Offset等一些类似属性的使用
1.offset系列
// offset 系列 var father = document.querySelector('.father'); var son = document.querySelector('.son'); // 1.可以得到元素的偏移 位置 返回的不带单位的数值 console.log(father.offsetTop); console.log(father.offsetLeft); // 它以带有定位的父亲为准 如果么有父亲或者父亲没有定位 则以 body 为准 console.log(son.offsetLeft); var w = document.querySelector('.w'); // 2.可以得到元素的大小 宽度和高度 是包含padding + border + width console.log(w.offsetWidth); console.log(w.offsetHeight); // 3. 返回带有定位的父亲 否则返回的是body console.log(son.offsetParent); // 返回带有定位的父亲 否则返回的是body console.log(son.parentNode); // 返回父亲 是最近一级的父亲 亲爸爸 不管父亲有没有定位 ript>
offset和style有关属性的比较
1.是否可读写:
拿offsetWidth和style.width来说,我们执行一下以下代码:
.box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: pink; padding: 10px; }
我们把盒子的长度和宽度都设置为了200px,log一下二者:
var box = document.querySelector('.box'); console.log(box.offsetWidth);
// 220 console.log(box.style.width);
// 200px
从中我们得到了3个信息
1.二者都是可读的。
2.style会带单位。
并且根据规范对其赋值的时候也应该带单位,所以当我们通过offset获得的值再使用style时应在其后方加上px;
3.offset会把padding包含在内。
再分别对其进行赋值操作:
var box = document.querySelector('.box'); box.offsetWidth = '300'; console.log(box.offsetWidth); //220 console.log(box.style.width); //200px box.style.width = '300px'; console.log(box.offsetWidth); //320 console.log(box.style.width); //300px
发现前者并不能对元素的属性进行写的操作,这也意味着如果我们如果通过offset得到的属性而要对页面元素进行操作的时候,应该选用与style配合的方法;
这里有个动态拖拽框的小案例,有兴趣的朋友不妨试试。

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.login_header {
width: 100%;
/* height: 30px; */
line-height: 30px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
margin-top: 8px;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #000;
}
.login {
position: fixed;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
width: 512px;
height: 280px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #cccccc;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px #dddddd;
display: none;
}
.login_title {
margin-top: 20px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 20px;
cursor: move;
}
.login_uname,
.login_password {
margin: 20px 0;
}
.login_uname input,
.login_password input {
outline: none;
text-indent: 5px;
height: 38px;
width: 350px;
border: 1px solid #cccccc;
}
.login_button {
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
width: 256px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #cccccc;
}
label {
text-align: right;
display: inline-block;
width: 100px;
height: 35px;
padding-right: 10px;
/* width: 20px; */
}
.login_close a {
position: absolute;
top: -15px;
right: -15px;
display: block;
width: 35px;
height: 35px;
line-height: 35px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 14px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px #dddddd;
}
.mask {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #B2B2B2;
z-index: -99;
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="login_header"><a href="javascript:;" id="enter_login">点击,弹出登录框</a></div>
<div class="login">
<div class="login_title" id="title">登录会员</div>
<div class="login_uname">
<label for="uname">用户名:</label>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" id="uname">
</div>
<div class="login_password">
<label for="password">登录密码:</label>
<input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" id="password">
</div>
<a class="login_button" href="javascript:;">登录会员</a>
<div class="login_close">
<a href="javascript:;" id="close">关闭</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="mask"></div>
<script>
var title = document.querySelector('#title');
var enter_login = document.querySelector('#enter_login');
var login = document.querySelector('.login');
var login_uname = document.querySelector('.login_uname').querySelector('input');
var login_password = document.querySelector('.login_password').querySelector('input');
var close_button = document.querySelector('#close');
var mask = document.querySelector('.mask');
enter_login.addEventListener('click', function() {
login.style.display = 'block';
mask.style.display = 'block';
})
close_button.addEventListener('click', function() {
login.style.display = 'none';
mask.style.display = 'none';
})
function onFocus(input) {
input.addEventListener('focus', function() {
this.style.borderColor = 'skyblue';
})
input.addEventListener('blur', function() {
this.style.borderColor = '#ccc';
})
}
onFocus(login_uname);
onFocus(login_password);
title.addEventListener('mousedown', function(e) {
var x = e.pageX - login.offsetLeft;
var y = e.pageY - login.offsetTop;
function move(e) {
var moveX = e.pageX - x;
var moveY = e.pageY - y;
login.style.left = moveX + 'px';
login.style.top = moveY + 'px';
}
title.addEventListener('mousemove', move);
title.addEventListener('mouseup', function() {
title.removeEventListener('mousemove', move);
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.鼠标当前的坐标及其在某盒子内的坐标
在事件的函数中传入e,通过e.pageX,e.pageY获取当前鼠标在页面中的位置坐标。
这里我们综合上面的offset来计算一下鼠标在当前盒子中的坐标:
思路:盒子中的x坐标为鼠标再页面中距离左端的距离e.pagex减去盒子距离左端的长度box.offsetLeft。
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
var div = document.querySelector('div');
div.addEventListener('mousemove', function(e) {
var x = e.pageX - div.offsetLeft;
var y = e.pageY - div.offsetTop;
console.log(x);
console.log(y);
div.innerHTML = '鼠标在盒子内的X坐标是' + x + ' y坐标是' + y;
})
})
3.Client系列
这里我们用一张图来解释一下
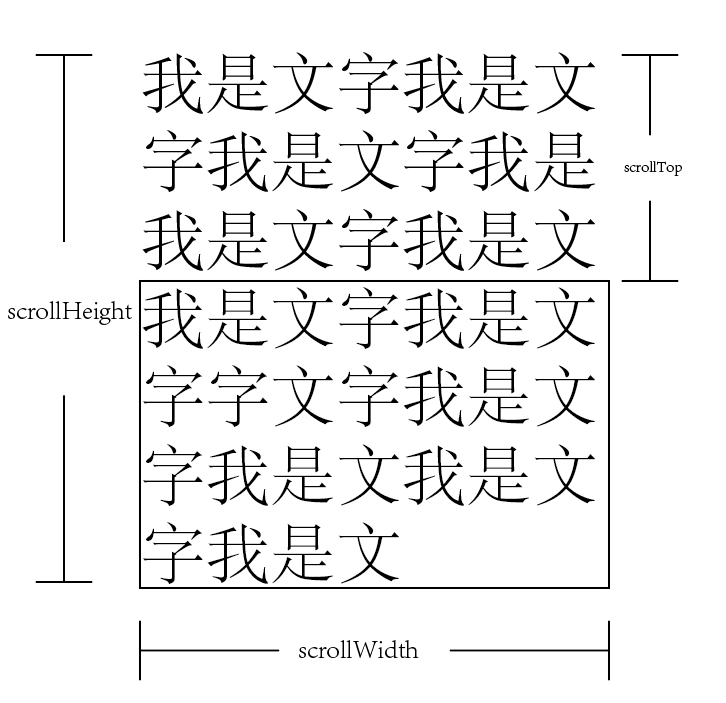 scrollTop是指被卷曲的长度,Height是文字的总长度。
scrollTop是指被卷曲的长度,Height是文字的总长度。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号