试
python的库文件很大,还是跟上面调试bluez一样,采用nfs来调试
开发板添加环境变量
#add path
export PATH=/mnt/python/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/python/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
或者在/etc/profile里添加环境变量永久生效
export PATH=\
/bin:\
/sbin:\
/usr/bin:\
/usr/sbin:\
/usr/bin/X11:\
/usr/local/bin:\
/mnt/bluez/bin:\
/mnt/python/bin:\
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/bluez/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/python/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
source /etc/profile
挂载后运行python –V就可以看到python的版本信息了。
python /mnt/python/lib/python2.7/test/test___all__.py
运行结果
Following
modules have no __all__ and have been ignored: ['DocXMLRPCServer',
'HTMLParser', 'SimpleXMLRPCServer', 'UserDict', 'UserList',
'_LWPCookieJar', '_MozillaCookieJar', '__phello__.foo', 'abc', 'an]
Following modules failed to be imported: ['ctypes.wintypes', 'dbhash', 'gzip', 'idlelib.AutoComplete']
ok
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 1 test in 48.532s
OK
5、运行simple-agent 或者 BlueZ SPP Demo
[root@sama5d3x /mnt]# python simple-agent
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "simple-agent", line 7, in <module>
import dbus
ImportError: No module named dbus
缺了dbus模块
交叉编译dbus-python-1.2.4
折腾一天看见这个心碎了
https://www.zhihu.com/question/34573048
找了一圈,只能用buildroot来制作支持python的文件系统
http://www.at91.com/linux4sam/bin/view/Linux4SAM/BuildRootBuild
https://www.cnblogs.com/chencanjian/p/6060448.html
6、buildroot编译dbus-python库
dbus-python
gobject
其实不用像上面那样单独移植python也可以,就在buildroot里把python和需要的库都选上更方便,
buildroot还可以压缩库文件,还更省空间。
用yocto或者 OpenEmbedded来构建文件系统貌似也行,没有验证
[root@sama5d3x /mnt]# python Python 2.7.2 (default, Jan 20 2018, 15:29:23) [GCC 4.7.3 20121205 (prerelease)] on linux4 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> from __future__ import absolute_import, print_function, unicode_literals >>> import gobject as GObject >>> import sys >>> import dbus >>> import dbus.service >>> import dbus.mainloop.glib >>> from optparse import OptionParser >>> dbus.mainloop.glib.DBusGMainLoop(set_as_default=True) <dbus.mainloop.NativeMainLoop object at 0x2ecc08> >>> bus = dbus.SystemBus() Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/dbus/_dbus.py", line 194, in __new__ File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/dbus/_dbus.py", line 100, in __new__ File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/dbus/bus.py", line 122, in __new__ dbus.exceptions.DBusException: org.freedesktop.DBus.Error.FileNotFound: Failed to connect to socket /var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket: No such file or directory
连不上dbus的socket,就差一口气了......
突然发现dbus-1.8.0库编译的时候没打开--with-system-socket
参考http://www.linuxfromscratch.org/blfs/view/svn/general/dbus.html
./configure --prefix=/usr \ --sysconfdir=/etc \ --localstatedir=/var \ --disable-doxygen-docs \ --disable-xml-docs \ --disable-static \ --docdir=/usr/share/doc/dbus-1.8.0 \ --with-console-auth-dir=/run/console \ --with-system-pid-file=/run/dbus/pid \ --with-system-socket=/run/dbus/system_bus_socket && make
更改上面dbus-1.8.0的编译配置,上面已经改过来了,重新编译,再运行配对例子
[root@sama5d3x test]# hciconfig hci0 pscan [root@sama5d3x test]# hciconfig hci0 noauth [root@sama5d3x test]# python simple-agent Agent registered RequestConfirmation (/org/bluez/hci0/dev_E4_46_DA_6E_8D_85, 565038) Confirm passkey (yes/no): yes [root@sama5d3x test]# cd .. [root@sama5d3x /mnt]# python SPP-loopback.py NewConnection(/org/bluez/hci0/dev_E4_46_DA_6E_8D_85, 9) received: aaa received: step by step received: BlueZ SPP OK !
配对simple-agent和蓝牙透传SPP-loopback.py都正常,再把bluez和python库裁剪,整理好就可以植入产品里了。
SPP-loopback.py蓝牙串口透传例子是intel的Edison模块的,也可以用在这里。
intel edison bluetooth guide 这个文档比较完整。
http://download.intel.com/support/edison/sb/edisonbluetooth_331704004.pdf
我整理的启动脚本 bluez_init.sh
#power on echo 49 > /sys/class/gpio/export echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/direction echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value sleep 0.2 echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value sleep 0.2 #load firmware hciattach -s 115200 /dev/ttyS2 texas 115200 flow sleep 1 hciconfig hci0 up sleep 0.1 hciconfig hci0 iscan sleep 0.1 #add dbus dir rm -r /usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus ln -s /run/dbus/ /usr/local/bluez/var/run/ rm -rf /usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus/pid mkdir /run/dbus #boot bluez process dbus-daemon --system sleep 1 bluetoothd & sleep 1 #run user app python simple-agent & sleep 0.1 python SPP-loopback.py & sleep 0.1 hciconfig hci0 name "bluez_test" hciconfig hci0 piscan
将bluez-5.18的simple-agent文件中配对认证注释掉,设备就不认证了
def AuthorizeService(self, device, uuid): print("AuthorizeService (%s, %s)" % (device, uuid)) #authorize = ask("Authorize connection (yes/no): ") #if (authorize == "yes"): # return #raise Rejected("Connection rejected by user") ... ... def RequestConfirmation(self, device, passkey): print("RequestConfirmation (%s, %06d)" % (device, passkey)) #confirm = ask("Confirm passkey (yes/no): ") #if (confirm == "yes"): set_trusted(device) # return #raise Rejected("Passkey doesn't match") @dbus.service.method(AGENT_INTERFACE, in_signature="o", out_signature="") def RequestAuthorization(self, device): print("RequestAuthorization (%s)" % (device)) #auth = ask("Authorize? (yes/no): ") #if (auth == "yes"): # return #raise Rejected("Pairing rejected")
给板子上电,挂载好bluez和python的库文件,然后运行上面的启动脚本 ./bluez.init.sh
[root@sama5d3x /root]# mount -t nfs -o nolock 192.168.10.6:/home/dong/nfs /mnt
[root@sama5d3x /root]# cd /mnt/
[root@sama5d3x /mnt]# ./bluez.init.sh
Found a Texas Instruments' chip!
Firmware file : /lib/firmware/ti-connectivity/TIInit_11.8.32.bts
Loaded BTS script version 1
Device setup complete
[root@sama5d3x /mnt]# Agent registered
RequestConfirmation (/org/bluez/hci0/dev_E4_46_DA_6E_8D_85, 345760)
NewConnection(/org/bluez/hci0/dev_E4_46_DA_6E_8D_85, 9)
received: step by step
received: step by step
received: step by step
7、python与c之间的交互
可以用的方式很多,共享内存,消息队列,管道,进程池或者直接封装接口互相调用函数。
搜一下就有了.下面是我找的共享内存机制
1) Python读取c语言进程的内存块
http://chl0000.iteye.com/blog/1915303
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/57430.htm
2) python和c语言参数传递
c--->python
http://blog.csdn.net/JoeBlackzqq/article/details/10441017
http://blog.csdn.net/chenyulancn/article/details/8158168
python--->c
http://blog.csdn.net/mrcheny/article/details/79022973
3) 实例:导出python进程的数据
我这个项目需要导出python进程的数据给c进程处理
给c语言进程提供一个数据结构
bluetooth_data.c
#include <stdio.h> struct bluetooth_t{ int status; char *buf; }; int bluetooth_cb(struct bluetooth_t bluetooth) { printf("bluetooth status:%d, bluetooth buf:%s \n", bluetooth.status,bluetooth.buf); return 0; }
编译成so库文件
gcc/arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -o bluetooth_data.so -shared -fPIC bluetooth_data.c
然后python进程把需要的数据写到上面的数据结构
data_test.py
#!/usr/bin/python import ctypes from ctypes import * class bluetooth(Structure): _fields_=[('status',c_int),('buf',c_char_p)] if __name__ == "__main__": func = ctypes.cdll.LoadLibrary("./bluetooth_data.so") s = bluetooth() s.status = 1 s.buf = bytes('hello,world') func.bluetooth_cb(s)
运行python data_test.py就可以打印出导出的数据
bluetooth status:1, bluetooth buf:hello,world.
8、bluez的BLE工作模式
只有bluez-5.xx以上版本才支持低功耗模式,配置跟普通模式有细微差别
我配置的BLE模式启动脚本 bluez_le_init.sh
#power on echo 49 > /sys/class/gpio/export echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/direction echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value sleep 0.2 echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value sleep 0.2 #load firmware hciattach -s 115200 /dev/ttyS2 texas 115200 flow sleep 1 hciconfig hci0 up sleep 0.1 hciconfig hci0 iscan sleep 0.1 #add dbus dir rm -r /usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus ln -s /run/dbus/ /usr/local/bluez/var/run/ rm -rf /usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus/pid mkdir /run/dbus #boot bluez process dbus-daemon --system sleep 1 bluetoothd & sleep 1 #run user app python simple-agent & sleep 0.1 if false ; then #Bluetooth SPP python SPP-loopback.py & else #Bluetooth profile hciconfig hci0 up sleep 0.1 hciconfig hci0 leadv fi sleep 0.1 hciconfig hci0 name "bluez_test" hciconfig hci0 piscan
用了个
if false ; then
...
else
...
fi
把普通模式和BLE模式分开
给板子上电后运行./bluez.le.init.sh
找个蓝牙4.0的工具( 我用的BLE Tool )就能扫到BlueZ-5.18的设备, 读几个自带的特征值profile都正常。
9、蓝牙NFS挂载模式应用(nfs_debug)
首次运行需要配置相关系统参数
1)#配置内核蓝牙选项
2)#添加进程消息通道
addgroup -S messagebus
adduser -S messagebus -G messagebus
3#添加lp
vi /etc/group
lp:x:7:
4)#配置网卡
modprobe g_multi.ko file=/dev/mmcblk0p5,/dev/mmcblk0p6 ro=0,0 luns=2 stall=0 removable=1,1 iSerialNumber=3000111
ifconfig usb0 192.168.10.2
5)在ubuntu端打开网卡
不同主机生成的网卡名称可能不一样,ifconfig查看,这个是我的台式机,下面那个是我的笔记本
sudo ifconfig enp0s20f0u2 192.168.10.6 netmask 255.255.255.0
sudo ifconfig enp0s20f0u2 up 192.168.10.6
sudo ifconfig enp0s20f0u4 192.168.10.6 netmask 255.255.255.0
sudo ifconfig enp0s20f0u4 up 192.168.10.6
6)#在开发板端挂载ubuntu上的nfs服务器
mount -t nfs -o nolock 192.168.10.6:/home/dong/nfs /mnt/nfs
#umount -t nfs -a nolock 192.168.10.6:/home/dong/nfs /mnt/nfs
7)#添加环境变量
export PATH=\
/bin:\
/sbin:\
/usr/bin:\
/usr/sbin:\
/usr/bin/X11:\
/usr/local/bin:\
/mnt/nfs/bluez/bin:\
/mnt/nfs/python/bin:\
...
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/nfs/bluez/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/mnt/nfs/python/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
source /etc/profile
8)添加bluez配置文件
#cp -r /mnt/bluez /usr/local/
#cp -r /mnt/python /usr/local/
cp -r config/bluez /usr/local/
9) 启动蓝牙应用
./bluez.init.sh
10、蓝牙正式应用(readme)
蓝牙文件系统构建:
1) 配置内核蓝牙选项
2) 添加进程消息通道
addgroup -S messagebus
adduser -S messagebus -G messagebus
3) 添加lp
vi /etc/group
lp:x:7:
4) 拷贝库文件
cp -r bluez /usr/local/
cp -r python /usr/local/
5)拷贝应用程序
cp bluez.init.sh SPP-loopback.py /usr/local/project/
cp -r test /usr/local/project/
6)添加dbus软链接
rm -r /usr/local/bluez/var/run/dbus
ln -s /run/dbus/ /usr/local/bluez/var/run/
7)启动蓝牙进程bluez_init.sh
三、Bluetooth Audio ALSA Backend
https://github.com/Arkq/bluez-alsa
四、BLE4.0 Gatt-server
除了bluez的test目录python脚本 example-gatt-server(依赖的组件比较多,可能运行起来有点困难)
还有两种方案添加gatt自定义服务,都是开源的
一种是用bleno库,一种是go-server
我用的芯片不支持完整的BLE4.0,不能自定义用户profile 和 gatt service
一般完整支持BLE4.0或以上的芯片都是带flash的,需要更改蓝牙协议栈固件,能够作为IoT场景应用的蓝牙IC除了少部分通用芯片,大部分都是定制的专用芯片,像csr1000系列,TI的cc25xx cc26xx系列,nordic的rf51xx rf52xx系列等,都需要用厂商的专用工具来配置profile和gatt service.
下面参考文献是我收集的蓝牙自定义gatt-server方案和应用实例。
参考文献
2)用树莓派玩转蓝牙
3)A Node.js module for implementing BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) peripherals
4)Package gatt provides a Bluetooth Low Energy GATT implementation
6)Implementation of BLE peripheral using bleno
7)Python BLE GATT Server (peripheral)
越折腾越深入,工作上做的产品最多也就用到这些内容,你愿意将业余时间花在蓝牙协议栈上面,深挖到底吗?对不起,我不舍得,就此打住!
最后总结:从0到调试完成,整个过程需要点耐心,我前面因为太急躁导致多做了不少无用功,欲速则不达。
end


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号