Android——Activity与Service通信
Activity和Service之间有个常用的通信方式,通过Binder来进行通信,这里举一个进度条更新的例子来解释一下
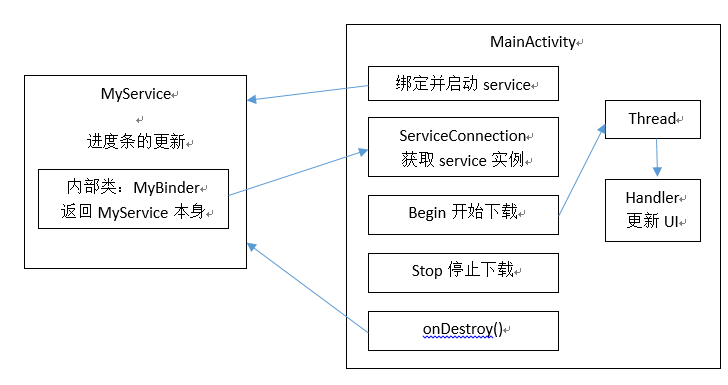
先看一下整体的图,整个的构造大概就是这样的,Activity启动一个service,后台进行service的更新,并将数据传递给前台,前台控制数据的下载和暂停
1. xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.ld.servicetest.MainActivity"> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/pb" style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="begin"/> <Button android:id="@+id/stop" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="stop"/> </LinearLayout>
一个进度条,两个按钮
2. MyService
package com.example.ld.servicetest; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Binder; import android.os.IBinder; public class MyService extends Service { private int progress = 0; private boolean stop = false; public int getProgress(){ return progress; } public void setStop(boolean temp){ stop = temp; } public boolean getStop(){ return stop; }
//进度条更新操作 public void startDownLoad(){ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while(progress<100 && !stop){ progress += 5; try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start(); } public MyService() { }
//为了返回Service本身的操作 @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // TODO: Return the communication channel to the service. return new MyBinder(); } public class MyBinder extends Binder{ public MyService getService(){ return MyService.this; } } }
3. MainActivity
package com.example.ld.servicetest; import android.content.ComponentName; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.Message; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.ProgressBar; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private int progress = 0; private MyService mService; private ProgressBar mProgressBar; private Button begin, stop;
//跟新UI的handler private Handler mHandler = new Handler(){ @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { Bundle mBundle = msg.getData(); int progress = mBundle.getInt("progress"); mProgressBar.setProgress(progress); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); //启动后台服务 Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyService.class); bindService(intent,conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); mProgressBar = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.pb); begin = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn); stop = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stop); begin.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { mService.setStop(false); mService.startDownLoad(); updateProgress(); } }); stop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { mService.setStop(true); } }); } public void updateProgress(){ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while(progress<100 && !mService.getStop()){ progress = mService.getProgress(); Message msg = new Message(); Bundle temp = new Bundle(); temp.putInt("progress",progress); msg.what = 1; msg.setData(temp); mHandler.sendMessage(msg); } } }).start(); } //获取mService实例 ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) { mService = ((MyService.MyBinder)iBinder).getService(); } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) { } };
//关掉服务并退出 protected void onDestroy(){ unbindService(conn); super.onDestroy(); } }
整个代码比较简单,注释也比较清晰,不再赘述。本人博客里也介绍过handler的使用和Service的启动,不明白的可以看看另外两篇文章
还有其他的通信方式,由于还没有代码实现,后期会持续更新。。。。。




