[swarthmore cs75] Lab 0 Warmup & Basic OCaml
课程回顾
Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业。本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第1次大作业。
什么是编译
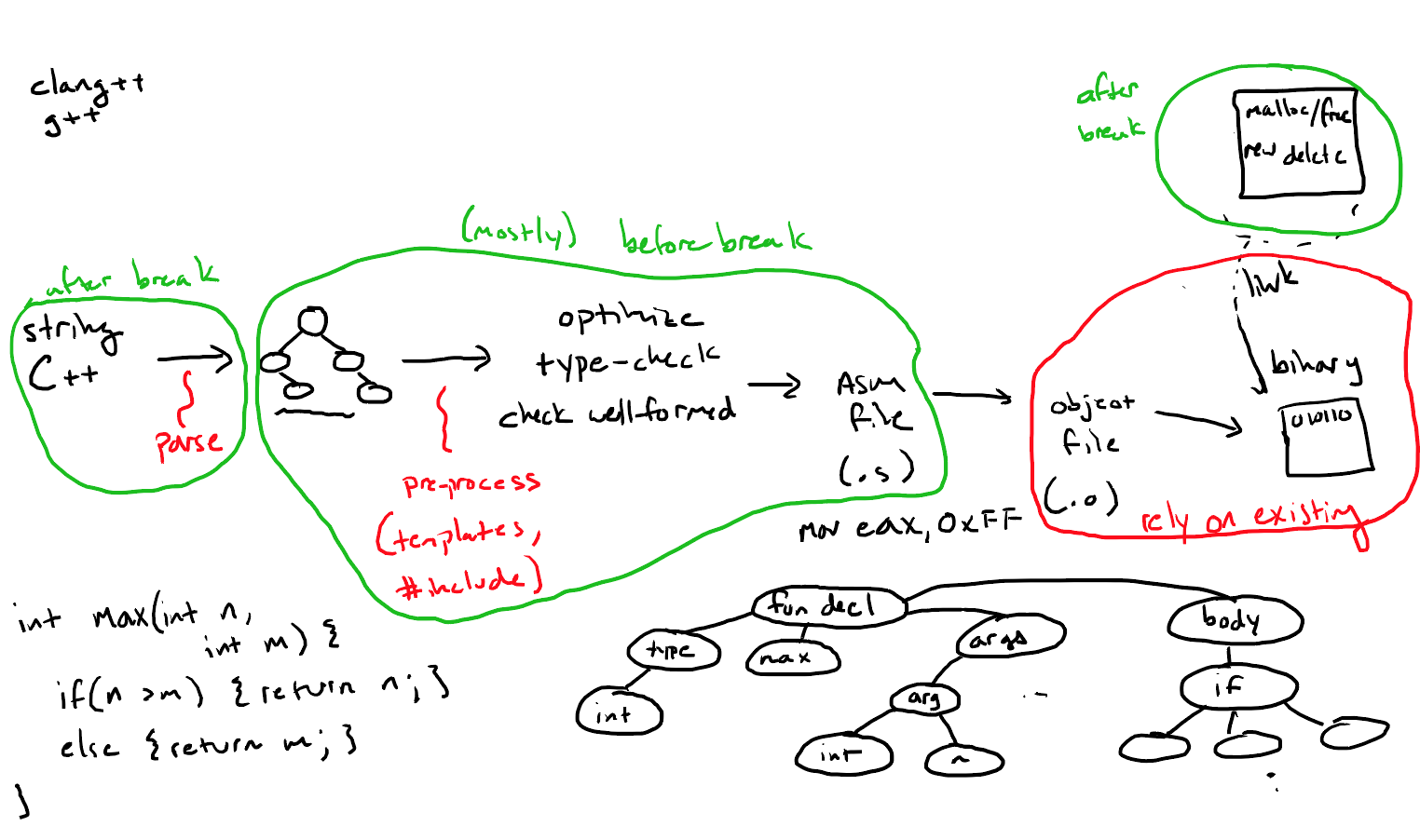
编译就是执行Program->Program'转换的过程,如下图所示:

这个过程需要满足两个条件:
- The input and output program mean the same thing.
- The output is executable in a context we care about.
编译执行过程:
不可变数据结构(persistent data structure)
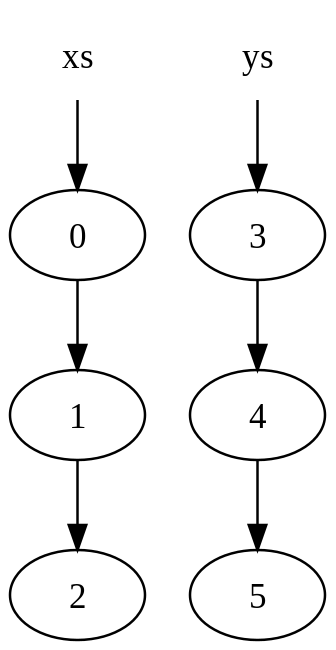
例1: 下图是两个列表在内存中的表示:
xs = [0, 1, 2]
ys = [3, 4, 5]
 执行了连接操作,zs在内存中的表示:
```haskell
zs = xs ++ ys
```
执行了连接操作,zs在内存中的表示:
```haskell
zs = xs ++ ys
```
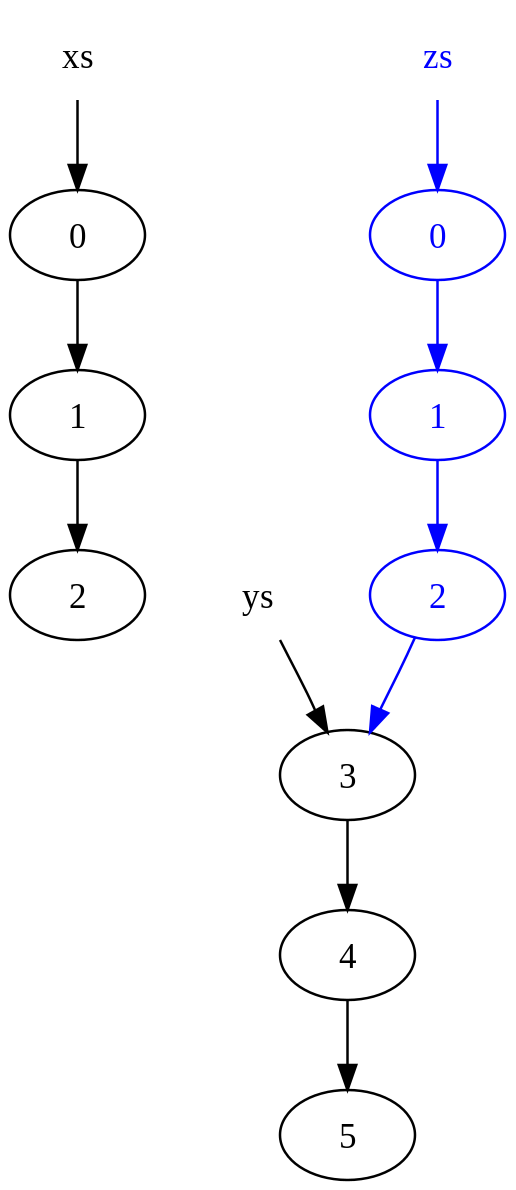 注意到,xs被复制了一份,但是ys被共享了。最终xs和ys都没有被改变。其中xs被复制是因为,xs中最后一个元素2不能够指向ys的起始地址,因为这样的话xs就被改变了。
注意到,xs被复制了一份,但是ys被共享了。最终xs和ys都没有被改变。其中xs被复制是因为,xs中最后一个元素2不能够指向ys的起始地址,因为这样的话xs就被改变了。
例2: 假设下面的数据代表下图的二叉搜索树
xs = [a, b, c, d, f, g, h]
 在执行插入操作后,内存中的数据结构变为下图:
```haskell
ys = insert ("e", xs)
```
在执行插入操作后,内存中的数据结构变为下图:
```haskell
ys = insert ("e", xs)
```
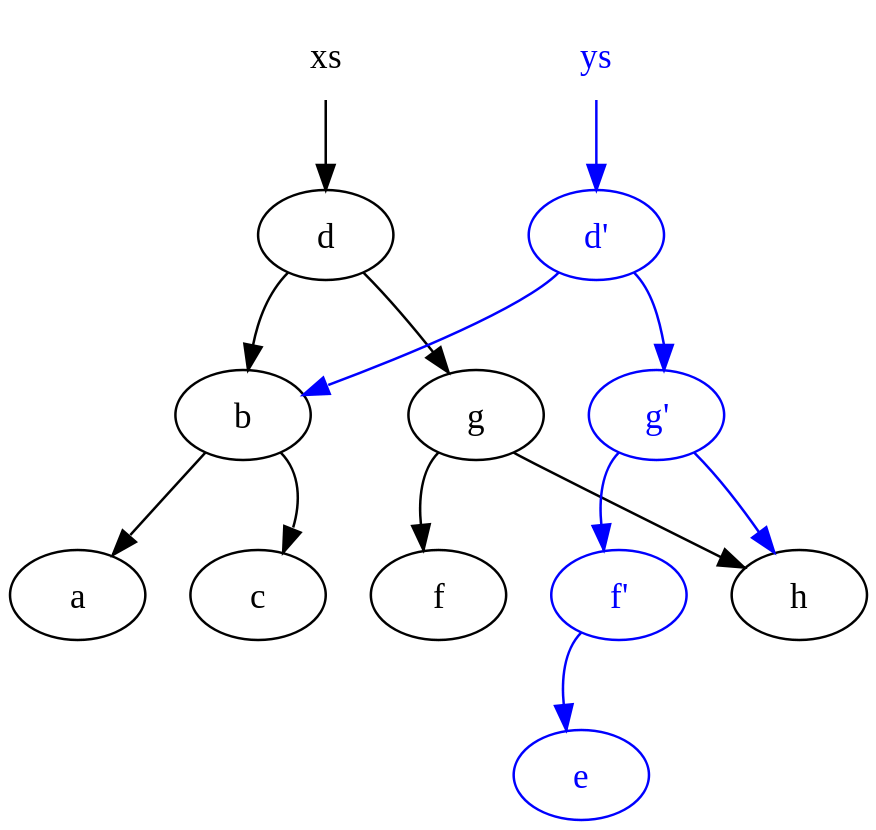 可以看到两个指针xs和ys,其中ys共享了xs中的节点。
可以看到两个指针xs和ys,其中ys共享了xs中的节点。
编程作业
*OSX安装Ocaml
brew install ocaml opam
opam init
opam install extlib ounit
1.Implement fibonacci as an OCaml function that takes an integer n and returns the nth fibonacci number. Write out the evaluation of (fibonacci 3) in substitution style.
- 递归计算fibonacci数列
let rec fibonacci (n : int) : int =
if n <= 2 then 1
else (fibonacci (n - 1)) + (fibonacci (n - 2));;
- The evaluation of (fibonacci 3) in substitution style is :
=> (if 3 <= 2 then 1 else (fibonacci (3 - 1)) + (fibonacci (3 - 2)))
=> (if false then 1 else (fibonacci (3 - 1)) + (fibonacci (3 - 2)))
=> ((fibonacci (3 - 1)) + (fibonacci (3 - 2)))
=> ((fibonacci 2) + (fibonacci (3 - 2)))
=> ...
=> (1 + (fibonacci (3 - 2)))
=> (1 + (fibonacci 1))
=> ...
=> (1 + 1)
=> 2
2.Write tests for max and fibonacci using t_int.
- 测试用例
(* a helper for testing integers *)
let t_int name value expected = name>::
(fun _ -> assert_equal expected value ~printer:string_of_int);;
let max_test = t_int "" (max 4 5) 5;;
let fibonacci_test = t_int "fibonacci_test" (fibonacci 10) 55;;
let suite = "suite">:::[max_test; fibonacci_test;];;
run_test_tt_main suite
- >:: is a function that creates a TestLabel for a TestCase
val (>:😃 : string -> test_fun -> test
- >::: is a function that creates a TestLabel for a TestList
val (>::😃 : string -> test list -> test
- 这里使用printer的作用是,可以打印出expected和value的值。而不是仅仅打印not equal这样的信息。
3.Write a test function t_string that’s like t_int, but tests for equality of strings. Can you write a function that produces a string form of the results like t_int did for integers?
(* a helper for testing strings *)
let t_string name value expected = name>::
(fun _ -> assert_equal expected value ~printer:(fun x -> x));;
- 首先看一下参数printer的声明,如果数据是string类型,就不用像t_int那样做int到string的数据转换;但是这里需要传入一个函数,所以可以用f(x)=x来填充。
?printer:('a -> string) ->
printer : value printer, don't print value otherwise
* 因为4~8题会用到二叉树,先定义了一个btnode类型。
type btnode =
| Leaf
| Node of string * btnode * btnode;;
4.Write at least five interesting tests for inorder_str.
- 中序遍历二叉树
let rec inorder_str (bt : btnode) : string =
match bt with
| Leaf -> ""
| Node(s, left, right) ->
(inorder_str left) ^ s ^ (inorder_str right);;
- 测试用例
"" Leaf
inorder_str: ""
"a" Node("a", Leaf, Leaf)
inorder_str: "a"
"b" Node("b",
/ \ Node("a", Leaf, Leaf), Node("c", Leaf, Leaf))
"a" "c"
inorder_str: "abc"
"a" Node("a",
/ Node("b",
"b" Node("c", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf), Leaf)
/
"c"
inorder_str:"cba"
"1" Node("1",
\ Leaf, Node("3",
"3" Node("2", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf))
/
"2"
inorder_str: "123"
let inorder_str_test = t_string "inorder_str_test1" (inorder_str 填入相应的btnode) 填入中序遍历结果;;
let suite = "suite">:::[inorder_str_test;];;
run_test_tt_main suite
5.Write out the substitution-based evaluation of inorder_str on a tree with at least 3 nodes.
- The evaluation of (inorder_str (Node("1", Leaf, Node("3", Node("2", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf)))) in substitution style is :
=> match (Node("1", Leaf, Node("3", Node("2", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf))) with
| Leaf -> ""
| Node(s, left, right) -> (inorder_str left) ^ s ^ (inorder_str right);;
=> (inorder_str Leaf) ^ s ^ (inorder_str right)
=> "" ^ s ^ (inorder_str right)
=> "" ^ "1" ^ (inorder_str right)
=> "1" ^ (inorder_str (Node("3", Node("2", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf)))
=> ...
=> "1" ^ (inorder_str (Node("2", Leaf, Leaf))) ^ "3" ^ (inorder_str Leaf)
=> ...
=> "1" ^ "" ^ "2" ^ "" ^ "3" ^ ""
=> "123"
6.Write a function size that takes a btnode and produces an integer that is the number of Nodes in the tree.
- 递归计算二叉树节点数
let rec size (bt : btnode) : int =
match bt with
| Leaf -> 0
| Node(s, left, right) -> 1 + (size left) + (size right);;
7.Write a function height that takes a btnode and produces an integer that is the height of the tree.
- 递归计算二叉树高度
let rec height (bt : btnode) : int =
match bt with
| Leaf -> 0
| Node(s, left, right) ->
1 + (max (height left) (height right));;
8.Make sure to test the above two functions.
- 测试用例
let size_test = t_int "size_test" (size (Node("1", Leaf, Node("3", Node("2", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf)))) 3;;
let height_test = t_int "height_test" (height (Node("1", Leaf, Node("3", Node("2", Node("a", Leaf, Leaf), Leaf), Leaf)))) 4;;
"1"
\
"3"
/
"2"
/
"a"
let suite = "suite">:::[size_test; height_test;];;
run_test_tt_main suite
*因为9~12题需要分别测试int list,string list以及int list of int list,并且assert_equal中的~printer参数需要传入一个类型为'a->string的函数,也就是说需要把int,string以及int list分别转换为string;所以要分别实现这样的函数。
(* 将一个'a list转换为字符串, 转换方法是f, f因数据类型不同而不同 *)
let string_of_list (f : 'a -> string) (l : 'a list) : string =
"[" ^ String.concat ";" (List.map f l) ^ "]";;
(* 测试string list,需要传入的f是我定义的匿名函数 *)
let string_of_string_list = string_of_list (fun x -> "\"" ^ x ^ "\"");;
let t_string_list name value expected =
name>::(fun _ -> assert_equal expected value ~printer:string_of_string_list);;
(* 测试int list,需要传入的f是string_of_int *)
let string_of_int_list = string_of_list string_of_int;;
let t_int_list name value expected =
name>::(fun _ -> assert_equal expected value ~printer:string_of_int_list);;
(* 测试int list of int list,因为处理的是列表的列表,上一步已经定义了如何处理列表,所以f只需传入string_of_int_list *)
let string_of_int_list_list = string_of_list string_of_int_list;;
let t_int_list_list name value expected =
name>::(fun _ -> assert_equal expected value ~printer:string_of_int_list_list);;
9.Write and test a function increment_all that takes an int list and produces a new int list with all the elements increased by 1.
let rec increment_all (l : int list) : int list = List.map (fun x -> x + 1) l;;
- 测试用例
let increment_all_test = t_int_list "increment_all_test" (increment_all [1; 2; 3]) [2; 3; 4];;
let suite = "suite">:::[increment_all_test;];;
run_test_tt_main suite
10.Write and test a function long_strings that takes a string list and an int and produces a new string list that contains all the strings that had length greater than the given int. You can get the length of a string with the function String.length. Other string functions are documented here.
- 这里要把字符串长度大于len的舍弃,递归处理即可
let rec long_strings (l : string list) (len : int) : string list =
match l with
| [] -> []
| first::rest ->
if String.length(first) > len then first::(long_strings rest len)
else (long_strings rest len);;
- 测试用例
let long_strings_test = t_string_list "long_strings_test" (long_strings [""; "a"; "ab"; "abc"; "abcd"] 2) ["abc"; "abcd"];;
let suite = "suite">:::[long_strings_test;];;
run_test_tt_main suite
11.Write and test a function every_other that takes a ’a list (a list with elements of any one type), and produces a new list that contains every other element from the given list, starting with the first element.
- 递归计算every other element from the given list。比如:[1; 2;] 返回 [1; ], [1;2;3;] 返回 [1;3;];这里注意下只有一个元素的情况,如果没考虑会导致match不exhaustive。
let rec every_other (l : 'a list) : 'a list =
match l with
| [] -> []
| [first] -> [first]
| first::second::rest -> first::(every_other rest);;
- 测试用例
let every_other_test1 = t_int_list "every_other_test1" (every_other [1]) [1];;
let every_other_test2 = t_string_list "every_other_test2" (every_other ["a"; "b"; "c"; "d"]) ["a"; "c"];;
let every_other_test3 = t_int_list_list "every_other_test3" (every_other [[]; [0;1;2]]) [[]];;
let suite = "suite">:::[every_other_test1; every_other_test2; every_other_test3;];;
run_test_tt_main suite
12.Write and test a function sum_all that takes an int list list (that is, a list of lists of integers), and returns an int list that contains the sums of the sub-lists.
- 计算子数组的和。
let sum (l : int list) : int = List.fold_left (+) 0 l;;
let sum_all (ll : int list list) : int list = List.map sum ll;;
- 左折叠函数的定义
val fold_left : ('a -> 'b -> 'a) -> 'a -> 'b list -> 'a
List.fold_left f a [b1; ...; bn] is f (... (f (f a b1) b2) ...) bn.
- 测试用例
let sum_all_test = t_int_list "sum_all_test" (sum_all [[]; [0;1]; [0;1;2]; [0;1;2;3]]) [0; 1; 3; 6];;
let suite = "suite">:::[sum_all_test;];;
run_test_tt_main suite



