2020微软笔试题
1.将N个数字划分成N/K组,每组K个数字,每组中的数字互不相同,求每个子数组最大最小元素的差值之和的最小值。
输入:
N=12, K=4
arr=3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,8,8,10,10
输出:
15
{3,4,5,6} 6-3=3
{3,4,8,10} 10-3=7
{5,6,8,10} 10-5=5
3+7+5=15
思路:先对数组从小到大排序,统计重复数字出现最多的个数,如果大于N/K的话,不能划分,直接返回0。
然后枚举每一种情况,dfs+剪枝。
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int solve(int N, int K, int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int dup_max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
map.put(arr[i], map.getOrDefault(arr[i], 0) + 1);
dup_max = Math.max(dup_max, map.get(arr[i]));
}
//重复数字出现最多的个数,如果大于N/K的话,不能划分,直接返回0
if (dup_max > N / K) {
return 0;
}
int[] num = new int[N];
int[] flag = new int[N];
//用于判断分组中的重复元素
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
helper(N, K, 0, arr, num, flag, set);
return ans;
}
//dfs + 剪枝
public void helper(int N, int K, int index, int[] arr, int[] num, int[] flag, Set<Integer> set) {
//index==N,说明分组完毕,计算每个子数组最大最小元素的差值之和
if (index == N) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i += K) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int j = i; j < i + K; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, num[j]);
max = Math.max(max, num[j]);
}
res += Math.abs(max - min);
}
if (res < ans) {
ans = res;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
System.out.print(num[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(res);
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
//剪枝
if (flag[i] == 0) {
if (set.contains(arr[i])) {
continue;
}
set.add(arr[i]);
flag[i] = 1;
num[index] = arr[i];
if ((index + 1) % K == 0) {
set = new HashSet<>();
}
helper(N, K, index + 1, arr, num, flag, set);
set.remove(arr[i]);
flag[i] = 0;
num[index] = 0;
}
}
}
2.给一个字符串,每次可以移除其中一个字符,或者移除一个回文子串,求 全部移除所需最少次数
例如:1,4,3,1,5. 先移除 3,再移除 1 4 1,再移除 5,得到最少次数 3.
leetcode原题:https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-removal/description/
两种情况:
- 直接删除
- 找到该字符串对应的回文串,再删除

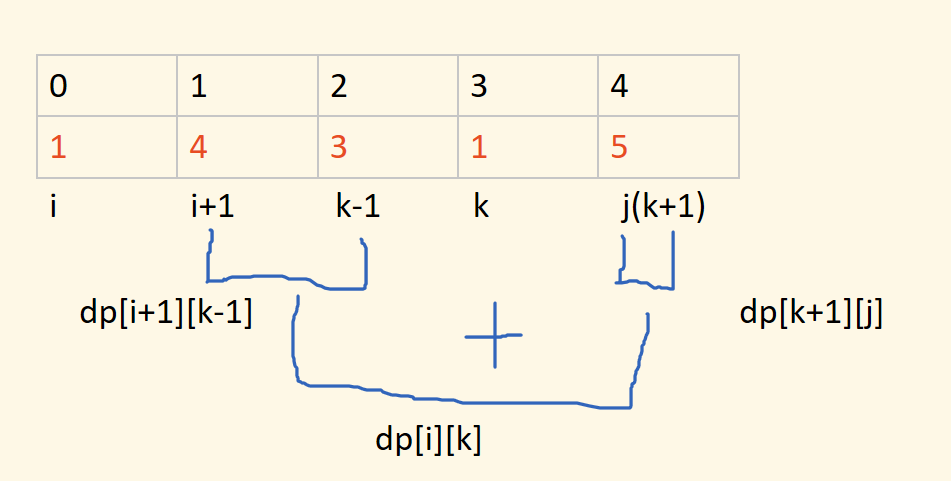
i+1==k考虑回文子串长度为空的情况
//动态规划。在原来题解的基础上,加了注释。
public static int minimumMoves(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
//dp[i][j]表示删除从i到j的数字所需的最少操作次数
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
//l表示当前数字的长度
for (int l = 1; l <= n; l++) {
int i = 0, j = l - 1;
while (j < n) {
if (l == 1) {
//base,每个数字的删除次数为1
dp[i][j] = 1;
} else {
//不考虑回文子串的情况下,删除次数为之前的删除次数+1
dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i + 1][j];
//考虑回文子串
for (int k = i + 1; k <= j; k++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[k]) {
//更新dp[i][j]
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i + 1][k - 1] + dp[k + 1][j] + (i + 1 == k ? 1 : 0));
}
}
}
i++;
j++;
}
}
return dp[0][n - 1];
}
3.给一个无向图,N个顶点,M条边,0为起点,N-1为终点,每条边初始权值为 1。图中除普通节点外有 4 种节点。
第一种:走过这种节点后的两条边权值翻倍(Sand)
第二种:走过这种节点后的两条边权值减半 (Nitro)
第三种:走到这个节点就停止,不能再走了(Cop)
第四种:走到这个节点,下一条边的权值+1(Crash)
求节点 0 到 N-1 的最短权值和路径。
类似于图的深度优先遍历,需要进行回溯
//Path记录起点到终点的路径path和花费cost
class Path {
List<Integer> path;
double cost;
public Path(List<Integer> path, double cost) {
this.path = path;
this.cost = cost;
}
}
//存储最短路径
Path minPath = new Path(new ArrayList<>(), Integer.MAX_VALUE);
public int[] minTimes(int city, String[] strs, int road, int[][] arr) {
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Set<Integer> set;
if (!map.containsKey(arr[i][0])) {
set = new HashSet<>();
} else {
set = map.get(arr[i][0]);
}
set.add(arr[i][1]);
map.put(arr[i][0], set);
}
Path path = new Path(new ArrayList<>(), 0);
dfs(0, city - 1, strs, map, path);
int[] res = new int[minPath.path.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i] = minPath.path.get(i);
}
return res;
}
//计算起点到终点的花费
public double cal(String[] strs, Path path) {
double res = 0;
int size = path.path.size();
double[] cost = new double[size - 1];
Arrays.fill(cost, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (strs[path.path.get(i)].equals("Nitro")) {
if (i < size - 1) {
cost[i] *= 0.5;
}
if (i + 1 < size - 1) {
cost[i + 1] *= 0.5;
}
} else if (strs[path.path.get(i)].equals("Sand")) {
if (i < size - 1) {
cost[i] *= 2;
}
if (i + 1 < size - 1) {
cost[i + 1] *= 2;
}
} else if (strs[path.path.get(i)].equals("Crash")) {
if (i < size - 1) {
cost[i] += 1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
res += cost[i];
}
return res;
}
//图的深度优先遍历
public void dfs(int begin, int end, String[] strs, Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map, Path path) {
if (begin == end) {
path.path.add(end);
double cost = cal(strs, path);
if (cost < minPath.cost) {
// 一定要使用new ArrayList<>(path.path)。
// 直接传入path.path,会导致返回的minPath.path为空,这是由于Java的值传递导致的。
minPath = new Path(new ArrayList<>(path.path), cost);
// System.out.println("cost:" + cost);
// System.out.println("minPath" + minPath.path.toString());
}
//回溯
path.path.remove(Integer.valueOf(end));
return;
}
Set<Integer> set = map.get(begin);
//寻找下一个可访问的节点
for (int nextCity : set) {
if (path.path.contains(nextCity) || strs[nextCity].equals("Cop")) {
continue;
}
path.path.add(begin);
dfs(nextCity, end, strs, map, path);
//回溯
path.path.remove(Integer.valueOf(begin));
}
}
测试用例:
Test1: int city = 5; int road = 5; String[] strs = {"None", "Cop", "None", "None", "None"}; int[][] map = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}}; result:{0,2,3,4} Test2: int city1 = 7; int road1 = 8; String[] strs1 = {"None", "Cop", "Sand", "None", "Nitro", "None", "None"}; int[][] map1 = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {3, 6}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}}; result:{0,2,4,5,6}
Talk is cheap,show me your code.

