牛客网刷题二
牛客网FPGA题库刷题之快速入门题库(一)9~13题
14-20没啥用 就是看图写,不需要做了
第九题
题目链接
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module main_mod(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
input [7:0]c,
output [7:0]d
);
//reg wire declaration
wire [7:0] tmp1;
reg [7:0] tmp2;
//buff c
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(rst_n==1'b0)begin
tmp2 <= 0;
end
else begin
tmp2 <= c;
end
end
//模块调用
sub_mod u1(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.a(a),
.b(b),
.d(tmp1)
);
sub_mod u2(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.a(tmp1),
.b(tmp2),
.d(d)
);
endmodule
//子模块的编写
module sub_mod(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output [7:0]d
);
reg [7:0] tmp;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(rst_n==1'b0)begin
tmp <= 0;
end
else if(a<b) begin
tmp <= a;
end
else begin
tmp <= b;
end
end
assign d = tmp ;
endmodule
题目解析
首先写子模块,比较双个数的大小。然后在主模块调用,需要注意子模块有一个时钟的时序延时,所以需要c延时一个时钟
第十题 函数、generate用法
题目链接
使用函数实现数据大小端转换_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module function_mod(
input [3:0]a,
input [3:0]b,
input clk,
input rst_n,
output [3:0]c,
output [3:0]d
);
assign c = rever(a);
assign d = rever(b);
function [3:0] rever;
input [ 3: 0] datain ;
integer i;
for(i=0; i <4; i++)
begin:revers
rever[i] = datain[3-i];
end
endfunction
endmodule
题目解析
verilog 里面函数的使用方法,一般函数都是组合逻辑,没有时序逻辑,然后这题的clk和rst_n没有任何作用
第十一题
题目链接
4位数值比较器电路_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
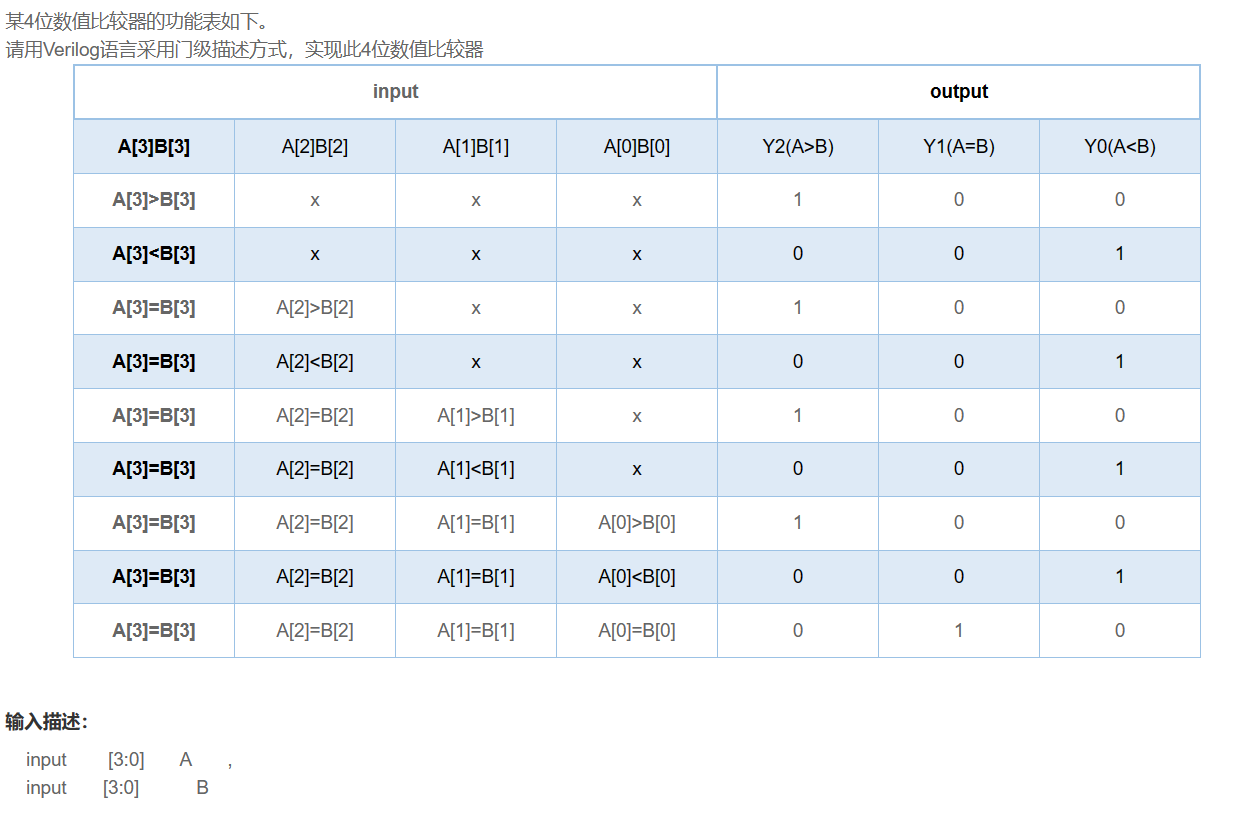
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module comparator_4(
input [3:0] A ,
input [3:0] B ,
output wire Y2 , //A>B
output wire Y1 , //A=B
output wire Y0 //A<B
);
assign Y2 = A[3]>B[3]||(A[3]==B[3]&&A[2]>B[2])||(A[3]==B[3]&&A[2]==B[2]&&A[1]>B[1])|||(A[3]==B[3]&&A[2]==B[2]&&A[1]==B[1]&&A[0]>B[0]);
assign Y1 =(A[3]==B[3]&&A[2]==B[2]&&A[1]==B[1]&&A[0]==B[0]);
assign Y0 = ~(Y2||Y1);
endmodule
题目解析
看真值表写就好了
第十二题
题目链接
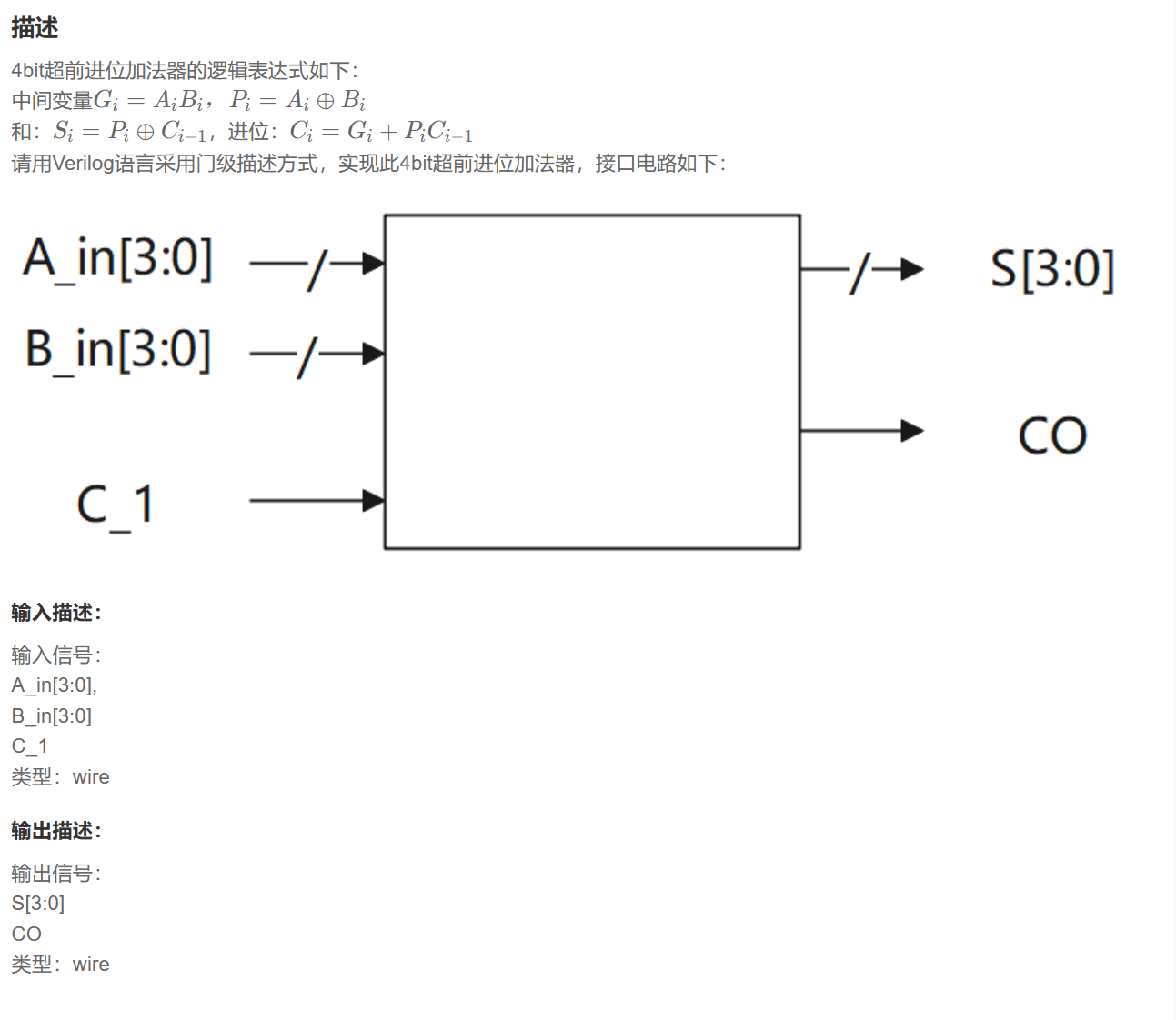
代码
module pg_gen(
input A,
input B,
output G,
output P
);
assign G = A & B;
assign P = A ^ B;
endmodule
module lca_4(
input [3:0] A_in,
input [3:0] B_in,
input C_1,
output [3:0] S,
output CO
);
parameter width = 4;
wire [width-1:0] G;
wire [width-1:0] P;
wire [width:0] C;
genvar i;
for( i=0; i<width; i=i+1) begin:sdad
pg_gen u_pg_gen(
.A( A_in[i]),
.B( B_in[i]),
.G( G[i] ),
.P( P[i] )
);
end
assign C[0] = C_1;
assign C[1] = G[0] || ( C[0] & P[0] );
assign C[2] = G[1] || ( C[1] & P[1] );
assign C[3] = G[2] || ( C[2] & P[2] );
assign C[4] = G[3] || ( C[3] & P[3] );
assign CO = C[4];
generate
genvar k;
for( k=0; k<width; k=k+1) begin:sdas
assign S[k] = P[k] ^ C[k];
end
endgenerate
endmodule
题目解析
简析
如果只是简单地将逻辑表达式转化为verilog语言,这道题算不上较难题。难点应该是借着这道题理解超前进位加法器。下面梳理一些常见的加法器。
半加器
半加器是最简单的加法器。它不考虑进位输入。其中A和B是两个加数,S是和,C_o是进位输出。
assign S = A ^ B;
assign C_out = A & B;
对于4bit LCA,进位输出C4的计算路径如下:S
13题 优先编码器电路
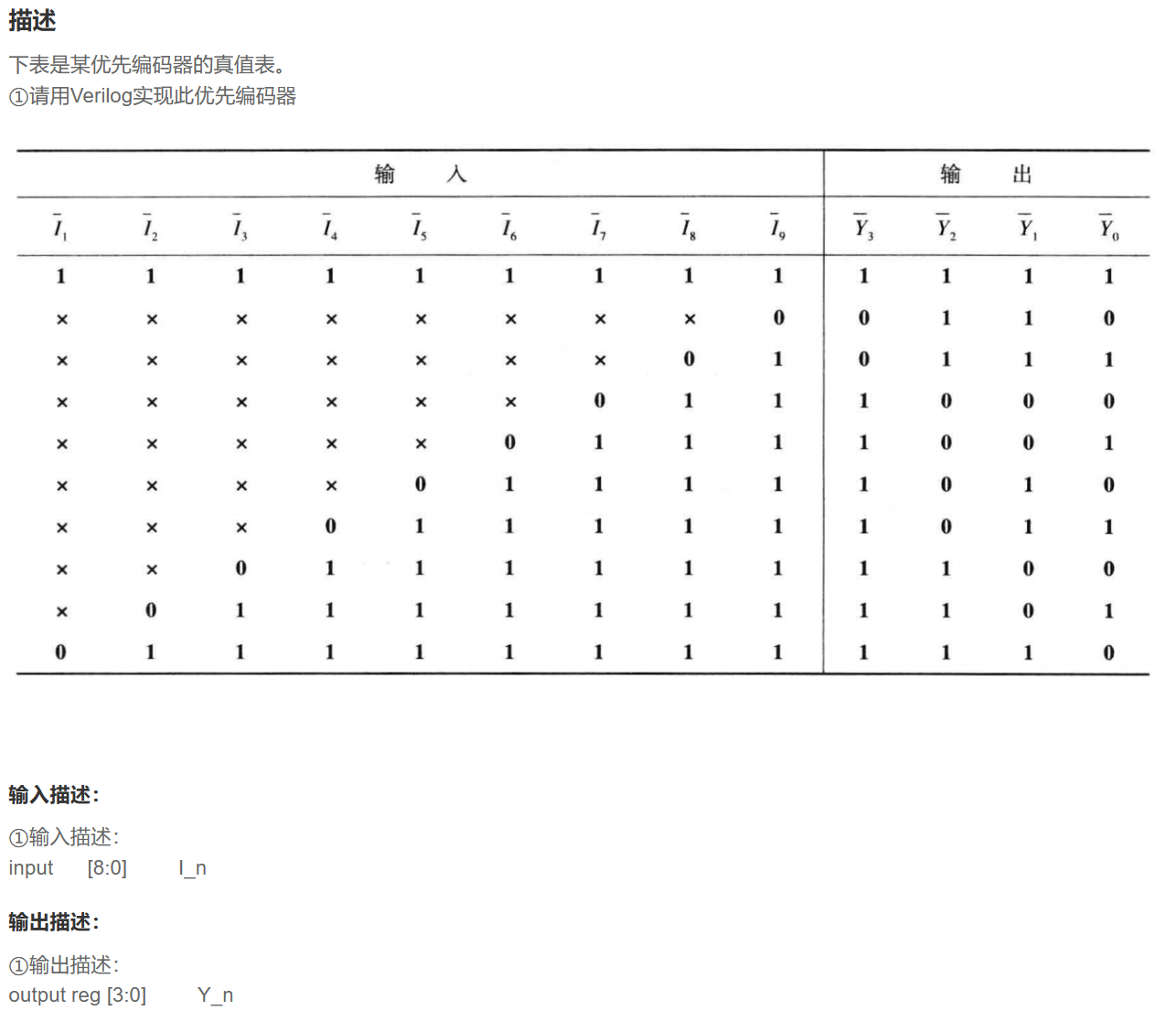
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module encoder_0(
input [8:0] I_n ,
output reg [3:0] Y_n
);
always @(*)begin
casex (I_n)
9'b0xxxxxxxx : Y_n = 4'b0110;
9'b111111111 : Y_n = 4'b1111;
9'b10xxxxxxx : Y_n = 4'b0111;
9'b110xxxxxx : Y_n = 4'b1000;
9'b1110xxxxx : Y_n = 4'b1001;
9'b11110xxxx : Y_n = 4'b1010;
9'b111110xxx : Y_n = 4'b1011;
9'b1111110xx : Y_n = 4'b1100;
9'b11111110x : Y_n = 4'b1101;
9'b111111110 : Y_n = 4'b1110;
endcase
end
endmodule




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号