Unpooled 类
-
Netty 提供一个专门用来操作缓冲区(即Netty的数据容器)的工具类
-
常用方法
//通过给定的数据和字符编码返回一个 ByteBuf 对象(类似于 NIO 中的 ByteBuffer 但有区别)
public static ByteBuf copiedBuffer(CharSequence string, Charset charset
- 案例1
public class NettyByteBuf01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个ByteBuf
//说明
//1. 创建 对象,该对象包含一个数组arr , 是一个byte[10]
//2. 在netty 的buffer中,不需要使用flip 进行反转
// 底层维护了 readerindex 和 writerIndex
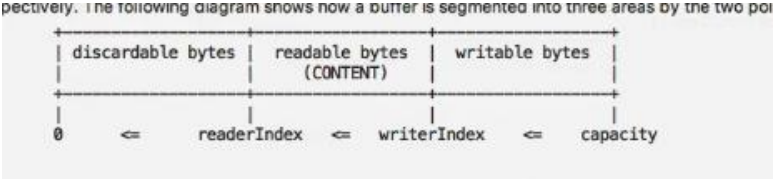
//3. 通过 readerindex 和 writerIndex 和 capacity, 将buffer分成三个区域
// 0---readerindex 已经读取的区域
// readerindex---writerIndex , 可读的区域
// writerIndex -- capacity, 可写的区域
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer(10);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buffer.writeByte(i);
}
System.out.println("capacity=" + buffer.capacity());//10
//输出
// for(int i = 0; i<buffer.capacity(); i++) {
// System.out.println(buffer.getByte(i));
// }
for(int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
}
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
- 案例2
public class NettyByteBuf02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,world!", Charset.forName("utf-8"));
//使用相关的方法
if(byteBuf.hasArray()) { // true
byte[] content = byteBuf.array();
//将 content 转成字符串
System.out.println(new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.out.println("byteBuf=" + byteBuf);
System.out.println(byteBuf.arrayOffset()); // 0
System.out.println(byteBuf.readerIndex()); // 0
System.out.println(byteBuf.writerIndex()); // 12
System.out.println(byteBuf.capacity()); // 36
//System.out.println(byteBuf.readByte()); //
System.out.println(byteBuf.getByte(0)); // 104
int len = byteBuf.readableBytes(); //可读的字节数 12
System.out.println("len=" + len);
//使用for取出各个字节
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuf.getByte(i));
}
//按照某个范围读取
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(0, 4, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(4, 6, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
}
}
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号